Topic how to edit video with blender: Unlock the full potential of video editing with Blender, a comprehensive tool that transforms your visual stories into masterpieces. This guide will walk you through the basics to advanced techniques, ensuring a smooth editing journey.
Table of Content
- What are the beginner steps for editing videos with Blender 2.8?
- Getting Started with Blender for Video Editing
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface for Video Editing
- Importing and Organizing Your Media
- Basic Video Editing Techniques: Cutting, Trimming, and Splicing
- YOUTUBE: Blender 3.0 Video Editing Tutorial Ep.1 Interface Output Timeline Import Render
- Advanced Editing Features: Effects, Transitions, and Color Grading
- Working with Audio: Syncing, Mixing, and Sound Effects
- Adding Text and Titles for Professional Finishing Touches
- Utilizing Blender\"s Animation Tools in Video Editing
- Rendering and Exporting Your Final Video Project
- Tips and Tricks for Efficient Video Editing in Blender
What are the beginner steps for editing videos with Blender 2.8?
To begin editing videos with Blender 2.8 as a beginner, you can follow these steps:
- Open Blender and go to the \'Video Editing\' workspace.
- Import your video file by clicking on \'File\' > \'Import\' > \'Video\' and selecting your video file.
- You can drag and drop the video strip into the \'Sequencer\' timeline at the bottom of the screen.
- To trim your video, use the \'Trim\' tool by pressing \'T\' on your keyboard and dragging the handles.
- You can add transitions by placing the playhead where you want the transition to start, right-clicking, and selecting \'Add\' > \'Effect Strip\' > \'Cross\' or any other transition available.
- To add text or graphics, click on \'Add\' > \'Text\' or \'Image\' and adjust their properties in the properties panel.
- To add audio, import your audio file and drag it into the audio timeline below the video timeline.
- Once you are satisfied with your edits, you can preview the video by pressing \'Play\' in the timeline or pressing \'Alt+A\' to play the sequence.
- Finally, to export your edited video, go to \'File\' > \'Export\' and select the desired video format and settings.
READ MORE:
Getting Started with Blender for Video Editing
Blender is a powerful tool for video editing that offers a wide range of features for creators of all levels. Starting with Blender for video editing can seem daunting, but with the right steps, you can quickly become proficient. Here\"s how to begin:
- Download and Install Blender: Visit the official Blender website to download the latest version compatible with your operating system. Installation is straightforward; just follow the prompts.
- Explore the Interface: Upon launching Blender, you\"ll encounter its default layout. Familiarize yourself with the interface, particularly the areas dedicated to video editing like the Video Sequence Editor (VSE).
- Switch to Video Editing Layout: Blender includes various layouts tailored to different tasks. For video editing, switch to the Video Editing layout found in the top menu to access the VSE.
- Import Media: Begin by importing your video clips, images, and audio files into the project. You can do this by dragging and dropping files into the VSE or using the Add menu.
- Basic Editing Functions: Start with simple edits like cutting clips and adjusting their positions on the timeline. Blender allows for non-linear editing, so you can experiment without affecting the original files.
- Preview Your Work: Use the playback controls to preview your edits in real-time. This is crucial for ensuring your video flows as intended.
- Save Your Project: Regularly save your work to prevent any loss of progress. Blender\"s project files are saved with a .blend extension.
As you become more comfortable with these initial steps, you can explore Blender\"s more advanced features, including color correction, special effects, and audio editing. Remember, practice is key to mastering video editing in Blender.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learning Blender\"s keyboard shortcuts can significantly speed up your editing process.
- Additional Resources: Blender\"s community and official documentation offer extensive tutorials and guides to help you along the way.
With patience and creativity, you\"ll find Blender to be an invaluable asset in your video editing toolkit.
Understanding Blender\"s Interface for Video Editing
Blender\"s interface is comprehensive, offering a wide array of tools for 3D modeling, animation, and video editing. For newcomers, understanding how to navigate and utilize the interface for video editing is crucial. This section will guide you through the essential components of Blender\"s interface focused on video editing tasks.
- Layout: When you first open Blender, you\"ll be greeted with the default layout. For video editing, you\"ll want to switch to the Video Editing layout, which optimizes the workspace for editing tasks.
- Video Sequence Editor (VSE): The heart of video editing in Blender is the VSE. It\"s where you\"ll spend most of your time, arranging clips, adding transitions, and applying effects.
- Preview Window: Located within the VSE, the Preview Window allows you to view your video project in real-time, play back edits, and scrutinize the details of your work.
- Timeline: The timeline is a critical component, enabling you to manage the sequence of your video clips, adjust their duration, and navigate through your project.
- Properties Panel: This panel offers access to various settings related to your video project, including render properties, scene settings, and object properties. It\"s essential for fine-tuning the output of your video.
- Tool Shelf: The Tool Shelf provides quick access to tools for cutting, moving, and applying effects to your video clips. It\"s a customizable toolbar that adapts to the selected task or editor.
As you familiarize yourself with these components, you\"ll find that Blender\"s interface is highly intuitive for video editing. Experiment with different layouts and tools to find a workflow that suits your project needs. Remember, practice and exploration are key to mastering Blender\"s video editing capabilities.
- Customization: Blender allows for extensive customization of its interface. You can adjust layouts, create new ones, and save them for future projects.
- Shortcuts: Learning keyboard shortcuts can significantly improve your efficiency in video editing. Blender offers customizable shortcuts to fit your editing style.
Understanding Blender\"s interface is the first step towards unlocking its full potential for video editing. With time and practice, you\"ll be able to leverage its powerful features to create stunning video content.
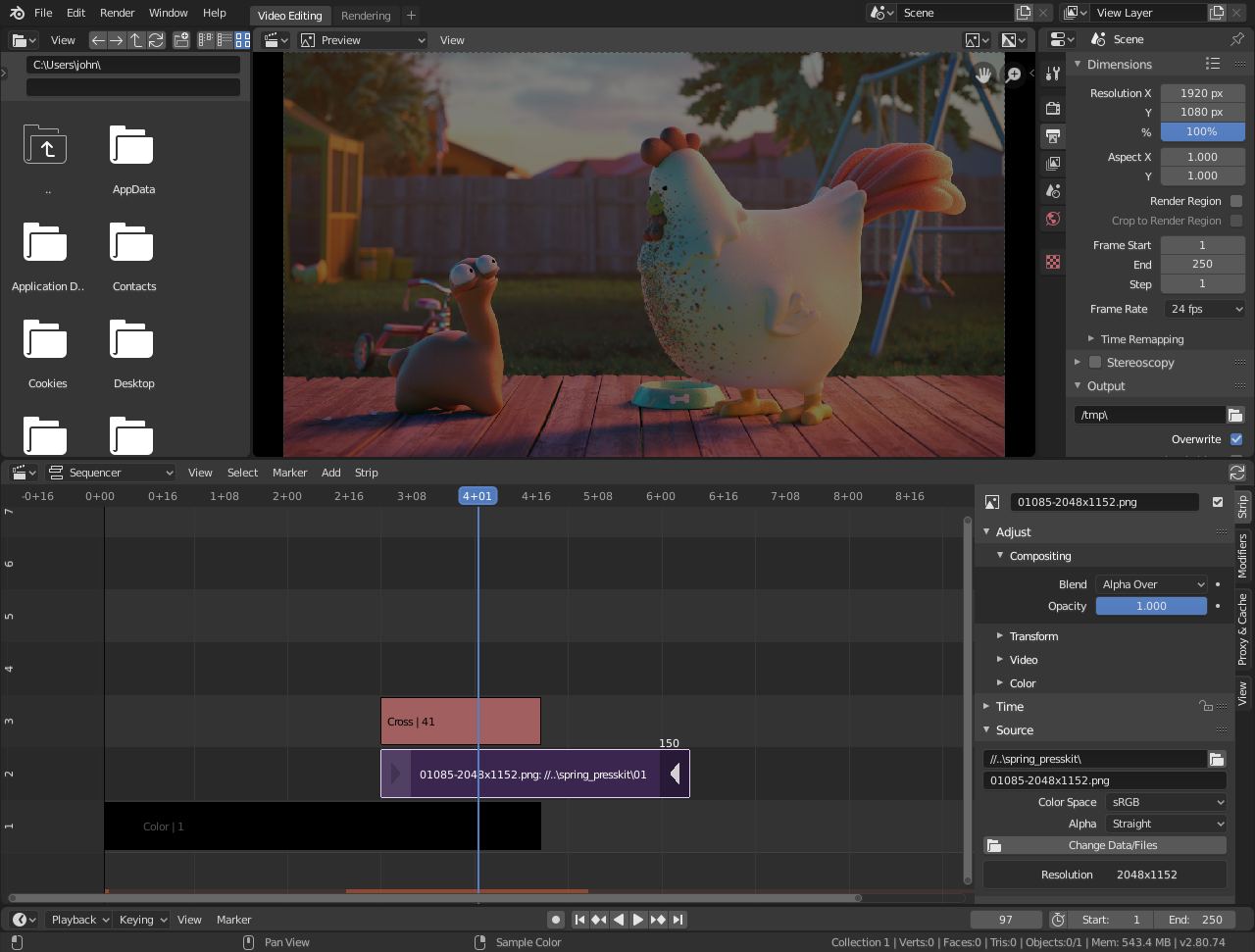
Importing and Organizing Your Media
Efficiently managing your media files is crucial for a smooth video editing process in Blender. This section outlines the steps to import and organize your video clips, images, and audio files, ensuring a streamlined workflow.
- Accessing the Video Sequence Editor: Start by switching to the Video Editing layout. This provides you with the Video Sequence Editor (VSE), where you\"ll import and arrange your media.
- Importing Media Files: To add your media to the VSE, you can either drag and drop files directly into the timeline or use the \"Add\" menu at the bottom of the VSE to select \"Movie\", \"Image\", \"Sound\", etc., and navigate to the files you wish to import.
- Organizing Your Media:
- Arrange your clips on different channels to keep your project organized. This also helps in applying effects to specific clips without affecting others.
- Use the \"Shift\" key to select multiple clips at once, allowing for bulk movement or adjustments.
- Rename your strips for easy identification by right-clicking on a strip and selecting \"Rename Strip\".
- Adjusting Properties: With your media imported, you can adjust each strip\"s properties in the strip properties panel. This includes transformations, such as scaling and positioning, and setting the strip\"s blend mode for layering effects.
- Previewing Your Edits: Use the preview window to review your edits in real-time. This helps in ensuring that your media is correctly positioned and plays as intended.
- Saving Your Project: Remember to frequently save your project to avoid losing any progress. Blender\"s auto-save feature can also help recover projects in case of an unexpected shutdown.
By following these steps, you can efficiently manage your media within Blender, creating a solid foundation for your video editing project. As you become more familiar with Blender\"s workflow, you\"ll find that organizing your media effectively is key to a successful edit.
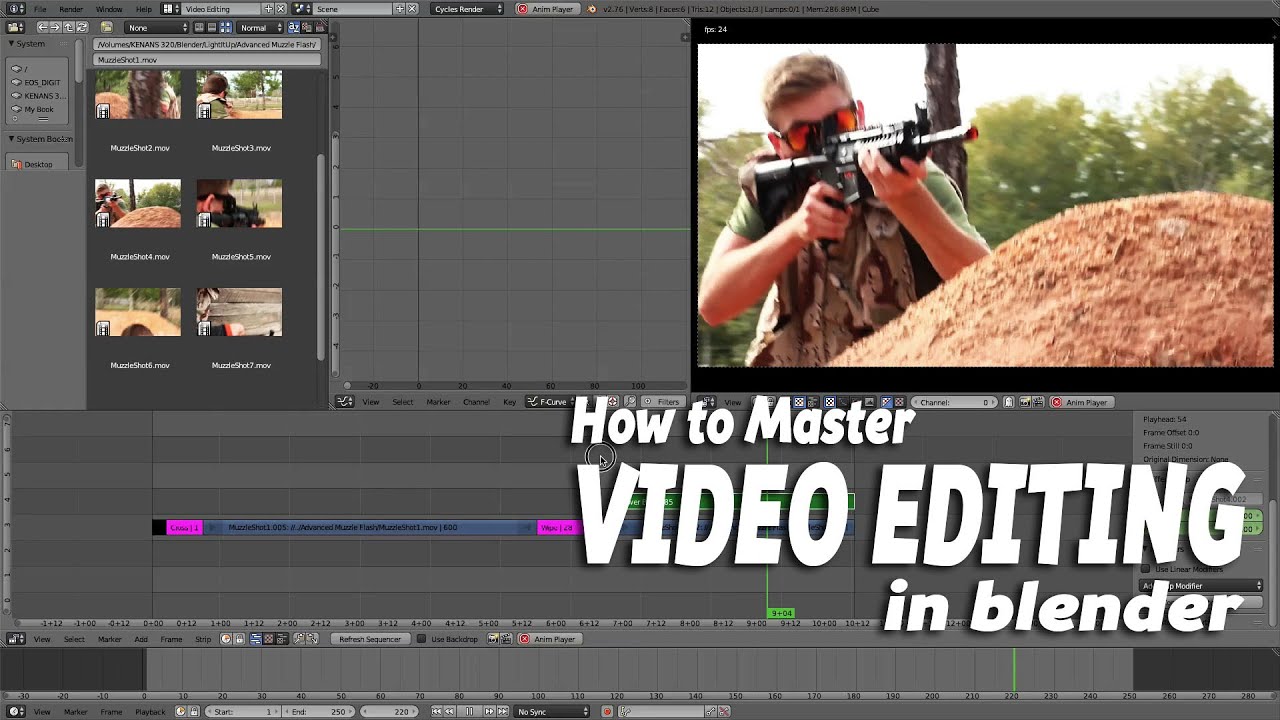
Basic Video Editing Techniques: Cutting, Trimming, and Splicing
Mastering basic video editing techniques in Blender is essential for creating compelling video content. This section covers the foundational skills of cutting, trimming, and splicing video clips within Blender\"s Video Sequence Editor (VSE).
- Cutting Clips: To cut a clip, first select it by clicking on it in the VSE. Position the playhead where you want to make the cut and press the \"K\" key. This splits the clip into two parts at the position of the playhead, allowing you to delete or move the sections independently.
- Trimming Clips: Trimming adjusts the start or end point of a clip without altering its content. To trim, select the edge of a clip and drag it towards or away from the center of the clip. This is useful for refining the in and out points of your clips to ensure tight editing.
- Splicing Clips: Splicing involves removing a section from the middle of a clip and joining the two ends together. After cutting the clip at both ends of the section you wish to remove, delete the middle section. Then, move the remaining pieces together to splice the clip.
Blender also offers advanced editing features like ripple editing and snapping to make cutting, trimming, and splicing more efficient. Ripple editing automatically shifts the adjacent clips to fill in gaps or create space when you make a cut, while snapping ensures that clips align perfectly without any gaps.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learning and using keyboard shortcuts can significantly speed up your editing process. For example, \"Shift + K\" for ripple cut or \"G\" to grab and move a clip.
- Useful Tools: Explore Blender\"s tools like the Soft Cut for non-destructive editing, allowing you to hide parts of clips instead of permanently removing them.
By mastering these basic techniques, you\"ll be well on your way to producing polished video projects in Blender. Practice these skills to enhance your video editing workflow and bring your creative visions to life.
_HOOK_
Blender 3.0 Video Editing Tutorial Ep.1 Interface Output Timeline Import Render
Tutorial: \"In this engaging tutorial video, you\'ll learn step-by-step instructions on how to master a new skill. Watch as a professional guides you through each process with clarity and expertise!\" Basics: \"Discover the essential basics you need to know in this informative video. Perfect for beginners, this video breaks down complex concepts into easy-to-understand fundamentals. Start your learning journey today!\"
How To Edit Video with Blender 2.90 Basics Walkthrough Beginner
In this video I go over how to set up a new video edit project and the required settings, importing files, and the basics of cutting and ...
Advanced Editing Features: Effects, Transitions, and Color Grading
Once you\"ve mastered basic video editing in Blender, you can enhance your projects with advanced editing features. This section delves into the application of effects, transitions, and color grading to elevate the visual appeal and narrative impact of your videos.
- Applying Effects: Blender\"s Video Sequence Editor (VSE) offers a range of effects strips such as Gaussian Blur, Glow, and Wipe transitions. To apply an effect, select your clip, then go to the Add menu and choose Effect Strip. Here, you can select the desired effect and adjust its properties to suit your project.
- Creating Transitions: Smooth transitions between clips are essential for maintaining viewer engagement. Blender allows for easy creation of transitions like crossfades and wipes by overlapping two clips and applying a transition effect from the Effect Strip menu.
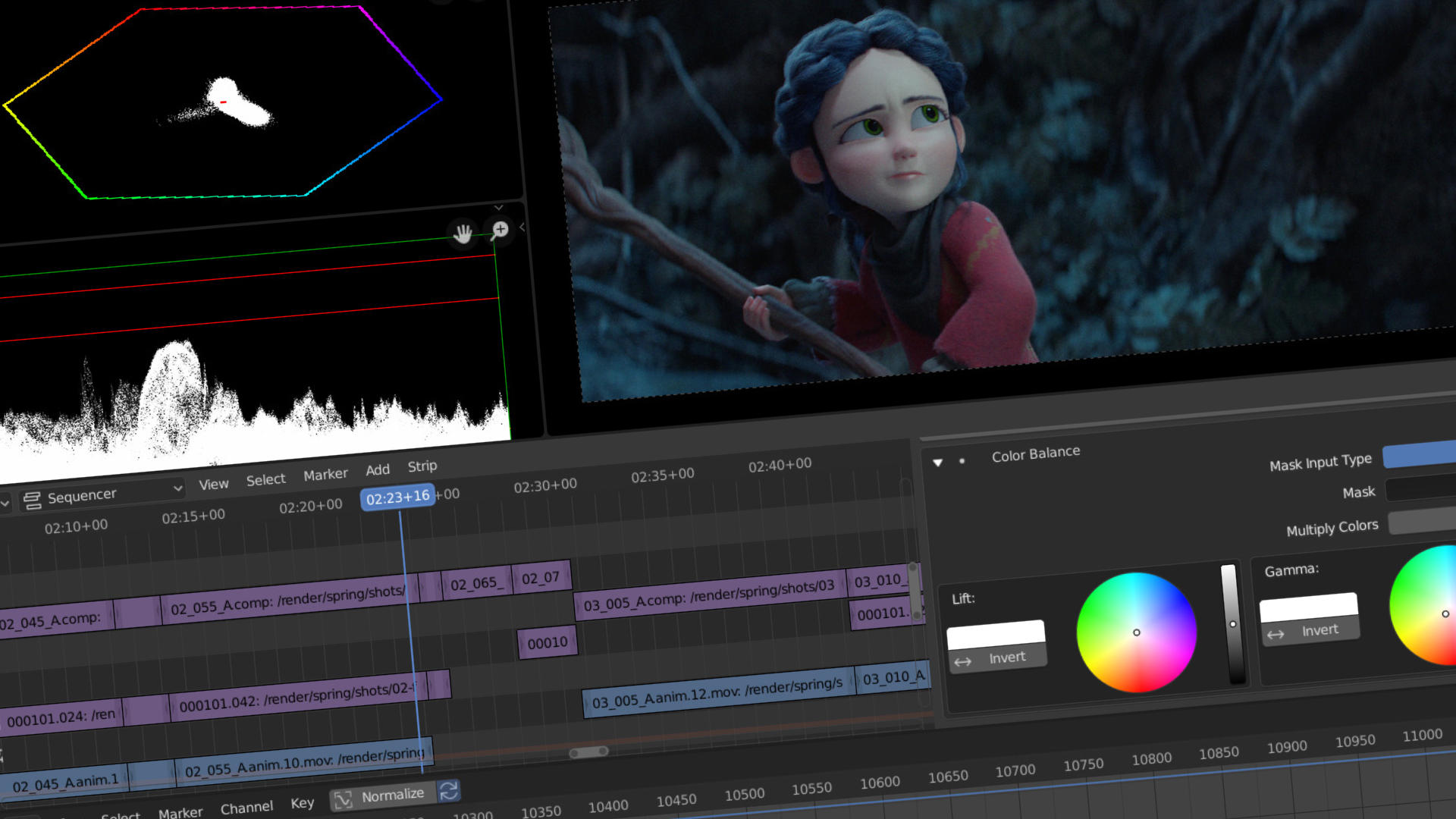
- Color Grading: Color grading is a powerful tool for setting the mood and style of your video. Blender\"s color grading functionalities are accessible through the Properties panel in the VSE. You can adjust contrast, brightness, saturation, and more. For more detailed color correction, use the node editor to apply color grading on a per-clip basis, utilizing nodes such as RGB Curves and Color Balance.
- Utilizing Blender\"s Compositor: For more complex effects and color grading, Blender\"s compositor offers a node-based editing system that allows for intricate manipulation of video layers, effects, and color correction.
- Keyframing for Dynamic Effects: Keyframing in Blender enables the animation of effect parameters over time, adding dynamism and interest to your edits. This can be used to animate transitions, effects, and color grading changes.
These advanced features in Blender provide a vast playground for creativity, allowing editors to craft visually stunning and emotionally resonant video content. As you become more familiar with these tools, you\"ll discover new ways to tell your stories through video.
Working with Audio: Syncing, Mixing, and Sound Effects
Audio plays a crucial role in video production, enhancing the overall viewer experience. Blender provides comprehensive tools for audio editing, including syncing, mixing, and adding sound effects. This section explores how to effectively work with audio in your video projects using Blender.
- Syncing Audio and Video: Accurate audio-video synchronization is essential. Import your audio files into the VSE alongside your video clips. You can then move the audio strips to match the video, using visual cues or waveform displays to ensure precise alignment.
- Mixing Audio Tracks: To mix multiple audio sources, import each track into the VSE and adjust their positions as needed. You can control the volume of each track from the strip properties panel, allowing for balanced audio levels. Use keyframes to animate volume changes over time for dynamic audio mixing.
- Adding Sound Effects: Sound effects can be added by importing them into the VSE just like any other audio file. Place them at the appropriate points in your timeline to enhance the storytelling. Adjust their volume and panning to fit within the audio landscape of your project.
- Audio Effects and Filters: Blender allows the application of various audio effects and filters through the properties panel. Experiment with these to achieve the desired sound quality and effect.
- Exporting with Audio: When rendering your final project, ensure that the audio codec settings are correctly configured to include the audio mix in your exported video.
By mastering these audio editing techniques in Blender, you can significantly improve the quality of your video projects, making them more engaging and immersive for your audience.
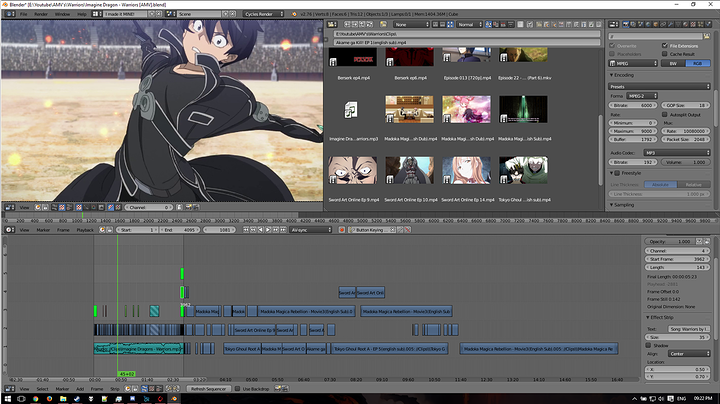
Adding Text and Titles for Professional Finishing Touches
Text and titles play a crucial role in video production, providing context and enhancing the professional quality of your project. Blender offers several methods for incorporating text into your videos, from simple titles to animated text effects. Follow these steps to add text and titles to your Blender projects for that professional finish.
- Creating Text Objects: In Blender, text is added as an object in the 3D View. Switch to the 3D Viewport, press \"Shift + A\" to add a new object, and select \"Text\". This creates a 3D text object that you can edit, position, and animate just like any other object in Blender.
- Editing Text: To edit the text, enter Edit Mode by pressing \"Tab\", and then type your desired text. You can adjust the font, size, and alignment properties in the Font properties panel to match your project\"s style.
- Animating Text: Blender allows for dynamic text animations, such as fades, slides, and typewriter effects. Use keyframes in the Timeline to animate the text object\"s properties, like location, rotation, and scale, creating engaging title sequences and text overlays.
- Adding Text to the Video Sequence Editor (VSE): For static titles or simple text overlays, you can create your text object in the 3D Viewport, render it out as an image or animation, and then import it into the VSE as a strip. This method integrates your text directly into your video timeline.
- Useful Tips:
- For a unified look, use consistent font styles and colors throughout your video.
- Consider the background colors and imagery to ensure your text stands out and remains readable.
- Experiment with shadows and outlines to enhance text visibility against complex backgrounds.
By adding text and titles to your videos in Blender, you can elevate the quality of your content, making it more informative and engaging. Whether you\"re creating opening titles, section headings, or informative captions, these steps will help you integrate text seamlessly into your projects.
Utilizing Blender\"s Animation Tools in Video Editing
Blender\"s robust animation tools can add a dynamic and professional touch to your video editing projects. From simple movements to complex sequences, animation can enhance the storytelling and visual appeal of your videos. This section outlines how to effectively use Blender\"s animation capabilities in your video editing workflow.
- Keyframing Basics: Keyframes are the foundation of animation in Blender. They allow you to define the start and end points of any animation. To animate an object, select it, move to the desired frame in the timeline, and press \"I\" to insert a keyframe. Choose the attribute you wish to animate, such as location, rotation, or scale.
- Animating Text and Titles: Bring your titles and text to life by applying animation. Use keyframing to animate the position, opacity, or scale of text objects over time, creating engaging intro sequences or informational overlays.
- Using the Graph Editor: For more control over your animations, the Graph Editor allows you to fine-tune the interpolation and timing of keyframes. This is especially useful for smoothing out movements or creating more complex animated effects.
- Incorporating Animation into the VSE: You can render your animations as standalone video clips and import them into the Video Sequence Editor (VSE) for inclusion in your final project. This method integrates animated elements seamlessly with your edited video content.
- Animation Effects: Blender includes a variety of animation effects, such as fades, wipes, and slides, that can be applied to video clips directly within the VSE. Experiment with these to add visual interest and transition effects between scenes.
- Animating Properties: Beyond object movement, you can animate properties like brightness, contrast, or color grading over time to enhance visual storytelling or highlight specific moments in your video.
By incorporating animation into your video editing projects, you can unlock new creative possibilities and produce content that captivates your audience. Blender\"s animation tools are powerful and versatile, making it possible to achieve professional-quality results with practice and experimentation.

Rendering and Exporting Your Final Video Project
Completing your video project in Blender involves a final crucial step: rendering and exporting. This process converts your edited sequence into a video file format that can be shared and viewed on various platforms. Follow these steps to render and export your video project efficiently.
- Setting Up Your Render Options: Before rendering, configure your render settings in the Properties panel under the Render tab. Select your desired output format, such as MPEG, AVI, or MOV, and choose the resolution and frame rate that match your project\"s requirements.
- Choosing the Right Codec: Depending on your output format, you may need to select an appropriate codec. A codec compresses or decompresses your video file; choosing the right one can significantly affect the quality and size of your final video. Popular codecs include H.264 for a good balance of quality and file size.
- Output Settings: In the Output properties, specify the file path where you want your rendered video to be saved. You can also set the file format to your preferred container (e.g., .mp4, .mov).
- Rendering Your Video: With your settings configured, go to the Render menu and select \"Render Animation\" or press \"Ctrl + F12\" to start rendering your project. The time it takes to render will depend on the complexity of your project and your computer\"s processing power.
- Exporting Audio: Ensure that your render settings include audio if your project contains sound. Check the Encoding settings under the Output properties to configure audio codec options.
- Preview Renders: It\"s advisable to perform a few test renders at a lower resolution to check for any issues before rendering the entire project at full quality.
- Post-Render: Once rendering is complete, you can find your final video file in the specified output location. It\"s ready to be shared or further processed in other software if needed.
Rendering and exporting are the final steps in the video editing process, transforming your Blender project into a shareable video file. By carefully configuring your render settings and understanding the options available, you can achieve high-quality results that fulfill your creative vision.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Tips and Tricks for Efficient Video Editing in Blender
Editing videos in Blender can be a highly rewarding experience, offering a vast array of tools and possibilities. To help you make the most out of your video editing journey, here are some tips and tricks for working more efficiently in Blender.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with Blender\"s keyboard shortcuts. Using shortcuts for common actions like cutting (K), adding strips (Shift+A), or switching between editing modes can significantly speed up your workflow.
- Proxy Strips: For large or high-resolution video files, consider using proxy strips to improve playback performance in the VSE. Proxies allow you to edit with lower-resolution versions of your clips, which can be swapped back to full resolution for final rendering.
- Templates and Presets: Save time by creating templates and presets for repetitive project setups or effects. This can be especially useful for intros, outros, or color grading settings that you use frequently.
- Use Blender\"s Compositing Nodes: For advanced effects and color correction, delve into Blender\"s node-based compositing. Nodes offer a powerful way to apply and control effects across your video clips.
- Batch Rendering: If you\"re working on a project with multiple scenes or segments, consider batch rendering. This allows you to render several sequences overnight or while you\"re away from your computer, maximizing your efficiency.
- Customize Your Workspace: Blender allows you to customize and save your workspace layouts. Tailor your layout to focus on the tools and panels you use most often for video editing to streamline your process.
- Regular Backups: Always keep regular backups of your Blender projects. Blender\"s auto-save feature is useful, but manual backups can save you from unexpected data loss.
By incorporating these tips and tricks into your video editing practice, you can enhance your efficiency and creativity in Blender. Remember, every video editing task offers an opportunity to learn and improve your skills, so keep experimenting and exploring Blender\"s vast capabilities.
Embark on your video editing journey with Blender and unlock the potential to create stunning visuals and captivating stories. With the right techniques and creativity, your projects will shine. Start editing today and transform your visions into reality.