Topic blenderbim: Discover BlenderBIM, the revolutionary open-source solution that integrates the power of Blender with BIM technology, transforming the AEC industry with unparalleled design and collaboration capabilities.
Table of Content
- How to import Ifc files into Blender using BlenderBIM?
- Overview of BlenderBIM
- Key Features and Capabilities
- Installation Guide for BlenderBIM
- Creating Your First Project with BlenderBIM
- Advanced Modeling Techniques
- Integration with Other Software
- YOUTUBE: BlenderBIM Addon Showcase
- Handling Large Models and Performance Optimization
- Collaboration and Sharing in BlenderBIM
- Learning Resources and Community Support
- Funding and Development Insights
How to import Ifc files into Blender using BlenderBIM?
To import Ifc files into Blender using BlenderBIM, follow these steps:
- First, make sure you have Blender and the BlenderBIM add-on installed on your computer.
- Open Blender and go to the \"Edit\" menu. Select \"Preferences\" from the dropdown menu.
- In the Preferences window, click on the \"Add-ons\" tab.
- At the top of the Add-ons tab, click on the \"Install...\" button.
- Navigate to the location where you have downloaded the BlenderBIM add-on and select the add-on file.
- Click on the \"Install Add-on\" button to install BlenderBIM.
- Once the installation is complete, enable the BlenderBIM add-on by checking the box next to its name.
- Close the Preferences window.
- To import an Ifc file into Blender, go to the \"File\" menu and select \"Import\".
- From the dropdown menu, choose the \"Industry Foundation Classes (.ifc)\" option.
- Navigate to the location where your Ifc file is stored and select it.
- Click on the \"Import IFC\" button to start the import process.
- Blender will now import the Ifc file and display its contents in the 3D viewport.
READ MORE:
Overview of BlenderBIM
BlenderBIM is a pioneering open-source add-on for Blender that brings Building Information Modeling (BIM) capabilities to the Blender environment. It aims to empower architects, engineers, and construction professionals with the tools to create detailed, data-rich BIM models within the familiar and versatile Blender interface. BlenderBIM is part of the broader movement towards open-source solutions in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, promoting greater collaboration, innovation, and accessibility in digital construction.
- Free and open-source, enabling users to inspect, modify, and enhance the software.
- Supports native IFC authoring, ensuring compatibility with other BIM software and adherence to industry standards.
- Facilitates detailed architectural, engineering, and construction modeling with tools for geometry creation, data management, and visualization.
- Includes features for drawing generation, structural analysis, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) system design, costing, and scheduling.
- Enables advanced BIM workflows, including model auditing, analysis, and collaboration across different project stages and disciplines.
- Supported by a vibrant community that contributes to its development, provides user support, and shares knowledge and resources.
By integrating BIM functionality directly into Blender, BlenderBIM offers a unique platform for the AEC industry to leverage the power of open-source software for building design and construction projects. Its commitment to interoperability, community-driven development, and the continuous addition of new features make it a compelling choice for professionals seeking flexible, cost-effective BIM solutions.
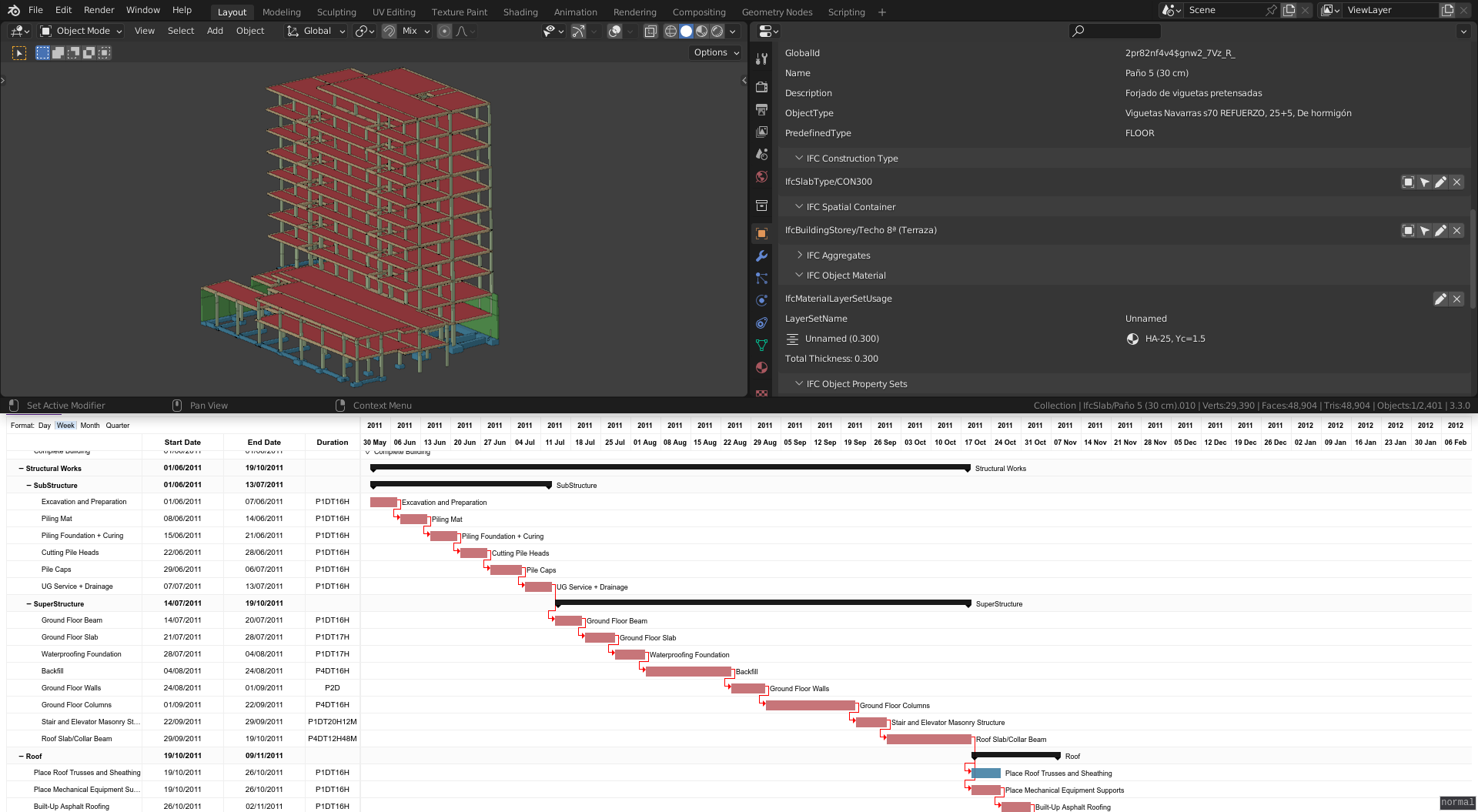
Key Features and Capabilities
BlenderBIM adds unparalleled features to the traditional BIM environment, leveraging Blender\"s advanced 3D modeling capabilities. Here are some of the key features and capabilities that set BlenderBIM apart:
- Native IFC authoring, which promotes seamless interoperability with other BIM software.
- Comprehensive support for building and infrastructure design, from initial concept to detailed construction models.
- Advanced tools for architectural visualization, including realistic rendering and animation capabilities for client presentations and stakeholder engagement.
- Capabilities for structural analysis and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) modeling, facilitating integrated project workflows.
- Automated drawing generation, which significantly reduces manual drafting time and helps maintain consistency across project documentation.
- Dynamic data management features that allow for the direct manipulation of BIM elements and their associated metadata within Blender.
- Open-source development model, encouraging community contributions, which constantly enhance the add-on\"s functionality and usability.
- A robust plugin system that supports the integration of external tools and services, enhancing BlenderBIM\"s functionality for specific project needs.
- Active and supportive community, offering extensive documentation, tutorials, and forums for troubleshooting and knowledge sharing.
With these features, BlenderBIM stands out as a powerful, flexible solution for professionals in the architecture, engineering, and construction sectors seeking to adopt or enhance their BIM workflows with open-source software.
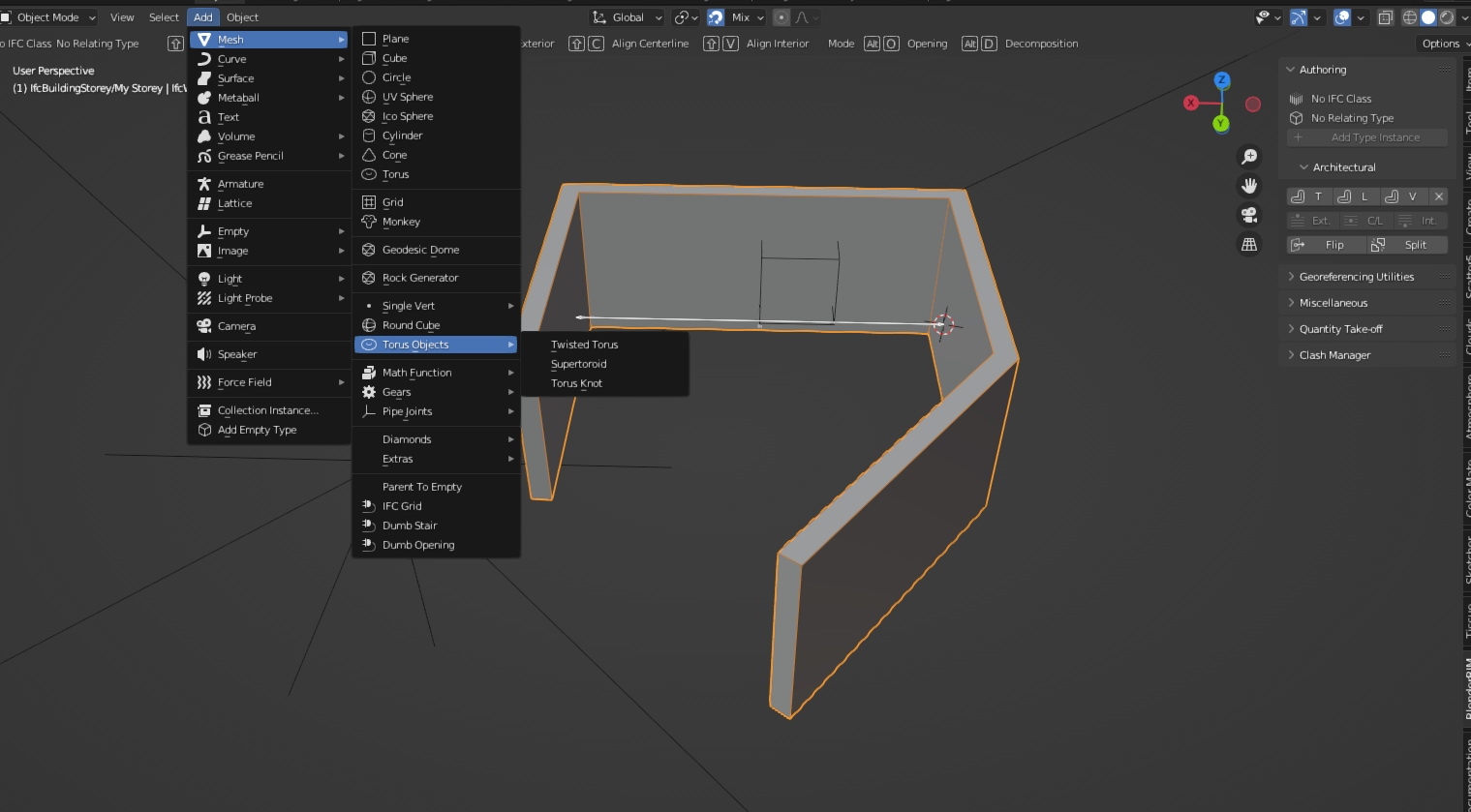
Installation Guide for BlenderBIM
Installing BlenderBIM is a straightforward process that brings powerful BIM capabilities to Blender. Follow these steps to get started:
- Download and install the latest version of Blender from the official Blender website. BlenderBIM supports multiple operating systems including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Visit the BlenderBIM official website and navigate to the download section to download the latest version of the BlenderBIM add-on.
- Open Blender and go to Edit > Preferences. In the Preferences window, navigate to the Add-ons tab.
- Click on \"Install\" and navigate to the downloaded BlenderBIM file. Select the file and click \"Install Add-on from File...\".
- Once the installation is complete, search for \"BlenderBIM\" in the Add-ons tab, and make sure to check the box next to the BlenderBIM add-on to activate it.
- After activation, you may need to restart Blender for the changes to take effect. You will now have access to BlenderBIM\"s features within the Blender interface.
For detailed documentation, tutorials, and support, the BlenderBIM community and official website offer a wealth of resources to help you get started and make the most out of BlenderBIM\"s capabilities.
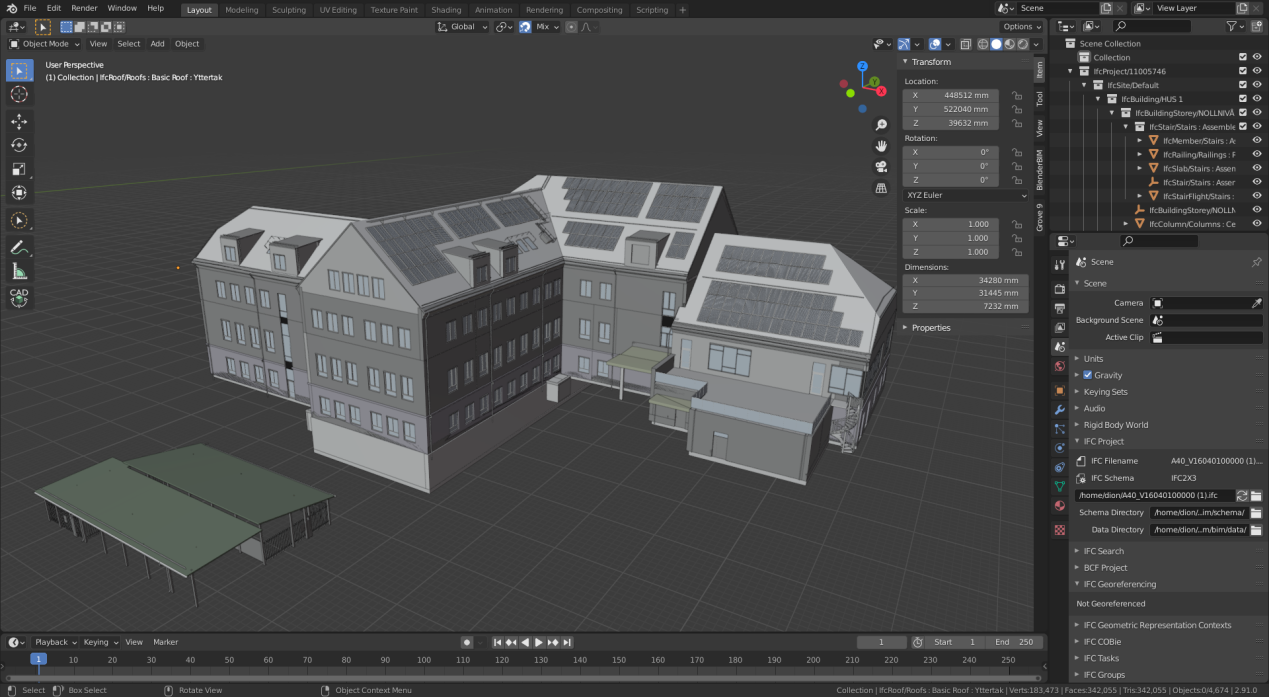
Creating Your First Project with BlenderBIM
Embarking on your first project with BlenderBIM is an exciting venture into the world of open-source BIM. Follow these steps to create a foundational project setup:
- Open Blender and ensure that the BlenderBIM add-on is installed and enabled.
- Create a new file in Blender and save it with an appropriate project name.
- In the 3D Viewport, press \"N\" to open the right sidebar and switch to the \"Scene\" tab to access BlenderBIM tools.
- Click on the \"Create Project\" button in the BlenderBIM UI to initiate a new BIM project.
- Select the appropriate project template or start from scratch depending on your project needs.
- Begin by setting up your project\"s structure. Define the Spatial Structure Elements (SSEs) like Site, Building, and Storeys.
- With the project structure in place, start modeling your design using Blender\"s modeling tools. Assign BIM properties to your elements as you go.
- Utilize BlenderBIM\"s library of predefined objects and materials to enhance your project or create custom elements as needed.
- As your project develops, continuously manage and update BIM data through the BlenderBIM interface.
- Export your project as an IFC file for sharing and collaboration with stakeholders and other BIM software.
This guide provides a foundational approach to start your journey with BlenderBIM. As you become more familiar with the toolset, explore advanced features and techniques to further enhance your projects.
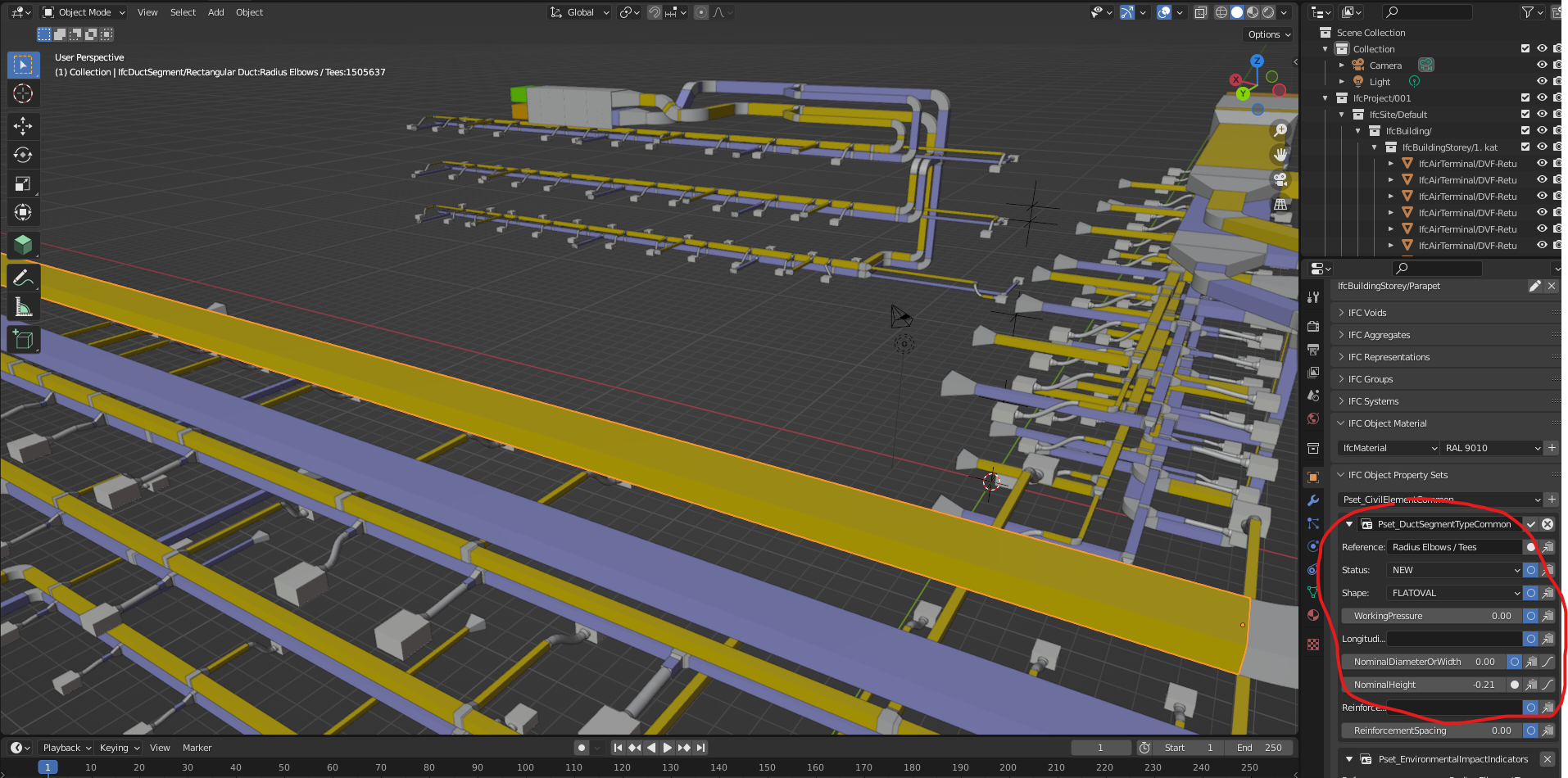
_HOOK_
Advanced Modeling Techniques
Expanding your skills with BlenderBIM involves mastering advanced modeling techniques to create more sophisticated and detailed BIM models. Here are some advanced strategies to elevate your BlenderBIM projects:
- Utilizing parametric modeling to create dynamic, adjustable models that can easily adapt to design changes.
- Implementing custom Python scripts to automate repetitive tasks and enhance model accuracy and efficiency.
- Exploring non-destructive modeling workflows using modifiers for flexibility in design iterations.
- Leveraging Blender\"s powerful sculpting tools for complex shapes and surfaces, particularly useful in organic architectural elements.
- Applying advanced texturing techniques, including UV mapping and procedural textures, to add realism to your models.
- Integrating photogrammetry for accurate real-world texturing and modeling, enhancing the realism of your BIM projects.
- Mastering the use of Blender\"s particle system for environmental simulations, such as vegetation and crowds, to bring life to your architectural scenes.
- Employing advanced lighting and rendering techniques to produce high-quality visualizations directly from your BIM models.
- Using BlenderBIM\"s features for clash detection and resolution to streamline collaboration and reduce construction conflicts.
By incorporating these advanced techniques, you can push the boundaries of traditional BIM modeling, leveraging BlenderBIM\"s full potential to create innovative, detailed, and data-rich architectural projects.

Integration with Other Software
BlenderBIM\"s ability to integrate with other software enhances its utility in a multi-disciplinary BIM environment. This integration is crucial for seamless project workflows, enabling professionals to collaborate across different platforms:
- Native Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) support ensures compatibility with a wide range of BIM software, facilitating easy exchange of 3D models and associated data.
- Integration with GIS (Geographic Information Systems) for site analysis, planning, and context modeling, enabling the use of georeferenced data within BlenderBIM projects.
- Connection with structural analysis software through IFC to apply and test structural concepts directly from BlenderBIM models.
- Compatibility with MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) design software, allowing for detailed design and coordination within the Blender environment.
- Use of Blender\"s robust rendering engines (Cycles and Eevee) for photorealistic visualizations, which can be enhanced with data from BlenderBIM for accurate representations of materials and lighting.
- Support for importing and exporting common file formats such as OBJ, STL, and COLLADA, in addition to IFC, broadens the scope for collaboration with various CAD and visualization tools.
- Integration with project management and collaboration tools, enabling the syncing of project timelines, tasks, and resources with BIM models.
- Ability to leverage Python scripting for custom integrations, automations, and extensions, enhancing the interoperability between BlenderBIM and other software solutions.
These integrations position BlenderBIM as a versatile tool within the BIM ecosystem, bridging gaps between different disciplines and software platforms, and fostering a more collaborative, efficient project delivery process.
BlenderBIM Addon Showcase
\"Looking to enhance your gaming experience? Check out this incredible addon that will take your favorite game to the next level! Discover new features, characters, and levels that will keep you hooked for hours on end. Don\'t miss out on this game-changing experience!\"
BlenderBIM for Beginners: Introduction
\"Are you new to the world of [topic]? This video is perfect for you! Join our experts as they break down the basics and provide helpful tips for beginners. You\'ll be a pro in no time! Start your journey towards mastering [topic] with this insightful video today!\"
Handling Large Models and Performance Optimization
Working with large models in BlenderBIM can be challenging, but following these guidelines can help optimize performance and manage complex projects efficiently:
- Use Blender\"s layer and collection system to organize your model, enabling you to hide or isolate parts of the model when not actively working on them.
- Implement viewport shading options like \"Bounding Box\" or \"Wireframe\" mode to reduce the graphical load when navigating large models.
- Leverage Blender\"s \"Simplify\" option to reduce the detail levels of objects in the viewport, which can significantly improve responsiveness without affecting the model\"s integrity.
- Optimize your model\"s geometry by merging objects or eliminating unnecessary vertices, faces, and edges. This can dramatically reduce the computational load.
- Make use of BlenderBIM\"s ability to work with external references, allowing for the management of large, federated models without the need to load everything into a single file.
- Consider splitting large projects into separate Blender files and using Blender\"s linking system to assemble them, which can help manage file sizes and improve performance.
- Regularly clean up your file by purging unused data blocks, such as meshes, materials, or textures, which can accumulate over time and slow down your project.
- For rendering, use Blender\"s render layers and scenes to manage and render parts of your project individually, reducing the memory footprint and processing time.
- Adjust Blender\"s memory management settings in the preferences to optimize how Blender utilizes your system\"s resources.
- Stay up to date with Blender and BlenderBIM updates, as performance improvements and optimizations are regularly introduced.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively handle large models in BlenderBIM, ensuring smoother workflows and better performance throughout your projects.
Collaboration and Sharing in BlenderBIM
BlenderBIM facilitates collaboration and sharing among project stakeholders, making it a powerful tool for team-based BIM projects. Here\"s how to maximize collaboration and sharing:
- Use the native IFC support to exchange models with other BIM software seamlessly, ensuring all team members can access and modify the shared model regardless of the software they are using.
- Leverage BlenderBIM\"s version control capabilities to track changes, manage revisions, and ensure that all collaborators are working on the most current version of the project.
- Implement collaborative design reviews using BlenderBIM\"s visualization tools to create walkthroughs, renderings, and animations that can be shared with clients and stakeholders for feedback.
- Utilize cloud storage solutions to share Blender files and associated BIM data, allowing team members to access and update models from any location.
- Explore the use of BlenderBIM\"s web-based collaboration platforms for real-time project communication, coordination, and management, facilitating smoother workflows and decision-making processes.
- Adopt BIM collaboration formats (BCF) for issue tracking and management within BlenderBIM, enabling efficient resolution of design and construction issues among team members.
- Engage in the BlenderBIM community for support, sharing experiences, and exchanging tips and tricks with other professionals, enhancing collective knowledge and skills in BIM practices.
By incorporating these strategies into your BlenderBIM workflow, you can enhance project collaboration, improve efficiency, and deliver higher quality projects through effective teamwork and information sharing.
Learning Resources and Community Support
The BlenderBIM community offers a wealth of learning resources and support for both new and experienced users. Here are key avenues to explore:
- Official BlenderBIM Add-on Website: Hosts comprehensive documentation, installation guides, and tutorials to get you started.
- OSArch Community Forums: A vibrant forum for asking questions, sharing projects, and learning from other BlenderBIM users.
- YouTube Tutorials: Numerous video tutorials are available, ranging from beginner introductions to advanced modeling techniques.
- BlenderBIM Wiki: An extensive repository of knowledge, including technical details, how-to guides, and best practices for using BlenderBIM effectively.
- GitHub Repository: The source code of BlenderBIM is openly available for those interested in contributing or exploring the codebase.
- Blender Artists Forum: A place to discuss Blender and BlenderBIM, share work, and connect with the creative community.
- Webinars and Live Streams: Regularly held sessions by experienced users and developers, providing deep dives into specific features and workflows.
- Workshops and Meetups: Opportunities to join live events and meetups for hands-on learning and networking with fellow BlenderBIM enthusiasts.
Engaging with these resources and the BlenderBIM community can greatly accelerate your learning curve and enhance your proficiency in BIM modeling with Blender.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Funding and Development Insights
The BlenderBIM add-on, a significant tool in the open-source BIM landscape, has seen remarkable development strides, thanks to diverse funding sources and a dedicated development team. Here\"s an overview of its funding and development:
- Received Epic MegaGrants, highlighting its importance and potential within the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) sectors.
- Supported by individual contributions and community funding, demonstrating the strong community belief in open-source solutions for BIM.
- Development led by a global community of contributors, ensuring that BlenderBIM remains on the cutting edge of BIM technology.
- Open-source construction grants, such as those from Cesium, further bolster its development, enabling integration with geospatial technologies.
- The IfcOpenShell project underpins BlenderBIM, providing critical infrastructure for IFC data manipulation and enhancing interoperability with other BIM software.
- Community-driven enhancements and bug fixes ensure BlenderBIM meets the evolving needs of its users.
- BlenderBIM\"s roadmap reflects a commitment to expanding its capabilities, with ongoing efforts to improve usability, functionality, and integration with other tools.
This collaborative and funded approach ensures BlenderBIM remains a powerful, evolving tool for the AEC industry, promoting innovation and accessibility in BIM practices.
Embrace the future of BIM with BlenderBIM, where innovation meets collaboration. Dive into this open-source revolution and transform your architectural, engineering, and construction projects with unparalleled flexibility and power.