Topic how to model character in blender: Discover the exciting journey of character creation in Blender, from basic modeling techniques to advanced sculpting, and bring your 3D characters to life with this comprehensive guide.
Table of Content
- How can I model a character in Blender?
- Getting Started
- Modeling Basics
- Advanced Techniques
- Rigging and Animation
- Finalizing Your Character
- Modeling Basics
- Advanced Techniques
- Rigging and Animation
- YOUTUBE: Blender Modelling Tutorial for Absolute Beginners - Simple Human
- Finalizing Your Character
- Advanced Techniques
- Rigging and Animation
- Finalizing Your Character
- Rigging and Animation
- Finalizing Your Character
- Finalizing Your Character
- Introduction to Blender and Character Modeling
- Essential Tools and Interface Overview
- Step-by-Step Guide to Starting Your Character Model
- Importing Reference Images for Accuracy
- Basic Modeling Techniques: From Blocking to Detailing
- Advanced Sculpting Methods for Character Enhancement
- Optimizing Mesh Topology for Animation
- Texturing and Material Application for Realism
- Rigging Your Character for Animation
- Animating Your Character: Basic to Advanced Techniques
- Rendering and Exporting Your Finished Character
- Tips and Tricks for Efficient Workflow
- Resources for Further Learning and Community Engagement
How can I model a character in Blender?
To model a character in Blender, follow these steps:
Gather references: Before you start, gather references of the character you want to model. This could include sketches, images, or even real-life references.
Open Blender: Launch Blender on your computer.
Create a new project: Start by creating a new project in Blender.
Select and delete the default cube: In the 3D viewport, select the default cube and press the Delete key to remove it.
Import reference images: Import the reference images that you gathered earlier. You can do this by going to \'View\' > \'Image Editor\' and then clicking \'Open\' to select and import your reference images.
Begin modeling: Start by creating a basic mesh structure of the character using primitive objects like cubes, spheres, or cylinders. You can use tools like extrude, scale, and rotate to shape the mesh according to your reference.
Refine the mesh: Once you have the basic structure, refine the mesh by adding more details and smoothing the topology. Use tools like loop cut, bevel, and subdivision surface modifier to enhance the geometry.
Add facial features: If modeling a human character, focus on adding facial features like eyes, nose, mouth, and ears. Pay attention to the reference images to ensure accuracy.
Create clothing and accessories: If necessary, model clothing and accessories for your character. This can involve creating separate meshes and attaching them to the character\'s body.
Texture and UV unwrap: Once the model is complete, you can unwrap the UVs and apply textures to give the character color and detail. This can be done using the UV editing workspace in Blender.
Optimize and finalize: Clean up the mesh, remove any unnecessary geometry, and optimize the topology. Make sure everything looks good from different angles.
Save and export: Save your project and export the character in a suitable file format for further use or rendering.
Remember, character modeling takes practice and patience. Keep refining your skills, studying anatomy, and experimenting with different techniques to improve your character modeling abilities in Blender.
READ MORE:
Getting Started
- Download and install the latest version of Blender.
- Familiarize yourself with the Blender interface and navigation controls.
- Set up your workspace by adjusting the layout to suit character modeling.

Modeling Basics
- Reference Images: Import reference images of your character to use as a guide.
- Blocking Out Shapes: Start by creating basic shapes to block out your character\"s proportions.
- Mesh Editing: Use Blender\"s Edit Mode to refine the shapes and add details.

Advanced Techniques
Once you have the basic shape, you can move on to more advanced techniques to bring your character to life.
- Sculpting: Use Blender\"s sculpting tools to add complex details and textures.
- Topology: Ensure your character has clean topology for better animation and rigging.
- Materials and Textures: Apply materials and textures to your character for realism.

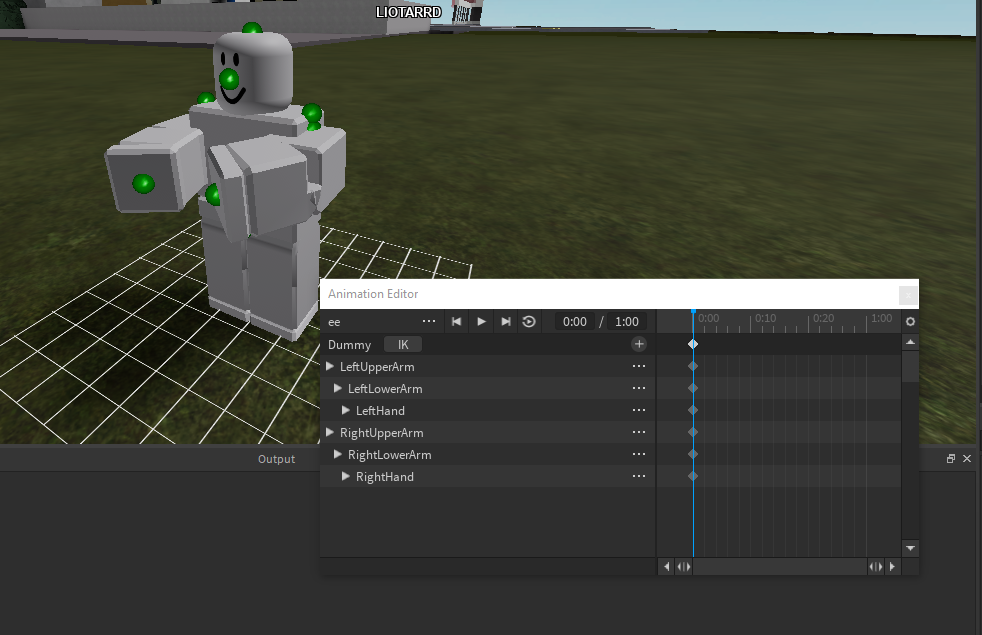
Rigging and Animation
After your character is modeled and textured, rigging is the next step before animation.
- Create a skeleton for your character.
- Parent the mesh to the skeleton with automatic weights.
- Adjust weight paints for accurate deformation.

_HOOK_
Finalizing Your Character
With modeling, texturing, and rigging completed, you\"re ready to animate your character or export it for use in other projects.
Tips for Success
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
- Explore Blender\"s vast array of tutorials and community resources.
- Experiment with different styles and techniques.
Modeling characters in Blender opens up a world of creativity and technical skill. By following this guide, you\"ll be well on your way to creating dynamic and detailed characters for any project.

Modeling Basics
- Reference Images: Import reference images of your character to use as a guide.
- Blocking Out Shapes: Start by creating basic shapes to block out your character\"s proportions.
- Mesh Editing: Use Blender\"s Edit Mode to refine the shapes and add details.

Advanced Techniques
Once you have the basic shape, you can move on to more advanced techniques to bring your character to life.
- Sculpting: Use Blender\"s sculpting tools to add complex details and textures.
- Topology: Ensure your character has clean topology for better animation and rigging.
- Materials and Textures: Apply materials and textures to your character for realism.

Rigging and Animation
After your character is modeled and textured, rigging is the next step before animation.
- Create a skeleton for your character.
- Parent the mesh to the skeleton with automatic weights.
- Adjust weight paints for accurate deformation.

Blender Modelling Tutorial for Absolute Beginners - Simple Human
Check out this fantastic video on Blender Modelling and learn how to create stunning 3D models with ease! Whether you\'re a beginner or an experienced artist, this step-by-step tutorial will take your skills to the next level. Don\'t miss out on the opportunity to unleash your creativity and become a master at Blender Modelling!
Blender Character Modeling Tutorial for Absolute Beginners - Part 1
Dive into the captivating world of Character Modeling with this mind-blowing video tutorial. Discover the secrets behind bringing characters to life as you watch an expert artist demonstrate advanced techniques and share invaluable tips. Whether you\'re an aspiring animator or simply have a passion for digital art, this video is a must-watch for anyone interested in creating incredible character models.
Finalizing Your Character
With modeling, texturing, and rigging completed, you\"re ready to animate your character or export it for use in other projects.
Tips for Success
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
- Explore Blender\"s vast array of tutorials and community resources.
- Experiment with different styles and techniques.
Modeling characters in Blender opens up a world of creativity and technical skill. By following this guide, you\"ll be well on your way to creating dynamic and detailed characters for any project.

_HOOK_
Advanced Techniques
Once you have the basic shape, you can move on to more advanced techniques to bring your character to life.
- Sculpting: Use Blender\"s sculpting tools to add complex details and textures.
- Topology: Ensure your character has clean topology for better animation and rigging.
- Materials and Textures: Apply materials and textures to your character for realism.

Rigging and Animation
After your character is modeled and textured, rigging is the next step before animation.
- Create a skeleton for your character.
- Parent the mesh to the skeleton with automatic weights.
- Adjust weight paints for accurate deformation.
Finalizing Your Character
With modeling, texturing, and rigging completed, you\"re ready to animate your character or export it for use in other projects.
Tips for Success
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
- Explore Blender\"s vast array of tutorials and community resources.
- Experiment with different styles and techniques.
Modeling characters in Blender opens up a world of creativity and technical skill. By following this guide, you\"ll be well on your way to creating dynamic and detailed characters for any project.
Rigging and Animation
After your character is modeled and textured, rigging is the next step before animation.
- Create a skeleton for your character.
- Parent the mesh to the skeleton with automatic weights.
- Adjust weight paints for accurate deformation.
Finalizing Your Character
With modeling, texturing, and rigging completed, you\"re ready to animate your character or export it for use in other projects.
Tips for Success
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
- Explore Blender\"s vast array of tutorials and community resources.
- Experiment with different styles and techniques.
Modeling characters in Blender opens up a world of creativity and technical skill. By following this guide, you\"ll be well on your way to creating dynamic and detailed characters for any project.
_HOOK_
Finalizing Your Character
With modeling, texturing, and rigging completed, you\"re ready to animate your character or export it for use in other projects.
Tips for Success
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
- Explore Blender\"s vast array of tutorials and community resources.
- Experiment with different styles and techniques.
Modeling characters in Blender opens up a world of creativity and technical skill. By following this guide, you\"ll be well on your way to creating dynamic and detailed characters for any project.
Introduction to Blender and Character Modeling
Blender is a powerful, free, and open-source 3D creation suite that supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline—modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing, and motion tracking. Character modeling in Blender is a fascinating process that allows artists to bring their visions to life. This section will introduce you to the basics of Blender and the fundamentals of character modeling, setting the foundation for your journey into 3D character creation.
- Understanding Blender’s Interface: Familiarize yourself with Blender’s comprehensive and customizable interface to navigate through tools and features efficiently.
- Setting Up Your Project: Learn how to set up your project for character modeling, including the importance of reference images and how to import them into Blender.
- Basic Modeling Techniques: Get started with basic modeling techniques such as mesh editing, extrusion, and subdivision to begin shaping your character.
- Introduction to Sculpting: Discover the sculpting tools that Blender offers for adding details and personality to your character.
- Essential Tips for Effective Character Modeling: Explore best practices for creating efficient, animation-ready models, including topology and edge flow considerations.
Character modeling in Blender is not just about creating a figure; it\"s about bringing a character to life with its unique story and personality. This introductory guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to embark on your character modeling journey.
Essential Tools and Interface Overview
Blender\"s interface is designed to offer maximum efficiency for artists and creators. Understanding the tools and layout is crucial for effective character modeling. This section will guide you through the essential tools and features of Blender\"s interface that you\"ll use most frequently in character creation.
- 3D Viewport: The main area where you\"ll model, sculpt, and animate your character. It offers various shading modes to visualize your work.
- Outliner: A hierarchical list of all objects in your scene, making it easy to select and manage your character components.
- Properties Panel: Provides access to all the properties of the selected object, including materials, modifiers, and physics settings.
- Tool Shelf: Contains tools for transforming, editing, and sculpting your character model.
- Timeline: For animation, the timeline allows you to manage keyframes and control animation playback.
Understanding Blender\"s layout customization is also key. You can arrange and adjust the interface to fit your workflow, ensuring the tools you need are always at hand. For character modeling, focusing on the 3D viewport, tool shelf, and properties panel will streamline your process.
- Shortcuts: Learning Blender\"s keyboard shortcuts can significantly speed up your modeling process. Shortcuts for tools like extrude (E), loop cut (Ctrl+R), and sculpting brushes will become invaluable.
- Add-ons: Blender supports a wide range of add-ons that can enhance your character modeling workflow, from sculpting brushes to topology tools.
By familiarizing yourself with these essential tools and the interface of Blender, you\"ll be well-prepared to start creating detailed and dynamic characters. Whether you\"re sculpting intricate details or rigging for animation, knowing how to navigate and utilize Blender\"s features is the first step towards bringing your creative visions to life.
Step-by-Step Guide to Starting Your Character Model
- Preparation:
- Gather reference images to ensure accuracy and consistency in your character’s design.
- Set up your Blender workspace by splitting your view for modeling and reference image comparison.
- Beginning with a Base Mesh:
- Start by creating a simple base mesh that outlines the basic shape of your character. This could be a sphere for the head, cylinders for limbs, etc.
- Use Blender\"s mirror modifier to ensure symmetry in human characters.
- Refining the Shape:
- Adjust the base mesh to match your character’s proportions more closely, using your reference images as a guide.
- Utilize the sculpting tools for detailed shaping and to add character features.
- Detailing:
- Once the basic shape is established, begin adding details such as facial features, clothing, and hair using finer sculpting tools and brushes.
- Consider the character’s anatomy and how muscles and clothing would realistically interact.
- Retopology:
- After sculpting, the next step is retopology, which involves creating a new mesh with clean topology over your sculpted character. This is essential for animation.
- Use Blender’s retopology tools to make this process easier and ensure your mesh has good flow and minimal polygons.
- UV Unwrapping and Texturing:
- Once your model has clean topology, unwrap the UVs to apply textures.
- Paint or import textures to add color, depth, and detail to your character.
- Rigging and Weight Painting:
- Create a skeleton (armature) for your character and bind the mesh to the skeleton.
- Adjust the weight painting to control how the mesh deforms in relation to the bones during animation.
- Basic Animation:
- With your character rigged, begin experimenting with simple animations to see how your character moves.
- Test the rig by posing the character or creating basic walk cycles.
This guide outlines the fundamental steps in character modeling within Blender, from initial concept and reference gathering to the final stages of rigging and basic animation. Each step is crucial in creating a character that is both visually appealing and ready for animation.
Importing Reference Images for Accuracy
Importing reference images into Blender is a crucial step for achieving accurate and realistic character models. This process allows you to use real-world references to guide your modeling, ensuring proportions and details are correct. Follow these steps to efficiently import and utilize reference images in your Blender projects.
- Prepare Your Reference Images: Before importing, ensure your images are clear and cover multiple views (front, side, and back) of your character for comprehensive guidance.
- Setting Up Background Images:
- Open Blender and select the camera, light, and default cube. Press delete to clear the scene.
- Switch to the orthographic view (numpad 1 for front view, numpad 3 for side view) where you want to place your reference.
- Go to the \"Properties Panel\" > \"Background Images\" > \"Add Image\". Choose the reference image from your files.
- Adjust the image\"s opacity, size, and position to match your modeling viewport for easy referencing.
- Modeling With Reference Images: As you model, continuously refer to these images to guide your work. Adjust your mesh to align with the key features and proportions seen in your references.
- Utilizing Layers for Multiple References: For complex characters, use different layers or collections for front, side, and back references, toggling visibility as needed to focus on specific aspects of your model.
Importing and properly setting up reference images in Blender can significantly enhance the accuracy and realism of your character models. This foundational step ensures that your creative vision is grounded in realistic proportions and details, providing a solid basis for further modeling, sculpting, and detailing work.
_HOOK_
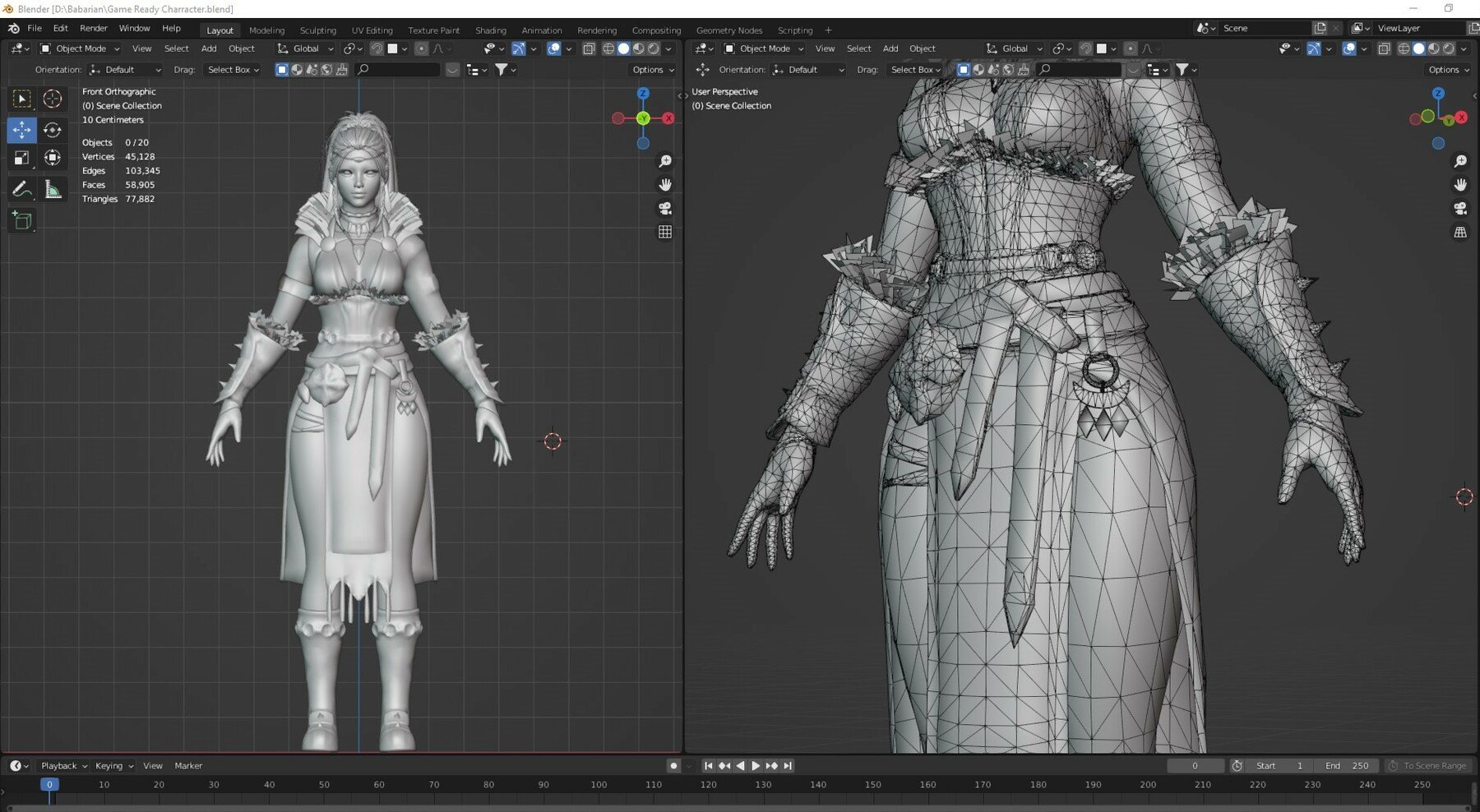
Basic Modeling Techniques: From Blocking to Detailing
Mastering the basics of modeling in Blender is essential for creating detailed and lifelike characters. This section breaks down the fundamental steps, from initial blocking to adding fine details, to guide you through the character modeling process.
- Blocking Out the Basic Shape: Begin by creating a simple, low-detail mesh that outlines the general shape of your character. This stage is crucial for establishing correct proportions and overall form.
- Refining the Blockout: Once the basic shape is established, start refining the blockout by adding more geometry and details. Use tools like the Extrude and Loop Cut to define muscles, facial features, and other character-specific details.
- Using Modifiers: Blender\"s modifiers can significantly streamline the modeling process. Utilize the Mirror Modifier for symmetrical models, and the Subdivision Surface Modifier to smooth out the geometry and add more detail without manually increasing the poly count.
- Sculpting for Details: After the basic form is refined, switch to sculpting mode to add complex details such as wrinkles, clothing folds, and facial expressions. Blender\"s sculpting tools offer a wide range of brushes and settings for detailed work.
- Topology and Edge Flow: Good topology is crucial for animation and the overall look of your character. Ensure your model has a clean edge flow, especially around joints and facial features, to facilitate smooth deformations during animation.
- Retopology: For characters with high detail sculpted in, retopology may be necessary. This process involves creating a new, cleaner mesh over your detailed sculpt. Blender\"s retopology tools, like the Shrinkwrap Modifier and the Snap to Faces feature, can help streamline this process.
By following these basic modeling techniques, you\"ll be able to create a solid foundation for your character, ready for further detailing, texturing, and rigging. Remember, patience and practice are key to mastering character modeling in Blender.
Advanced Sculpting Methods for Character Enhancement
Once you have a basic model, Blender\"s advanced sculpting tools allow you to enhance your character with intricate details and textures. These methods enable artists to add realism and personality to their characters, pushing the boundaries of digital art.
- Dynamic Topology (Dyntopo): Dyntopo allows for flexible sculpting by adding geometry dynamically where needed. This is ideal for creating complex surface details such as wrinkles, scars, or clothing textures.
- Multi-resolution Sculpting: Use the MultiRes modifier to sculpt on different levels of detail. Start with broad shapes at lower resolutions and gradually move to finer details at higher resolutions.
- Brushes and Stroke Methods: Blender offers a wide variety of sculpting brushes and stroke methods. Experiment with brushes like Clay Strips, Crease, Grab, and Layer to achieve different effects and textures.
- Masking: Mask areas of your model to protect them from being affected by sculpting. This is useful for isolating parts of your character during detailed work.
- Stencils and Alphas: Use stencils and alphas to apply complex patterns and textures to your character\"s surface. This technique can dramatically enhance the realism of skin, fabric, and other materials.
- Sculpting with Symmetry: For characters that require symmetry, use the symmetry tool to mirror your sculpting actions across the model. This ensures uniformity in features like faces and bodies.
- Remeshing and Retopology: After adding details, you may need to remesh or retopologize your model for animation. Use Blender\"s remeshing tools to create a more uniform and animation-friendly topology.
Advanced sculpting is a powerful way to bring your characters to life with depth, emotion, and detail. By mastering these techniques, you can create compelling and realistic characters that are ready for animation and rendering in Blender.
Optimizing Mesh Topology for Animation
Optimizing mesh topology is critical for creating characters in Blender that move realistically and are efficient to animate. Proper topology ensures smooth deformations and reduces rendering times, making your animation process more streamlined. Follow these steps to optimize your character\"s mesh topology for animation.
- Understand Edge Flow: Edge flow refers to the direction in which your mesh\"s edges travel, which should mimic the natural movement of muscles and skin. Good edge flow is essential for facial expressions and joint movements.
- Use Quads for Flexibility: Building your model with quads (four-sided polygons) is recommended because they deform more predictably during animation than triangles or n-gons.
- Maintain Even Geometry Distribution: Ensure that your model\"s geometry is evenly distributed to avoid deformations. Areas requiring more flexibility, like joints, may need more geometry to deform smoothly.
- Implement Edge Loops Around Joints: Insert edge loops close to each other around joints (knees, elbows, fingers) to create a mesh that bends correctly and maintains volume during movement.
- Minimize N-gons and Triangles: N-gons (polygons with more than four sides) and triangles can cause artifacts in animations. Try to keep your mesh topology to quads as much as possible, especially in deformable areas.
- Retopology Tools: Use Blender\"s retopology tools, such as the Shrinkwrap modifier or the F2 addon, to refine your mesh\"s topology after sculpting. These tools can help create a cleaner, more animation-friendly topology.
- Check Deformations with Test Rigs: Before finalizing your character, apply a basic rig and pose the model in extreme positions to check how the mesh deforms. Adjust the topology as necessary to improve deformations.
By focusing on clean, efficient topology, you can create characters that not only look great but also move naturally and are easier to animate. This optimization process is a crucial step in the character modeling workflow in Blender, enabling animators to bring characters to life with realistic movements.
Texturing and Material Application for Realism
Texturing and applying materials are crucial steps in bringing your Blender character models to life with realism and depth. These processes involve mapping detailed images and shaders onto your model to simulate real-world surfaces and appearances. Follow this guide to master texturing and material application.
- UV Unwrapping Your Model: Begin by unwrapping your model to create a 2D representation of its surface, which allows for accurate texture mapping. Use Blender’s UV editing tools to adjust seams and layout for minimal distortion.
- Selecting Textures: Choose high-quality textures that match your character’s environment and story. Consider using textures for skin, clothing, hair, and accessories to add detail and realism.
- Applying Textures: Apply your selected textures to the model using Blender’s material properties. Adjust mapping coordinates and scale to fit your UV layout perfectly.
- Creating Materials: Create materials to define the surface properties of your model, such as color, glossiness, and transparency. Use Blender’s shader nodes to combine textures and create complex materials like skin, metal, or fabric.
- Using Subsurface Scattering: For realistic skin, use subsurface scattering (SSS) to simulate light penetrating the surface of the skin. Adjust SSS settings to match the character’s skin tone and lighting conditions.
- Adding Bump and Normal Maps: Enhance surface details without adding geometry by using bump and normal maps. These maps simulate surface irregularities and are essential for creating realistic textures like pores, wrinkles, or fabric weaves.
- Final Adjustments: Fine-tune your materials and textures in context with lighting and environment to ensure they look as realistic as possible. Experiment with different lighting setups and render settings to achieve the best result.
By carefully unwrapping your model, selecting appropriate textures, and skillfully applying materials, you can achieve a level of realism in your Blender characters that brings them to life. Remember, the key to successful texturing and material application is attention to detail and an understanding of how surfaces interact with light.
Rigging Your Character for Animation
Rigging is the process of creating a skeleton for your character so that it can be animated. In Blender, rigging involves using armatures (bones) to create a rig that mimics the character\"s skeletal structure, enabling realistic and flexible movement. Follow these steps to effectively rig your character for animation.
- Creating the Armature: Start by adding an armature object to your scene. Each bone in the armature represents a part of the character\"s anatomy that will move independently.
- Positioning Bones: Carefully place bones within the mesh of your character, aligning them with the character’s anatomical structure. Use parent-child relationships between bones to establish hierarchy and movement constraints.
- Adjusting Bone Weights: Weight painting is used to define how much influence each bone has on different parts of the mesh. Paint weights carefully to ensure smooth and realistic deformations.
- Creating IK (Inverse Kinematics) Constraints: IK constraints can simplify animation by allowing for more natural movements with fewer controls. Set up IK on limbs for easier posing and animation.
- Adding Control Rig: For complex characters, a control rig made of custom bones and constraints can provide animators with intuitive controls for animation without directly manipulating the bones.
- Testing the Rig: Before moving to animation, pose your character in various positions to test the rig’s functionality. Make adjustments as needed to ensure the rig behaves as expected under different scenarios.
Rigging is a crucial step in character animation, providing the foundation for all future animations. By creating a well-structured rig, you enable your character to move in a lifelike and convincing manner, ready for animation in Blender.
_HOOK_
Animating Your Character: Basic to Advanced Techniques
Animating a character in Blender involves bringing your rigged model to life through movement. Whether you\"re aiming for subtle facial expressions or dynamic body movements, understanding both basic and advanced animation techniques is essential. This section will guide you through the animation process, from setting up your first keyframes to applying complex animation principles for lifelike results.
- Understanding Keyframes: Keyframes are the cornerstone of animation, marking the start and end points of any movement. Learn how to insert keyframes for different properties like location, rotation, and scale.
- Using the Dope Sheet and Graph Editor: The Dope Sheet provides an overview of all your keyframes, making it easier to organize and time your animations. The Graph Editor allows for fine-tuning of the animation curves, offering control over the pacing and smoothness of movements.
- Principles of Animation: Apply the 12 principles of animation, such as anticipation, squash and stretch, and secondary action, to add realism and appeal to your character\"s movements.
- Animating with Inverse Kinematics: Inverse Kinematics (IK) simplifies the animation of complex movements, particularly in limbs, by allowing you to manipulate the end effector (like a hand or foot) and have the system calculate the positions of the joints automatically.
- Morph Targets and Shape Keys: Use morph targets (shape keys in Blender) for facial expressions and subtle morphs. This technique is crucial for lip-syncing and conveying emotion through facial movements.
- Non-linear Animation (NLA) Editor: For complex animations, the NLA Editor allows you to blend and layer different actions. This is especially useful for reusing animation clips, like walk cycles or gestures.
- Adding Sound and Lip-sync: Incorporate sound files and use them to guide your lip-sync animation for dialogue. Blender\"s audio tools can help you match your character\"s mouth movements to spoken words accurately.
- Polishing and Smoothing: After blocking out the main movements, go back to refine and smooth out animations, ensuring that movements are fluid and natural-looking.
Animation breathes life into your character, transforming them from a static model to a dynamic personality within their world. By mastering both basic and advanced techniques, you can create animations that captivate and entertain your audience.
Rendering and Exporting Your Finished Character
After modeling, texturing, and animating your character in Blender, the final steps are rendering and exporting your creation. These processes transform your 3D model into beautiful images, animations, or files for use in other applications. Here\"s how to accomplish these crucial steps effectively.
- Preparing for Rendering: Before rendering, ensure all textures, materials, and animations are correctly applied and finalized. Adjust your scene\"s lighting and camera angles to highlight your character\"s best features.
- Choosing a Render Engine: Blender offers several render engines, including Eevee (real-time) and Cycles (ray-traced). Choose the one that best suits your project\"s needs for quality and speed.
- Render Settings: In the Render Properties panel, adjust settings such as resolution, samples (for Cycles), and output format. For animations, specify the frame range and frame rate.
- Rendering: Use the Render Image or Render Animation button to start the rendering process. For large projects, consider using Blender’s Render Farm or external services to speed up rendering times.
- Exporting Your Character: To use your character in other projects or applications, export it in a compatible format. Common formats include FBX, OBJ, or glTF. Go to File > Export and select the desired format. Ensure to include all necessary data such as textures, armatures, and animations.
- Testing Exported Files: After exporting, import your character into the target application or engine (like Unity or Unreal Engine) to test compatibility and performance. Make any required adjustments back in Blender if issues arise.
Rendering and exporting are the final steps in the character creation process in Blender, culminating in a project ready for presentation or integration into larger scenes or games. By carefully preparing your scene and understanding the best practices for rendering and exporting, you can ensure your character looks as intended in any context.
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Workflow
Creating characters in Blender can be a complex process, requiring attention to detail across modeling, texturing, rigging, and animation. To streamline your workflow and enhance productivity, here are some valuable tips and tricks.
- Use Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with Blender\"s keyboard shortcuts to speed up your workflow. Shortcuts for commonly used actions can significantly reduce modeling and editing time.
- Organize Your Workspace: Customize Blender\"s interface to suit your workflow. Use separate windows for the 3D viewport, UV/image editor, and shader editor for easy access during different stages of character creation.
- Start with Good Topology: Begin with a clean topology to make editing, texturing, and animating easier down the line. Use quads for better deformations and subdivision.
- Block Out Basic Shapes First: Start by blocking out your character\"s basic shapes before moving on to details. This helps in establishing correct proportions and saves time on adjustments later.
- Make Use of Modifiers: Modifiers like Mirror, Subdivision Surface, and Multiresolution can simplify the modeling process and allow for non-destructive editing.
- Keep a Reference Image Handy: Use reference images for accuracy in proportions and details. Blender\"s background image feature in the viewport can be a helpful guide.
- Utilize Blender’s Asset Libraries: Speed up your workflow by using assets from Blender’s libraries for common objects and materials, saving time on modeling and texturing from scratch.
- Learn to Retopologize: For high-detail sculpts, learn efficient retopology techniques to create animation-ready models with good flow and minimal polygons.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, proficiency in Blender comes with practice. Set aside regular time to work on different aspects of character creation to improve steadily.
- Stay Updated: Blender is continuously updated with new features and improvements. Stay informed about the latest tools and techniques to enhance your character modeling skills.
Implementing these tips into your Blender workflow can significantly improve your efficiency and quality of work, allowing you to focus more on creativity and less on repetitive tasks.
READ MORE:
Resources for Further Learning and Community Engagement
Expanding your knowledge and skills in character modeling in Blender is an ongoing journey. The following resources are invaluable for learners of all levels, offering tutorials, courses, and community support to enhance your character creation process.
- Blender Official Tutorials: Blender.org offers a comprehensive range of tutorials and documentation designed to help beginners to advanced users master Blender.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and YouTube host numerous courses ranging from basic Blender introductions to advanced character modeling techniques.
- Blender Community Forums: Engage with the Blender community through forums and discussion boards such as Blender Artists and the Blender subreddit. These communities are great for seeking advice, sharing work, and finding solutions to common problems.
- Blender Network: Connect with professionals and enthusiasts through the Blender Network, offering opportunities for collaboration, job listings, and networking.
- Blender Conferences and Meetups: Participating in Blender conferences, both virtual and in-person, can provide insights into the latest developments, techniques, and networking opportunities with other Blender users.
- Books and E-books: There are several detailed guides and books available for learning Blender, covering everything from the basics to specialized topics like character animation.
- Blender Studio Projects: Explore open projects and resources provided by Blender Studio for real-world examples of character modeling and animation.
Utilizing these resources can significantly enhance your learning curve and keep you updated with the latest trends and techniques in character modeling. Engaging with the Blender community also provides motivational support and inspiration for your projects.
Embark on a creative journey with Blender to bring your imaginative characters to life. Mastering character modeling is an adventure filled with endless possibilities, where your artistry and Blender\"s capabilities unite to craft truly dynamic creations.