Topic blender 3d tutorial beginner: Dive into the world of 3D modeling and animation with our Blender 3D tutorial for beginners, designed to equip you with all the essential skills to start creating stunning 3D artwork and animations from scratch.
Table of Content
- What are the basics of the new 2D workflow in Blender 2.80?
- Getting Started with Blender
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface
- Basic Navigation and Object Manipulation
- Introduction to Modeling
- Materials and Texturing Basics
- Lighting in Blender
- YOUTUBE: Learn Blender 3D in 20 Minutes! Blender Tutorial for Absolute Beginners
- Basic Animation Techniques
- Rendering Your First Scene
- Using Blender\"s Sculpting Tools
- Introduction to UV Mapping
- Basics of Compositing and Post-Processing
- Common Pitfalls for Beginners and How to Avoid Them
What are the basics of the new 2D workflow in Blender 2.80?
The basics of the new 2D workflow in Blender 2.80 are as follows:
- Start by launching Blender 2.80 and familiarize yourself with the user interface. The interface consists of various panels and menus.
- Create a new 2D workspace by selecting the \"2D Animation\" option from the workspace dropdown menu at the top of the screen.
- Import or create a 2D image that you wish to work with. You can import images by going to File > Import > Images as Planes.
- Once your image is imported, it will be placed as a plane object in the 3D viewport. You can manipulate the image using various tools and techniques.
- To start drawing on the image, switch to the Draw Mode by selecting the \"Draw\" option from the mode dropdown menu in the top toolbar.
- Select the draw brush and adjust its settings such as size, strength, and color in the Tool Shelf panel on the left side of the screen.
- Now you can start drawing on the image using your mouse or a graphics tablet. Use different brush strokes and colors to create your desired artwork.
- To animate your drawing, go to the Animation Workspace by selecting \"Animation\" from the workspace dropdown menu.
- In the Timeline panel, create keyframes for the different frames of your animation to define the movement and transformation of your drawing.
- Preview your animation by playing it in the viewport or rendering it as a video file. You can adjust the frame rate and other animation settings in the Output Properties panel.
These are the basic steps to get started with the new 2D workflow in Blender 2.80. Experiment with different tools and techniques to explore and enhance your 2D creations.
READ MORE:
Getting Started with Blender
Welcome to your first step into the exciting world of 3D modeling and animation with Blender! This section will guide you through the initial steps to get Blender installed on your computer, familiarize you with the basic interface, and set the foundation for your journey into 3D creation.
- Download and Install Blender: Visit the official Blender website to download the latest version. Blender is free and open-source, available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Explore the Interface: Upon launching Blender, you\"ll be greeted with the default screen. Spend some time familiarizing yourself with the layout, including the 3D viewport, timeline, and editor types.
- Basic Navigation: Learn how to navigate the 3D viewport. Use the middle mouse button to orbit, scroll wheel to zoom, and Shift + middle mouse button to pan.
- Adding Objects: Practice adding objects to your scene. Press Shift+A and choose from the mesh menu to add basic shapes like cubes, spheres, or cylinders.
- Simple Transformations: Select an object and use the G (grab), R (rotate), and S (scale) keys to manipulate it. Use the X, Y, or Z keys to lock these transformations to specific axes.
- Basic Rendering: Learn how to render your scene. Go to the Render menu and select Render Image to see a basic rendering of your scene.
By completing these steps, you\"ll have taken your first strides in Blender, setting up a solid base for further exploration and creativity. Remember, the key to mastering Blender is practice and exploration, so don\"t hesitate to experiment with what you\"ve learned!

Understanding Blender\"s Interface
Blender\"s interface might seem daunting at first, but it\"s designed to streamline your 3D modeling and animation workflow. This section will help you understand the key components of the interface, enabling you to navigate and use Blender more effectively.
- 3D Viewport: The heart of Blender, where you\"ll spend most of your time. It\"s where you can view and interact with your models. You can rotate, zoom, and pan around your scene using mouse controls.
- Timeline: Located at the bottom of the default layout, the timeline allows you to control animations, set keyframes, and change the current frame.
- Outliner: The Outliner shows a hierarchical list of all objects in the scene, making it easy to select and organize your models, cameras, lights, and more.
- Properties Editor: This panel provides access to all the properties of the selected object, including modifiers, materials, and physics settings.
- Shader Editor: For creating and editing materials and textures, the Shader Editor is where you\"ll define the visual aspects of your models.
Each area of Blender\"s interface is customizable. You can adjust the layout to suit your workflow by dragging the borders between areas to resize them or by changing the editor type of any area. Remember, mastering Blender\"s interface is a significant first step towards becoming proficient in 3D modeling and animation.

Basic Navigation and Object Manipulation
Navigating the 3D space and manipulating objects are fundamental skills in Blender. This section will guide you through basic navigation controls and essential techniques for moving, rotating, and scaling objects within your scene.
- Viewport Navigation:
- Rotate View: Hold the middle mouse button and move the mouse.
- Pan View: Hold Shift + middle mouse button and move the mouse.
- Zoom: Scroll the middle mouse wheel or hold Ctrl + middle mouse button and move the mouse up or down.
- Selecting Objects: Left-click on an object to select it. Shift + left-click allows you to select multiple objects.
- Moving Objects: With an object selected, press G to grab/move. You can also constrain movement to an axis by pressing X, Y, or Z after G.
- Rotating Objects: With an object selected, press R to rotate. Similar to moving, you can constrain rotation to an axis by pressing X, Y, or Z after R.
- Scaling Objects: With an object selected, press S to scale. To scale uniformly, simply move the mouse. For axis-specific scaling, press X, Y, or Z after S.
- Using the 3D Cursor: The 3D cursor acts as a point of reference for object placement and origin setting. Left-click anywhere in the 3D viewport to reposition the 3D cursor.
Mastering these basic navigation and object manipulation techniques will significantly enhance your efficiency and precision in Blender, laying the groundwork for more advanced 3D modeling and animation tasks.

Introduction to Modeling
Modeling is the heart of creating 3D art in Blender. This section introduces the basics of mesh modeling, from creating your first model to understanding Blender\"s powerful modeling tools.
- Starting with Basic Shapes: Learn how to add primitive shapes (cube, sphere, cylinder, etc.) as the foundation of your models. Use Shift+A in the 3D viewport to open the Add menu.
- Editing Meshes: Enter Edit Mode by pressing Tab. Here, you can select, move, rotate, and scale vertices, edges, and faces to shape your object.
- Using Modifiers: Modifiers are automatic operations that affect an object\"s geometry in a non-destructive way. Access them in the Properties panel under the Modifiers tab.
- Extruding: One of the most essential modeling techniques. Select a face or edge and press E to extrude, creating new geometry connected to the original.
- Loop Cuts: Add more geometry to your models for detailed shaping. Press Ctrl+R and move the mouse over a mesh to see the loop cut preview, then click to add.
- Smoothing and Subdivision: Smooth out your models by applying a Subdivision Surface modifier. This adds geometry and smooths the model without manually adding more vertices.
As you become comfortable with these basic modeling techniques, you\"ll start to see your 3D creations take shape. Modeling is a skill that improves with practice, so don\"t hesitate to experiment with Blender\"s extensive toolset.

_HOOK_
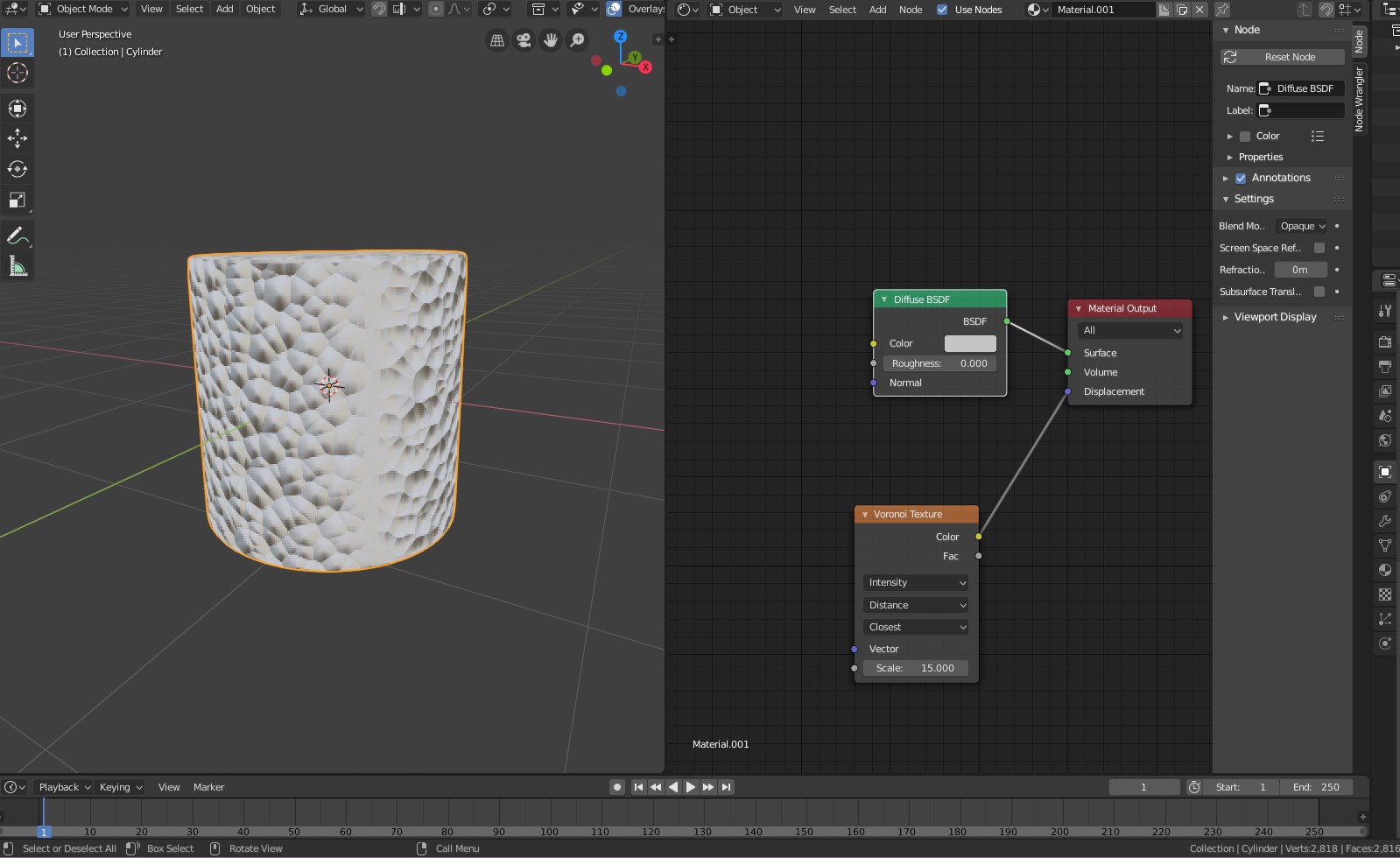
Materials and Texturing Basics
Materials and textures are crucial for bringing your 3D models to life in Blender. This section covers the basics of applying colors, materials, and textures to your creations, making them more realistic and visually appealing.
- Creating and Applying Materials: Learn how to create new materials in the Properties panel under the Material tab. Assign colors and adjust properties like specularity and roughness to change the appearance of your object.
- Understanding Textures: Textures add detail to your materials. Discover how to add texture images or procedural textures to your materials in the Shader Editor.
- UV Mapping: For accurate texture placement, you\"ll need to unwrap your model. This process projects the 3D model onto a 2D surface, allowing you to accurately map textures.
- Shader Editor Basics: Use the Shader Editor to create complex material setups with nodes. Combine different shaders, textures, and colors to craft unique material effects.
- Using the Principled BSDF Shader: This versatile shader is a good starting point for most materials, offering controls for metallic, roughness, transparency, and more.
- Applying Textures to Models: Learn how to apply your textures to models using the UV maps you created, adjusting them for perfect fit and appearance.
With a solid understanding of materials and texturing, you\"ll be able to add depth, realism, and character to your 3D projects. Experiment with different settings and textures to see how they affect the look and feel of your models.

Lighting in Blender
Lighting is a pivotal aspect of 3D visualization that affects mood, tone, and realism. This section introduces the basics of lighting in Blender, helping you illuminate your scenes effectively.
- Types of Lights: Understand the different types of lights available in Blender, including Point, Sun, Spot, and Area lights, each with unique characteristics and uses.
- Positioning Lights: Learn how to place and orient lights within your scene to achieve desired effects, such as highlighting specific features or creating dynamic shadows.
- Adjusting Light Properties: Explore how to adjust light settings like color, intensity, and falloff to modify the atmosphere and look of your render.
- Using Three-Point Lighting: Master the three-point lighting technique, a standard method involving key, fill, and back lights to achieve a balanced and professional look.
- Shadows: Discover how to control shadow hardness, distance, and color to add depth and realism to your scenes.
- Environmental Lighting: Learn about using HDRI images for realistic environmental lighting, adding complex light setups with ease.
- Light Baking: Understand the process of baking lights for static scenes, improving render times without sacrificing quality.
Effective lighting can dramatically change the perception of your 3D models and scenes. Experiment with different lighting setups and properties to find what works best for your project.

Learn Blender 3D in 20 Minutes! Blender Tutorial for Absolute Beginners
Get ready to take your 3D animation skills to the next level with this incredible Blender tutorial! Whether you\'re a beginner or an experienced artist, this video will teach you all the tips and tricks you need to create jaw-dropping visual effects. Don\'t miss out on this chance to unleash your creativity and become a master Blender artist! Watch now and prepare to be amazed!
Absolute Beginner Basics: Blender For Noobs
Are you new to the world of Blender? Fear not, because this video has got you covered with its comprehensive Blender basics tutorial! Learn how to navigate the user interface, work with objects, apply materials, and so much more. By the end of this video, you\'ll have a solid understanding of the fundamental tools and techniques in Blender. Don\'t wait any longer- dive into the exciting world of 3D animation today!
Basic Animation Techniques
Animation brings your 3D creations to life. This section covers the foundational techniques of animating in Blender, from keyframing to playback, to start making your models move.
- Understanding Keyframes: Learn how to set keyframes, which are points that define the start and end of any animation. Right-click on a property and choose \"Insert Keyframe\" to animate position, rotation, or scale over time.
- Timeline and Dope Sheet: Use the Timeline to scrub through your animation and the Dope Sheet to manage keyframes and timing, providing a comprehensive view of your animation\"s flow.
- Animating with Auto-Keyframe: Enable Auto-Keyframe mode to automatically insert keyframes when you change a property, simplifying the animation process for beginners.
- Interpolation and Easing: Understand how Blender interpolates between keyframes, and how to adjust the easing of animations for more natural movement.
- Simple Animation Loops: Create looping animations by carefully planning your keyframes and using cyclic modifiers in the Graph Editor.
- Animating Materials and Lights: Discover how to animate non-mesh objects like materials and lights for dynamic visual effects.
- Previewing Your Animation: Learn how to play back your animation within Blender, adjusting playback settings for a smooth preview experience.
With these basic animation techniques, you\"ll be able to start adding motion to your 3D models, opening up a world of creative possibilities in Blender.

Rendering Your First Scene
Rendering is the process of turning your 3D scene into a final image or animation. This section guides you through the basics of rendering in Blender, helping you to produce your first rendered image.
- Understanding Render Engines: Blender comes with several render engines like Eevee (real-time) and Cycles (ray-traced). Choose the one that fits your project\"s needs in the Render Properties tab.
- Camera Setup: Position your camera to frame your scene. Select the camera, then press Numpad 0 to see through it. Use G and R to adjust its position and rotation.
- Lighting Your Scene: Ensure your scene is well-lit by adding light sources. Good lighting is crucial for a high-quality render.
- Render Settings: Access the Render Properties panel to adjust settings like resolution, samples (for Cycles), and output format.
- Using Render Layers: For complex scenes, use render layers to render different elements separately, giving you more control in post-processing.
- Initiating Render: With everything set up, click on Render > Render Image (F12) to start rendering your scene. For animations, use Render > Render Animation.
- Post-Processing: After rendering, you can use Blender\"s Compositor to make adjustments or add effects to your rendered image or animation.
Rendering your first scene can be an exciting step, showcasing your work in its final form. Experiment with different settings and techniques to find the best results for your projects.

Using Blender\"s Sculpting Tools
Blender\"s sculpting tools allow for intuitive, artist-friendly shaping of models. This section delves into the basics of sculpting, helping you add detail and character to your 3D creations.
- Entering Sculpt Mode: Select your object and switch to Sculpt Mode from the mode menu in the 3D viewport.
- Understanding Brushes: Get familiar with different sculpting brushes, each designed for specific tasks like adding volume (Clay strips), creating sharp details (Crease), or smoothing surfaces (Smooth).
- Dyntopo (Dynamic Topology): Enable Dyntopo for dynamic mesh tessellation, allowing you to sculpt high levels of detail without worrying about the initial mesh density.
- Symmetry: For characters and objects that require symmetry, activate the symmetry option to mirror your sculpting strokes across the model.
- Masking: Use masks to protect certain areas of your model from being affected by your sculpting strokes, allowing for more precise control.
- Shaping Your Model: Start with broad strokes to define the general shape and volume. Gradually move to smaller brushes for details like wrinkles or textures.
- Remeshing: After significant sculpting, remesh your model to ensure a uniform distribution of polygons, which is essential for smooth shading and further detailing.
With practice, Blender\"s sculpting tools can become a powerful part of your 3D modeling toolkit, enabling you to create detailed and expressive models.

_HOOK_
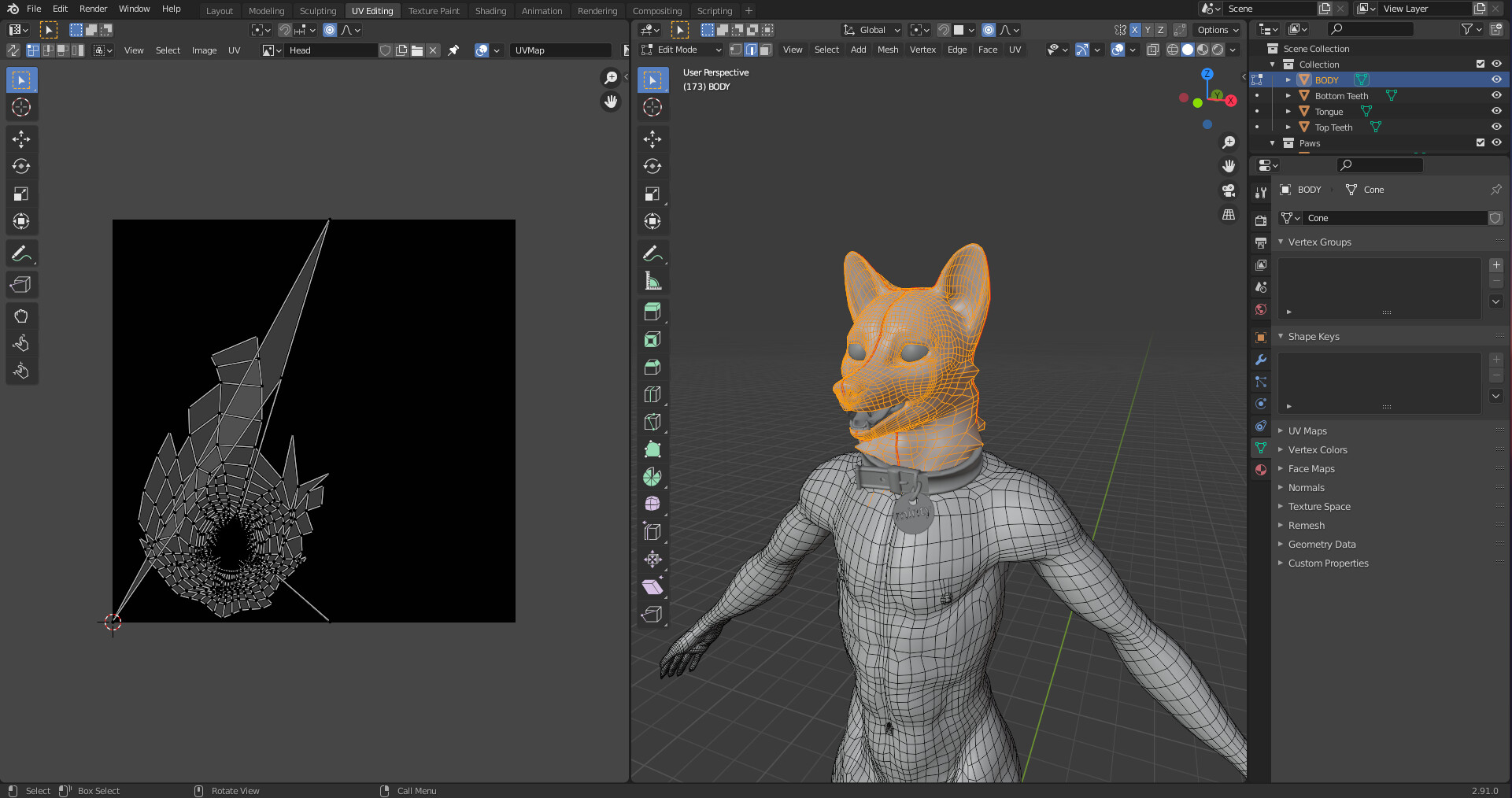
Introduction to UV Mapping
UV mapping is the process of projecting a 3D model\"s surface onto a 2D plane for texturing. This section introduces the fundamentals of UV mapping in Blender, guiding you through unwrapping models and applying textures accurately.
- Understanding UV Maps: UV maps are essential for accurately applying textures to 3D models. They translate the 3D surface into a 2D representation.
- Entering Edit Mode: To start UV mapping, select your object and switch to Edit Mode. UV mapping works with the geometry of your model, so it\"s necessary to be in this mode.
- Marking Seams: Identify and mark seams on your model. Seams act as the \"cuts\" in the 3D mesh that allow it to be unfolded into a 2D image. Select edges where you want seams and press Ctrl+E > Mark Seam.
- Unwrapping the Model: With seams marked, select all faces of your model and press U > Unwrap. Blender will unfold the model based on the seams you\"ve marked, creating a UV map.
- Editing UV Maps: Open the UV Editor window to see the unwrapped UV map. Here, you can move, rotate, and scale UV islands to match your texture.
- Applying Textures: Once your UV map is arranged, you can apply textures in the Shader Editor. The texture will follow the layout of your UV map on the model.
- Checking for Distortion: Use the UV Editor\"s overlay options to check for stretching or distortion, ensuring your textures will look natural on the model.
Mastering UV mapping is key to creating realistic and detailed textures on your models. With practice, it becomes an invaluable tool in your 3D texturing workflow.
Basics of Compositing and Post-Processing
Compositing and post-processing are crucial final steps in the 3D creation process, allowing you to enhance and finalize your renders. This section introduces the basics of using Blender\"s Compositor and other tools to refine your images and animations.
- Understanding the Compositor: Blender\"s Compositor is a powerful node-based editor used for post-processing and combining different render layers and passes.
- Using Nodes: In the Compositor, you create and connect nodes to apply effects, adjust colors, mix images, and much more. Familiarize yourself with key nodes such as Color Balance, Blur, and Glare.
- Render Layers and Passes: Render your scene in layers and passes to have more control in compositing. This allows you to adjust, for example, the lighting and shadows separately.
- Adding Effects: Use the Compositor to add final touches like depth of field, bloom, or color grading to enhance the realism or artistic feel of your render.
- Masking and Matte: Learn how to create and use masks to isolate and apply effects to specific parts of your image, providing greater creative control.
- Output Settings: Finally, configure the output settings in the Compositor to ensure your rendered image or animation is saved with the correct resolution and file format.
With these compositing and post-processing basics, you can elevate the quality of your renders, adding polish and depth to your 3D projects.
READ MORE:
Common Pitfalls for Beginners and How to Avoid Them
Starting with Blender can be overwhelming, and it\"s common to run into a few hurdles. This section highlights some typical beginner mistakes and offers solutions to help you avoid them, ensuring a smoother learning journey.
- Ignoring Keyboard Shortcuts: Blender\"s efficiency largely depends on using keyboard shortcuts. Start learning them early to significantly speed up your workflow.
- Overlooking the Importance of Learning Basics: Jumping into complex projects too soon can be discouraging. Focus on mastering basic tools and techniques first.
- Not Using Reference Images: Working without reference can lead to unrealistic results. Always use reference images for accuracy and inspiration.
- Avoiding the Manual and Tutorials: Blender has a comprehensive manual and a large community. Utilize these resources to understand tools and solve problems.
- Forgetting to Save Frequently: Losing work due to crashes or mistakes is frustrating. Develop a habit of saving often and using versioning in your file names.
- Ignoring Object Origin Points: The origin point affects object rotation and scaling. Learn to adjust it appropriately for better control over your models.
- Underestimating the Power of Modifiers: Modifiers can simplify many tasks. Explore them to non-destructively enhance your models.
- Not Organizing the Project: A cluttered workspace can complicate your project. Use layers, collections, and meaningful naming conventions to stay organized.
Avoiding these common pitfalls will help you navigate the initial challenges of learning Blender, making your 3D modeling and animation journey more enjoyable and successful.
Embarking on your Blender journey opens up a world of creative possibilities. With patience and practice, you\"ll soon transform your ideas into stunning 3D models and animations, joining a vibrant community of artists and designers.