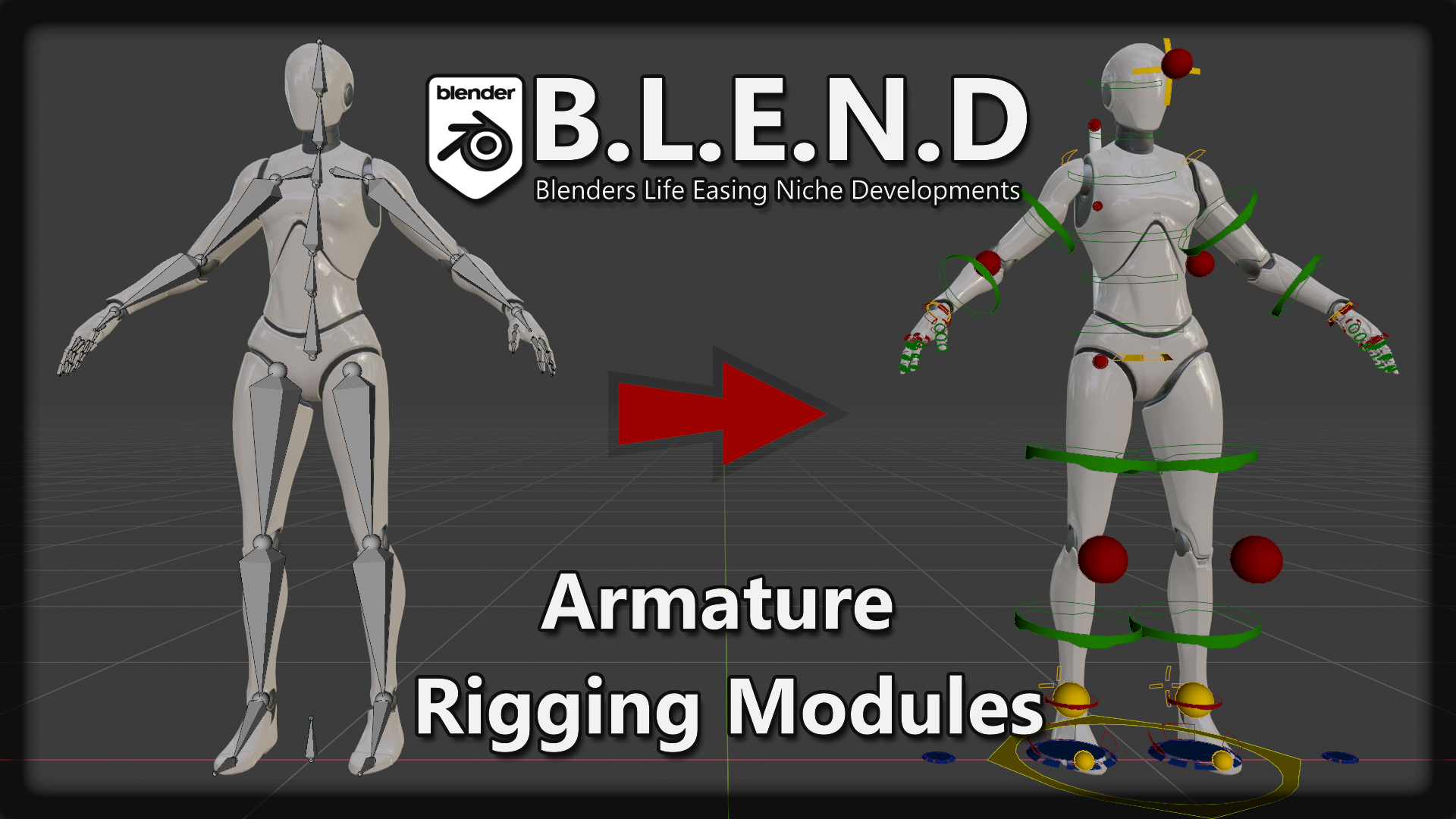
Topic blender simple rigging: Embark on a journey to master Blender simple rigging, a crucial skill for bringing your 3D models to life with animation. This guide is designed to equip beginners with the fundamentals, ensuring a solid foundation for creating dynamic and compelling characters.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Basics
- Step-by-Step Guide to Rigging
- Tools and Resources
- How can I rig objects in Blender in a simple manner?
- YOUTUBE: Blender - Completely Rigging A Character in 5 Minutes
- Step-by-Step Guide to Rigging
- Tools and Resources
- Tools and Resources
- Introduction to Blender Rigging
- Getting Started with Blender Rigging
- Step-by-Step Guide to Your First Rig
- Essential Tools for Effective Rigging
- Advanced Rigging Techniques
- Common Rigging Challenges and Solutions
- Resources and Tutorials for Further Learning
- Practical Exercises to Sharpen Your Rigging Skills
- Animating Your Rigged Models
- Conclusion: Next Steps in Your Rigging Journey
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into rigging, it\"s crucial to position your mesh correctly in the scene. Ensuring the model is correctly aligned will facilitate easier rigging and animation. A key step is setting the origin of the model to a logical point, like the base of the feet for characters, to ensure rotations and movements are natural.
Creating Your First Rig
Blender uses \"armatures\" for rigging, which are essentially skeletons that drive the movement of the mesh. Start by adding an armature and positioning it within your model. Utilizing X-ray mode can help you see the armature through the model, making it easier to position bones accurately.
READ MORE:
Step-by-Step Guide to Rigging
- Preparation: Combine your models if necessary and recalculate normals to ensure the mesh behaves predictably.
- Adding Armature: Place the first bone at the center of the torso and enable X-ray mode to see it through the mesh.
- Bone Placement: Extend bones from the central armature to key points like the neck, shoulders, and hips to start shaping the skeleton.
Advanced Rigging Concepts
- Introduction to Inverse Kinematics (IK) for more natural movements.
- Utilizing constraints and drivers for complex animation control.
- Weight painting for detailed mesh deformation.
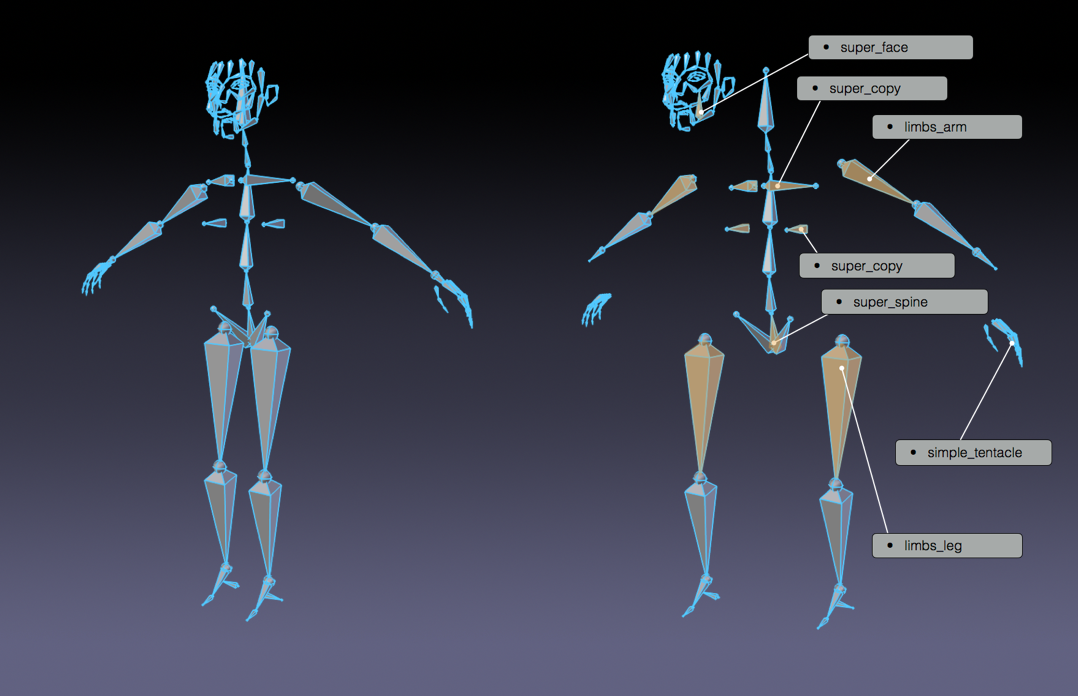
Tools and Resources
Blender offers a comprehensive set of tools for rigging, including automatic skinning, easy weight painting, and bone layering for organized rigs. The community provides extensive tutorials and guides, from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced rigging techniques.
| Resource | Description |
| GameDev Academy Guide | A beginner\"s guide to basic rigging in Blender, focusing on the initial steps and positioning the mesh. |
| Blender Guru Tutorial | Comprehensive rigging tutorial covering from basic to advanced techniques, including character and facial rigging. |
| Instructables Rigging Process | Step-by-step basic rigging process, ideal for understanding the fundamentals of armature and bone placement. |
| CG Cookie Rigging Course | Detailed course on rigging fundamentals, offering hands-on practice with multiple exercises. |
Embarking on your rigging journey in Blender can seem daunting at first, but with the right resources and a bit of practice, you\"ll find it\"s a rewarding and essential skill for any 3D animator. Whether you\"re creating a simple character or a complex creature, these guidelines will help you start with confidence.

How can I rig objects in Blender in a simple manner?
To rig objects in Blender in a simple manner, you can follow these steps:
- Select the object you want to rig by clicking on it in the 3D viewport.
- Switch to the \"Object Data Properties\" tab in the right panel (it looks like a green triangle).
- Click on the \"Add\" button located in the \"Vertex Groups\" section to create a new vertex group for the object.
- With the object still selected, go into Edit Mode by pressing Tab.
- Select the parts of the object that you want to be controlled by the rig (e.g., a bone).
- In the \"Vertex Groups\" section, click on the \"Assign\" button to assign the selected vertices to the vertex group you created earlier.
- Exit Edit Mode by pressing Tab again and then switch to Object Mode.
- Create an armature by pressing Shift + A and selecting \"Armature\" from the menu. This will add a new armature object to the scene.
- Position the armature so that it aligns with the object you want to rig.
- Parent the object to the armature by selecting the object first, then the armature, and pressing Ctrl + P. Choose \"With Automatic Weights\" from the menu that appears.
- You can now test the rig by moving the bones of the armature and seeing how the object deforms.
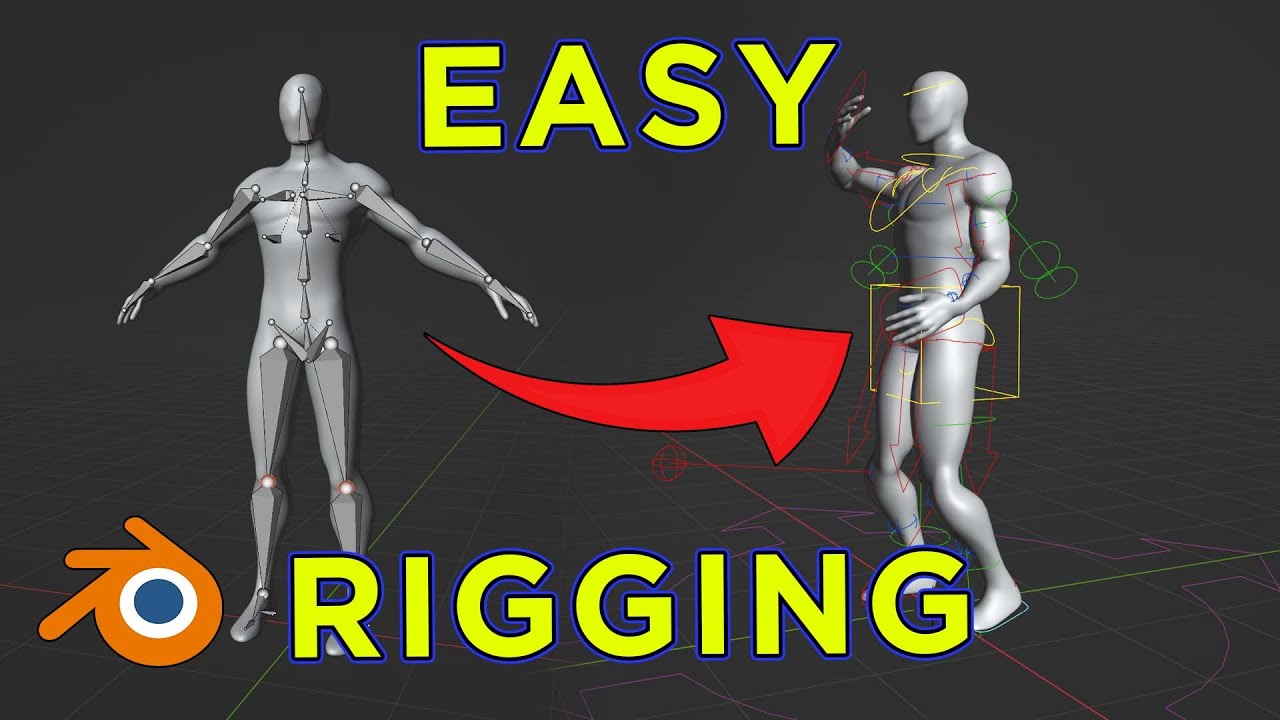
Blender - Completely Rigging A Character in 5 Minutes
Character: Dive into the captivating world of character development with this engaging video. Discover how characters come to life through depth, complexity, and relatability, drawing you into their stories with every frame. Blender: Unleash your creativity with Blender in this must-watch video. Explore the endless possibilities of 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, and learn how to bring your ideas to life in stunning detail.
Simple Rigging in Blender
In this quick blender tutorial I show how to create a simple and super useful rig in Blender. If you are interested in the full process, ...
Step-by-Step Guide to Rigging
- Preparation: Combine your models if necessary and recalculate normals to ensure the mesh behaves predictably.
- Adding Armature: Place the first bone at the center of the torso and enable X-ray mode to see it through the mesh.
- Bone Placement: Extend bones from the central armature to key points like the neck, shoulders, and hips to start shaping the skeleton.
Advanced Rigging Concepts
- Introduction to Inverse Kinematics (IK) for more natural movements.
- Utilizing constraints and drivers for complex animation control.
- Weight painting for detailed mesh deformation.
_HOOK_
Tools and Resources
Blender offers a comprehensive set of tools for rigging, including automatic skinning, easy weight painting, and bone layering for organized rigs. The community provides extensive tutorials and guides, from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced rigging techniques.
Embarking on your rigging journey in Blender can seem daunting at first, but with the right resources and a bit of practice, you\"ll find it\"s a rewarding and essential skill for any 3D animator. Whether you\"re creating a simple character or a complex creature, these guidelines will help you start with confidence.

Tools and Resources
Blender offers a comprehensive set of tools for rigging, including automatic skinning, easy weight painting, and bone layering for organized rigs. The community provides extensive tutorials and guides, from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced rigging techniques.
| Resource | Description |
| GameDev Academy Guide | A beginner\"s guide to basic rigging in Blender, focusing on the initial steps and positioning the mesh. |
| Blender Guru Tutorial | Comprehensive rigging tutorial covering from basic to advanced techniques, including character and facial rigging. |
| Instructables Rigging Process | Step-by-step basic rigging process, ideal for understanding the fundamentals of armature and bone placement. |
| CG Cookie Rigging Course | Detailed course on rigging fundamentals, offering hands-on practice with multiple exercises. |
Embarking on your rigging journey in Blender can seem daunting at first, but with the right resources and a bit of practice, you\"ll find it\"s a rewarding and essential skill for any 3D animator. Whether you\"re creating a simple character or a complex creature, these guidelines will help you start with confidence.