Topic how to edit video blender: "Unlock the power of Blender for video editing with our easy-to-follow guide. Perfect for beginners looking to master video cuts, transitions, effects, and more. Start your journey to become a video editing pro today!"
Table of Content
- How to edit video using Blender?
- Understanding Blender\"s Video Editing Capabilities
- Getting Started with Blender for Video Editing
- Importing Media and Basic Editing
- Advanced Editing Techniques
- Adding Effects and Transitions
- YOUTUBE: Video Editing with Blender for Complete Beginners - Part 1
- Color Grading and Correction
- Exporting Your Final Video
- Keyboard Shortcuts for Efficient Editing
- Resources for Further Learning
How to edit video using Blender?
To edit video using Blender, follow these steps:
- Open Blender and go to the Video Editing workspace.
- Import your video footage by clicking on \"Add\" and selecting \"Movie\".
- Drag and drop your video clips onto the timeline to arrange them in the desired order.
- Trim and cut your video clips by selecting them and pressing \"K\" to split and \"X\" to delete.
- Add transitions between clips by right-clicking on the border of two clips and selecting a transition.
- Adjust the speed of your video clips by selecting them and pressing \"G\" to change the speed curve.
- Add effects and color corrections by using the various options available in the Video Editing workspace.
- Add music or audio by importing audio files and dragging them onto the timeline.
- Preview your video by clicking the play button and make any necessary adjustments.
- Once you are satisfied with your edit, export your video by going to \"File\" > \"Export\" and selecting your desired settings.
READ MORE:
Understanding Blender\"s Video Editing Capabilities
Blender is not just a 3D modeling and animation tool; it\"s also equipped with a comprehensive Video Sequence Editor (VSE) that allows for intricate video editing tasks. From basic video cuts and splicing to more advanced functions such as video masking and color grading, Blender\"s VSE is a powerful, free tool for video editors and filmmakers.
- Non-linear editing: Blender offers a non-linear approach to video editing, enabling you to arrange video clips and layers in any order without altering the original footage.
- Live preview: See your edits in real-time with live preview, complete with luma waveform, chroma vectorscope, and histogram displays.
- Audio mixing and syncing: Blender allows for detailed audio editing, including mixing, syncing, scrubbing, and waveform visualization.
- Up to 32 slots: Easily manage your project by adding up to 32 tracks for video, images, audio, scenes, masks, and effects.
- Effects and transitions: Apply various effects and transitions between your clips to create a professional-looking video.
- Color grading tools: Enhance the visual appeal of your video with advanced color correction and grading tools.
Whether you\"re a beginner looking to learn video editing or a seasoned professional seeking a cost-effective solution, Blender\"s video editing suite offers a range of tools to fulfill your creative needs.
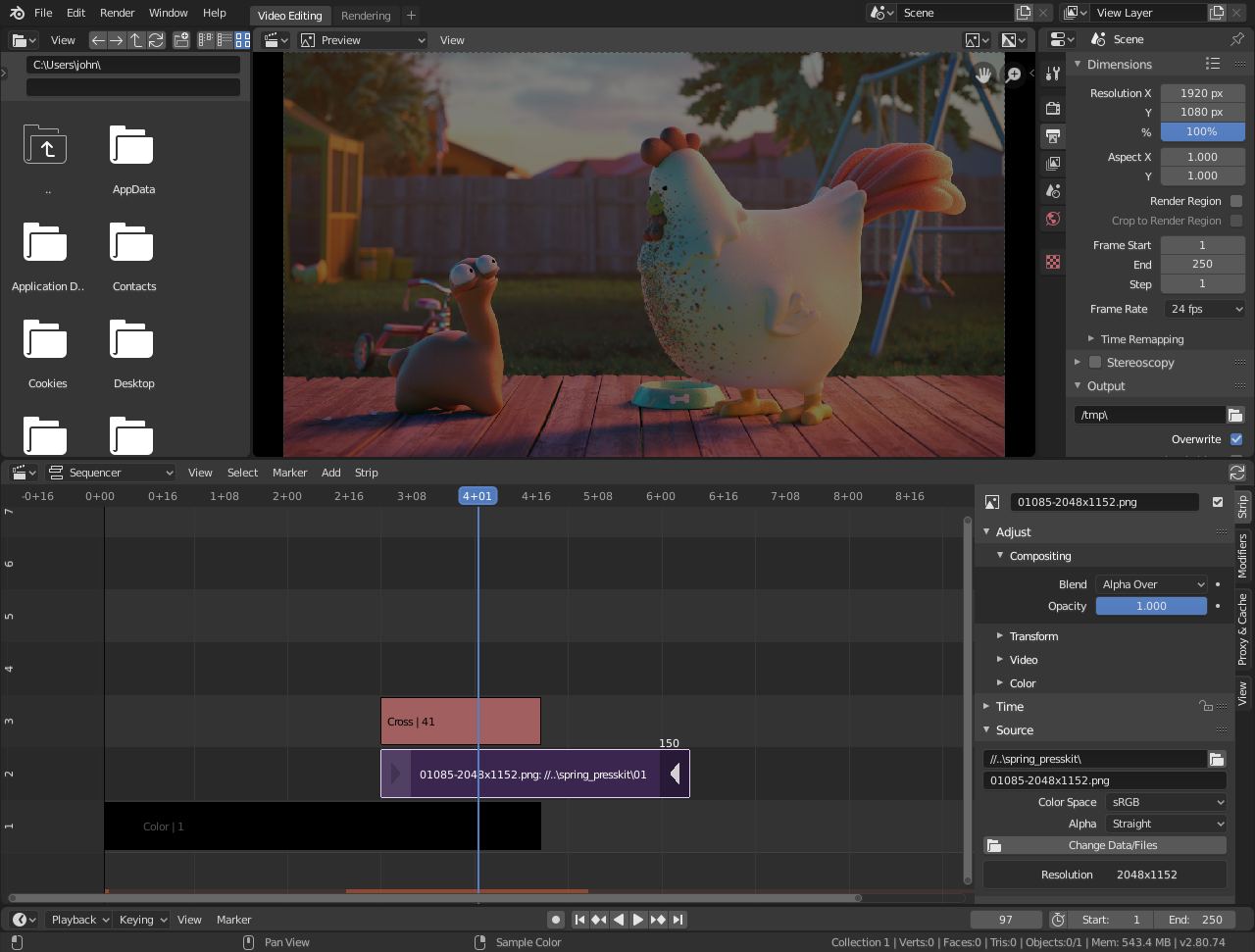
Getting Started with Blender for Video Editing
Starting your video editing journey with Blender opens up a world of possibilities, from simple cuts to complex visual effects. Here\"s how to get started:
- Download and Install Blender: Ensure you have the latest version of Blender installed from the official website. Blender is free and open-source, available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Choose the Video Editing Layout: Upon opening Blender, select \"Video Editing\" from the layout dropdown menu. This action sets up the interface for video editing tasks.
- Import Your Media: Use the \"Add\" menu in the sequencer to import your video, audio, and image files. You can drag and drop files directly into the timeline as well.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Interface: Explore the preview window, sequencer, and properties panel to understand the basic layout. Blender\"s interface is highly customizable to fit your workflow.
- Learn Basic Operations: Practice basic editing tasks such as cutting clips with the \"K\" key, moving them with \"G\", and applying cross transitions between clips.
- Explore Blender\"s Features: Delve into more advanced features such as color grading, applying effects, and using Blender\"s compositing tools for visual effects.
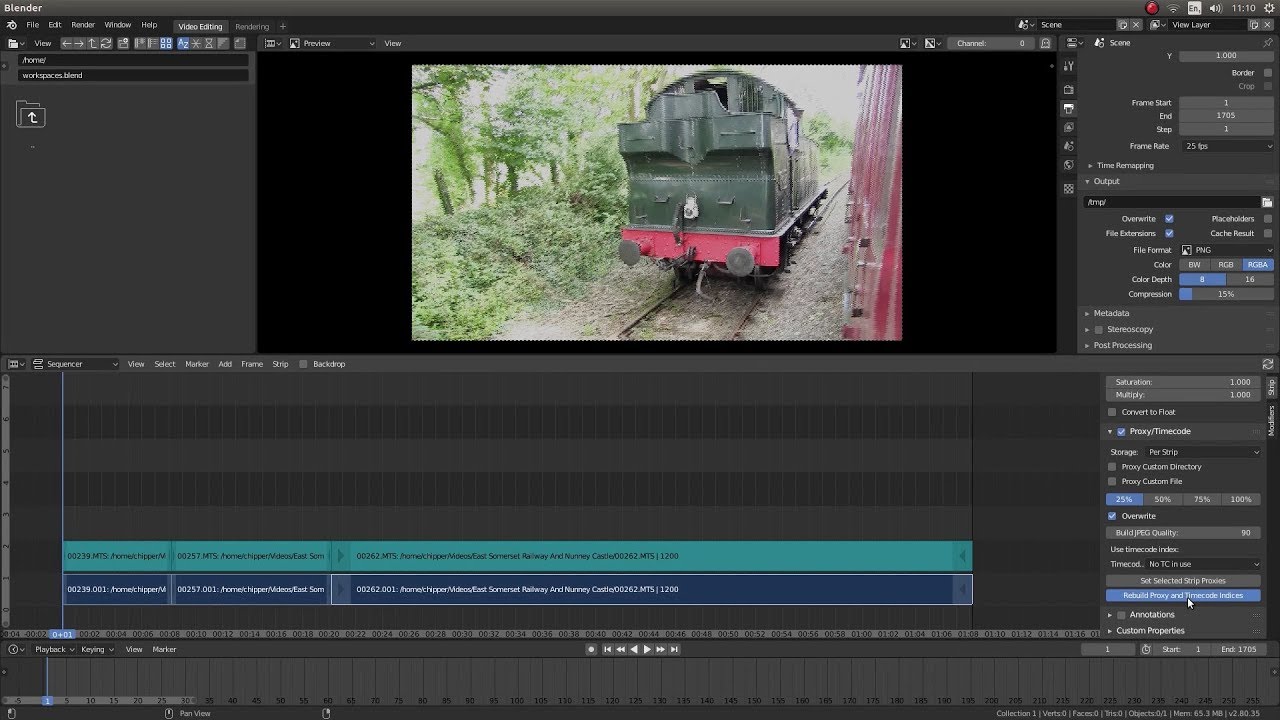
- Render Your Project: Once your edit is complete, navigate to the \"Output Properties\" tab to set your video\"s resolution, frame rate, and file format, then render your project to create the final video file.
Blender might seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes an incredibly powerful tool for video editing. Start with simple projects to build your confidence and gradually explore more complex features as you become more comfortable.
Importing Media and Basic Editing
To start editing your video in Blender, you first need to import your media files. Blender supports a wide range of video, audio, and image formats, making it easy to work with almost any type of media you have.
- Open Blender and select Video Editing from the screen layout menu at the top of the window or choose Video Editing from the New file menu if you\"re starting from scratch.
- To import media, go to the Add menu in the Sequencer view, choose the type of media (video, audio, or image), and navigate to the file you wish to add. You can also drag and drop files directly into the Sequencer.
- After importing, you\"ll see your media appear as strips in the Sequencer. You can move these strips around to arrange your timeline. Left-click to select a strip, and G to grab and move it.
With your media imported, you can begin basic editing:
- Trimming Clips: Select a strip and press K to use the blade tool for cutting. You can also use Shift+K to make a soft cut, which doesn\"t split the strip but defines a new start or end point.
- Moving Clips: Click and drag to reposition clips along the timeline. Use G to move them freely or G then X or Y to constrain movement to the X (time) or Y (channels) axis.
- Adjusting Clip Properties: With a clip selected, adjust its properties in the Sidebar on the right. You can modify its start and end frames, transparency, and other attributes.
- Adding Transitions: Place two clips close to each other, select them both, then use the Add menu to include transitions like crossfade or wipe.
- Adding Audio: Import audio files the same way you import video and place them in your timeline to add sound to your project.
To preview your project, use the playback controls below the Sequencer. You can play, pause, skip to the start or end, and even scrub through your timeline to review your edits.
Remember, the key to efficient editing in Blender is learning the keyboard shortcuts. They can significantly speed up your workflow and make the editing process smoother.
Advanced Editing Techniques
Once you\"re comfortable with basic editing in Blender, you can elevate your video projects with advanced techniques that add polish and dynamics to your work. These methods can help you create more professional-looking videos.
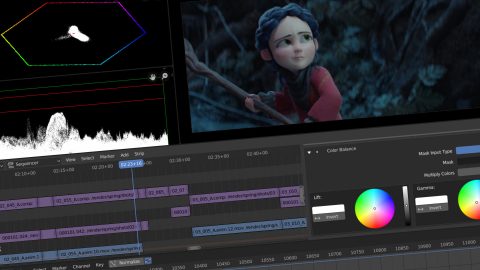
- Masking and Compositing: Use the Mask editor to create custom shapes that can hide or reveal parts of your footage. This is useful for creating effects like text behind objects or changing the background of a clip. Combine this with the Node editor for advanced compositing.
- Color Correction and Grading: Blender’s color correction tools allow you to adjust the look and feel of your video. Use the Color Balance modifier or go into the Sequencer\"s Strip properties to adjust the color wheels for shadows, midtones, and highlights. For more detailed work, use the Node editor to apply color grading.
- Speed Control: You can change the playback speed of your clips directly in the timeline. Select a clip, then add a Speed Control effect strip. This allows you to create slow-motion or fast-forward effects by adjusting the speed factor.
- Adding Effects: Blender offers a variety of effects that can be added to your clips. Use effects like Gaussian Blur, Glow, or Wipe transitions to enhance your video. These can be added from the Add menu in the Sequencer.
- Green Screen/Chroma Keying: For scenes requiring background replacement, use the Chroma Key feature. Import your green screen footage, and then use the Keying node in the Compositing layout to remove the background and replace it with another image or video clip.
- Multi-Cam Editing: Blender supports multi-cam editing, allowing you to switch between different camera angles easily. Set up your camera angles as different strips in the Sequencer and use the Multicam Selector to switch between them in real-time as you play back your project.
- Animation: Incorporate animations into your video by using Blender\"s powerful animation tools. Animate text, images, or even 3D models to add motion graphics to your video. Keyframe animations or use Blender’s graph editor for more control over movement.
- Audio Mixing and Effects: Improve your video\"s audio quality by using Blender’s audio tools. You can mix audio tracks, adjust volume levels, and apply effects like high-pass or low-pass filters to enhance sound quality.
These advanced techniques require practice and experimentation to master. By incorporating these skills into your video editing workflow, you can create captivating and visually appealing videos that stand out. Blender’s flexibility and comprehensive toolset make it a powerful choice for video editors looking to push their creative boundaries.
_HOOK_
Adding Effects and Transitions
Blender\"s video editing capabilities include a wide array of effects and transitions that can enhance your video projects. This section will guide you through the process of adding these elements to create visually appealing and seamless videos.
Accessing the Effects Strip
To begin, switch to the Video Editing layout in Blender. Here, you\"ll find the Sequencer, where you can add various types of strips, including effects strips. Effects strips can be applied to existing footage to create transitions or to add special effects.
Adding Transitions
Transitions are essential for a smooth change from one scene to another. Blender offers several transition options, such as cross, wipe, and fade:
- Cross: Overlap two strips and select them both. Press Shift+A and choose \"Effect Strip\" then \"Cross\" to add a crossfade transition.
- Wipe: For a wipe transition, select the strips you want to transition between, press Shift+A, go to \"Effect Strip\" and then select \"Wipe.\" You can customize the direction and angle of the wipe in the Effect Strip properties.
- Fade: To create a fade in or out, adjust the opacity of the strip by animating the opacity value in the strip\"s properties. This is done by inserting keyframes at the start and end points of the desired fade.
Applying Special Effects
Blender also allows for the application of special effects such as Gaussian Blur, Color Correction, and Glare:
- Gaussian Blur: Add a Gaussian Blur effect strip to soften or blur parts of your video. This can be particularly useful for creating a dreamy look or for obscuring parts of an image.
- Color Correction: Use the Color Balance effect strip to adjust the colors in your video. This is handy for fixing color issues or for creative color grading.
- Glare: The Glare effect strip can add a bloom or glare effect to bright areas, which is great for creating dramatic lighting effects or enhancing highlights.
Customizing Effects
After adding an effect strip, you can customize its properties in the Effect Strip properties panel. Here, you can adjust parameters such as intensity, duration, and other specific settings to achieve the desired effect.
Animating Effects
Many effect parameters can be animated over time to change their intensity or behavior. To animate an effect, hover over a property field and press I to insert a keyframe. Move to another frame, change the value, and press I again. Blender will interpolate the values between keyframes, creating a smooth transition.
Combining Effects
For more complex effects, you can combine multiple effect strips. For example, you might combine a color correction strip with a Gaussian Blur strip to create a unique look. Experiment with different combinations to find what works best for your project.
Tips for Effective Use of Effects and Transitions
- Plan your transitions and effects as part of your overall editing strategy to ensure they enhance, rather than distract from, your video.
- Use effects sparingly to avoid overwhelming the viewer and detracting from the content of your video.
- Experiment with different effects and transitions to see how they impact the mood and pace of your video.
By mastering the addition of effects and transitions in Blender, you can significantly improve the visual quality and dynamic of your videos. Practice with these tools to discover the vast creative possibilities they offer.
Video Editing with Blender for Complete Beginners - Part 1
Tutorial: Learn step-by-step with our engaging tutorial video, designed to help you master new skills quickly and easily. Join us in this informative session and unlock your full potential today! Basics: Dive into the fundamental concepts with our video on the basics - perfect for beginners and anyone looking to solidify their understanding. Start your learning journey with us now!
How To Edit Video with Blender 2.90 Basics Walkthrough Beginner
In this video I go over how to set up a new video edit project and the required settings, importing files, and the basics of cutting and ...
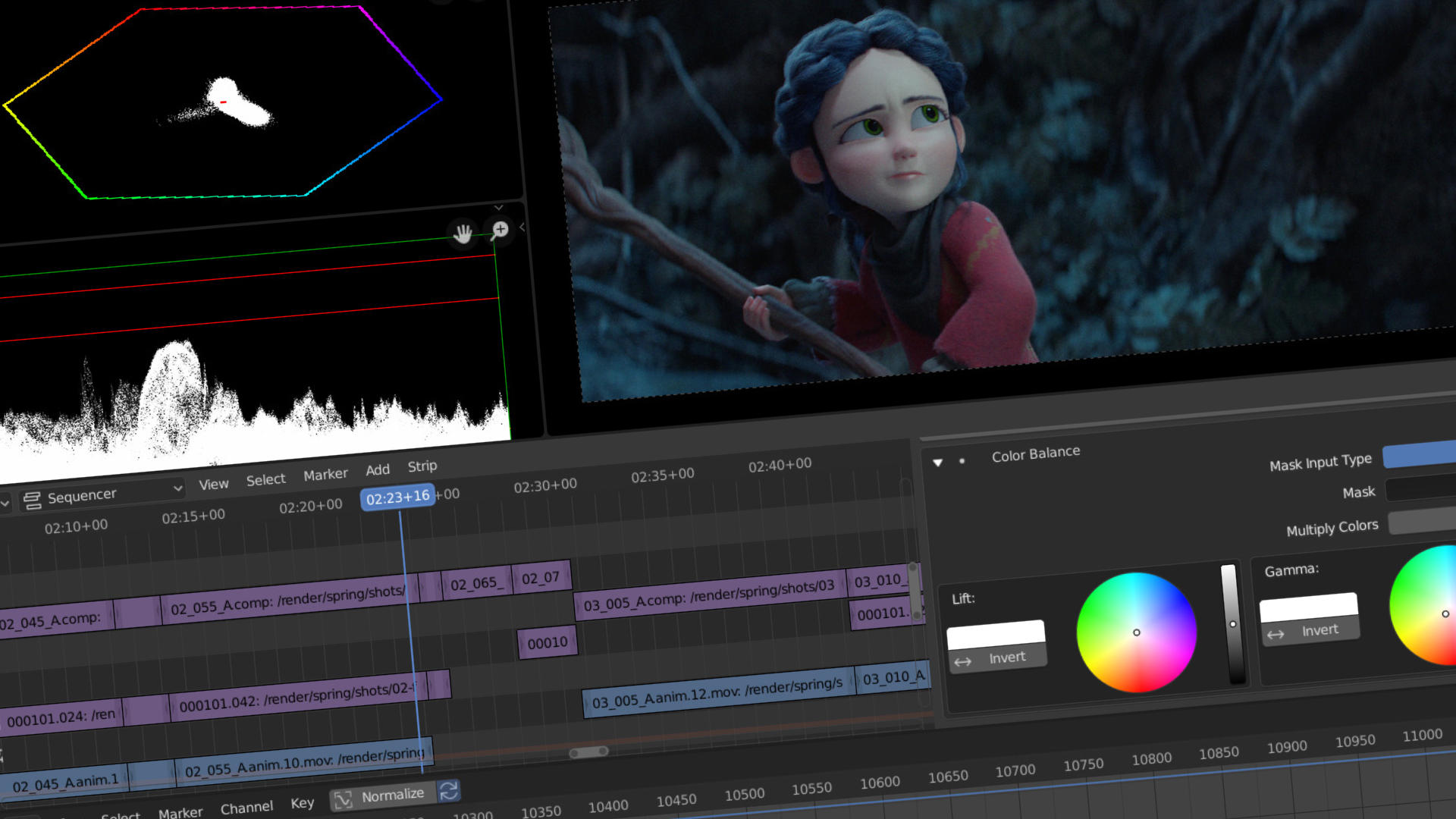
Color Grading and Correction
Color grading and correction are vital post-production processes that enhance the visual impact of your video by adjusting colors to convey the desired mood, atmosphere, and style. Blender\"s comprehensive color tools allow for precise control over the look of your footage. This section covers the basics of color grading and correction within Blender.
Understanding Color Correction
Color correction is the process of adjusting the white balance, exposure, and contrast of your video to ensure that colors are consistent and accurate throughout. This is especially important for footage shot in different lighting conditions or with different cameras.
Basic Color Correction Steps
- Adjusting White Balance: Use the Color Balance modifier in the Sequencer to correct any color casts and achieve a neutral starting point for further grading.
- Correcting Exposure: Adjust the brightness and contrast of your footage using the Bright/Contrast modifier to ensure that your video has the correct exposure.
- Enhancing Contrast: Use the Curves modifier to fine-tune the contrast and dynamic range of your video, making sure that your blacks are deep and your whites are bright without clipping.
Advanced Color Grading Techniques
Color grading goes beyond correction, allowing you to stylize your footage to support the narrative or thematic elements of your project:
- Using Look-Up Tables (LUTs): LUTs can be applied to instantly give your video a specific look or film stock emulation. Blender allows you to import and apply LUTs for quick and effective color grading.
- Creative Use of Color Curves: Manipulate the RGB curves individually to create a specific mood or feel. For example, a slight S-curve can add punch to your image, while adjusting individual color curves can help achieve a warm or cool look.
- Selective Color Grading: Use the Strip Modifier to apply color grading effects to specific areas of your footage, allowing for selective enhancement or alteration of certain colors.
Finalizing Your Grade
Once you have applied your desired corrections and grading:
- Review your footage in different viewing conditions to ensure consistency.
- Make final adjustments to saturation and vibrancy to ensure that your video looks appealing and maintains color accuracy across different displays.
- Use the Scopes feature in Blender to monitor your levels and ensure that your adjustments fall within the acceptable range for broadcast standards, if applicable.
Tips for Effective Color Grading
- Start with a neutral color palette by correctly white-balancing your footage before applying creative color grading.
- Remember that less is often more. Subtle changes can significantly affect the mood without distracting the viewer.
- Consider the emotional impact of color. Warm tones can convey happiness or nostalgia, while cool tones can create a sense of sadness or tension.
- Keep continuity in mind. Ensure that your color grading is consistent across shots to maintain immersion.
By understanding and utilizing Blender\"s color grading and correction tools, you can transform the visual quality of your video, enhancing both its narrative and aesthetic appeal.
Exporting Your Final Video
After completing your video editing and post-production work in Blender, the final step is to export your project so it can be shared and viewed on other devices. Exporting your video involves rendering your edits into a standard video format. This section provides a step-by-step guide to exporting your final video from Blender.
Choosing the Right Output Settings
Before exporting, it\"s crucial to select the appropriate settings for your project\"s needs. This includes the file format, codec, resolution, and frame rate:
- File Format: Blender supports various output formats, including AVI, MPEG, and QuickTime. Choose a format that best suits your distribution platform.
- Codec: The codec compresses your video to reduce file size while maintaining quality. H.264 is a widely compatible option for a balance between quality and file size.
- Resolution: Export your video in the resolution that matches your project settings, such as 1080p or 4K, to maintain visual quality.
- Frame Rate: Ensure the frame rate matches the original footage or the standard for your target medium (e.g., 24 fps for cinema, 30 fps for TV).
Exporting Your Video
- Navigate to the Properties panel and select the Output Properties tab.
- Under the Output section, choose your desired file format and click on the folder icon to specify the output directory for your video.
- In the Encoding section, select your codec, such as H.264, and adjust the quality settings. Lower bitrates reduce file size but may affect quality.
- Adjust any other settings as needed, such as audio codec and bitrate, if your project includes sound.
- Once you\"ve configured all settings, go to the top menu, select Render, and then Render Animation or press Ctrl + F12 to start the export process.
- Blender will render each frame of your video sequence and compile them into the final video file in the specified location.
Post-Export Checklist
After exporting your video, perform a few checks to ensure everything is as expected:
- Play the video in a media player to check for any rendering errors or glitches.
- Verify that the audio is synchronized and the quality meets your expectations.
- Ensure the video plays back smoothly on different devices and platforms, if applicable.
Exporting your video is the final step in the video editing process with Blender. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your video is ready for sharing, distribution, or further processing. Remember, exporting can be a time-consuming process, especially for high-resolution or lengthy projects, so allow sufficient time for Blender to render your final video.

Keyboard Shortcuts for Efficient Editing
One of the keys to efficient video editing in Blender is mastering keyboard shortcuts. These shortcuts allow you to speed up your editing process, making it easier to cut, trim, move, and apply effects to your clips without constantly navigating through menus. Here is a comprehensive list of essential keyboard shortcuts for video editing in Blender.
General Navigation
- Spacebar: Play/Pause the video playback.
- Right Arrow: Move one frame forward.
- Left Arrow: Move one frame backward.
- Shift + Right Arrow: Jump to the next keyframe.
- Shift + Left Arrow: Jump to the previous keyframe.
- Up Arrow: Jump 10 frames forward.
- Down Arrow: Jump 10 frames backward.
Editing Clips
- K: Cut (split) the selected strip at the current frame.
- Shift + K: Cut all strips at the current frame.
- G: Grab (move) the selected strip.
- S: Scale (trim or extend) the selected strip.
- X: Delete the selected strip.
- Ctrl + G: Group selected strips.
- Alt + G: Ungroup selected strips.
Timeline Navigation
- Home: Zoom the sequencer to fit the entire video sequence in view.
- End: Move the cursor to the end of the last strip.
- Page Up: Move to the next strip.
- Page Down: Move to the previous strip.
Effect Strips
- Shift + A: Open the Add menu to insert strips or effects.
- Shift + F: Add a Fade to or Fade from black effect to selected strips.
Advanced Editing
- Alt + C: Change the strip type (for example, from a video to a color strip).
- V: Ripple delete, removing the strip and closing the gap.
- Shift + R: Refresh the sequencer, useful if you\"ve made external changes to clips.
These shortcuts are just the beginning. As you become more familiar with Blender\"s video editing tools, you\"ll discover more shortcuts and techniques that can help streamline your workflow even further. Remember, practice is key to becoming proficient with these shortcuts and enhancing your video editing efficiency.
READ MORE:
Resources for Further Learning
Mastering video editing in Blender is a journey that involves continuous learning and practice. Fortunately, there are numerous resources available to help you enhance your skills and knowledge. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your expertise, these resources offer valuable insights and tutorials on how to get the most out of Blender\"s video editing capabilities.
Official Blender Tutorials
- Blender Foundation: The official Blender website hosts a variety of tutorials and guides covering all aspects of Blender, including video editing.
- Blender Cloud: Subscription service offering extensive training and resources from Blender Foundation.
Online Courses and Tutorials
- Blender Guru: Offers comprehensive tutorials on Blender, including a dedicated series for beginners.
- CG Cookie: Provides in-depth courses on Blender, focusing on both basics and advanced techniques.
- Udemy and Coursera: Feature courses on Blender video editing from beginner to advanced levels, taught by industry professionals.
YouTube Channels
- Tutor4u: Easy-to-follow video tutorials on Blender, great for beginners.
- CG Geek: Offers tutorials on a wide range of Blender topics, including video editing and animation.
- Blender Diplom: Focuses on more advanced tutorials, perfect for those looking to expand their skill set.
Books and E-Books
- \"Blender For Dummies\" by Jason van Gumster: A comprehensive guide to Blender, including sections on video editing.
- \"The Complete Guide to Blender Graphics\" by John M. Blain: Covers Blender\"s functionality, including detailed chapters on video editing.
Community Forums and Groups
- Blender Artists Community: An online community where Blender users share their knowledge, ask questions, and showcase their work.
- Reddit r/blender: A subreddit dedicated to Blender, including discussions on video editing techniques and projects.
- Blender Stack Exchange: A Q&A site for people who use Blender to create 3D graphics, animations, or videos.
These resources provide a solid foundation for learning and mastering video editing in Blender. By exploring tutorials, engaging with the community, and practicing your skills, you can significantly improve your video editing capabilities and bring your creative visions to life.
Embark on your Blender video editing journey with confidence and creativity. Harness the power of Blender to transform your videos into captivating stories, and explore the limitless possibilities that this comprehensive guide unlocks for filmmakers and enthusiasts alike.

_HOOK_