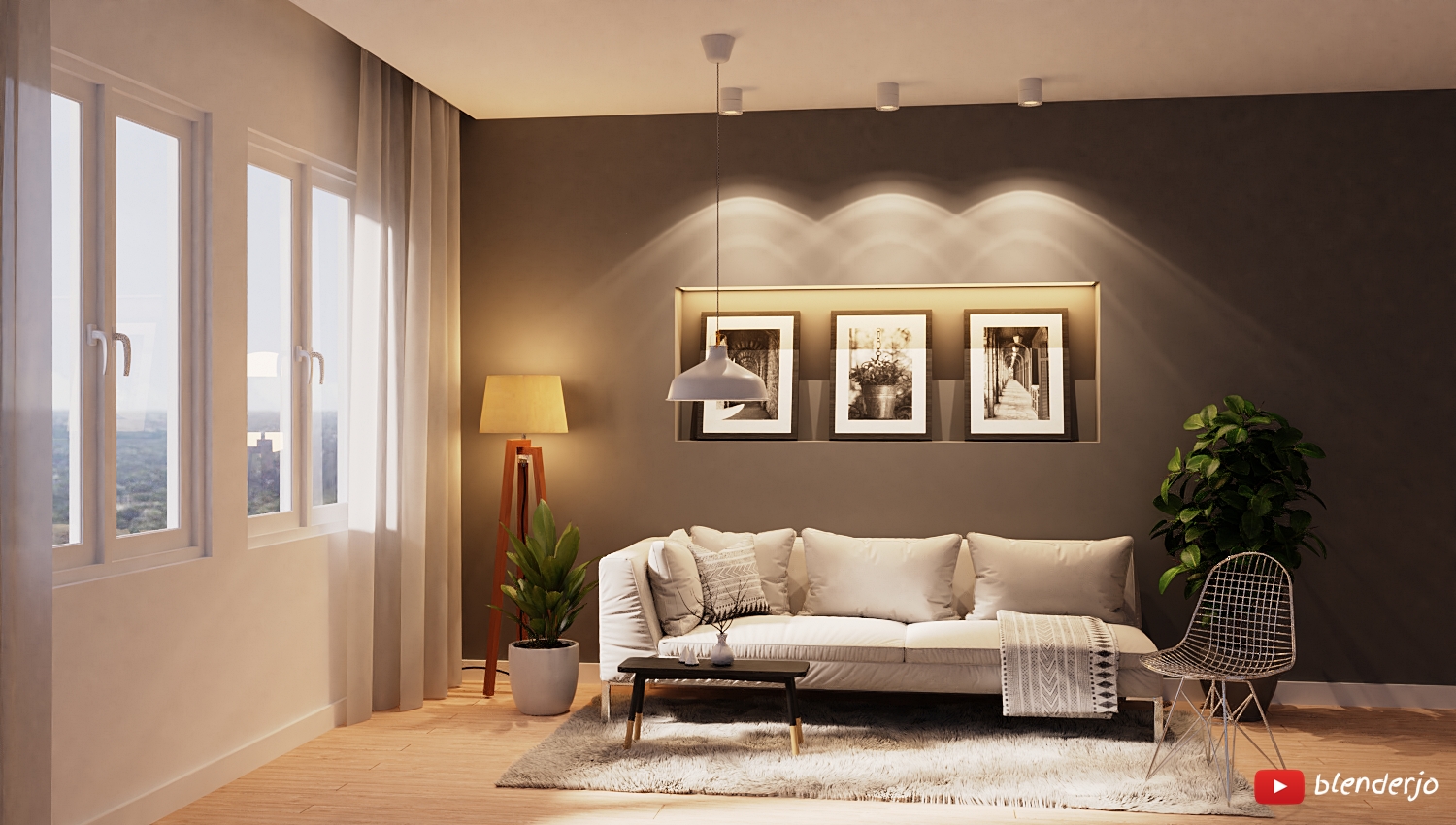
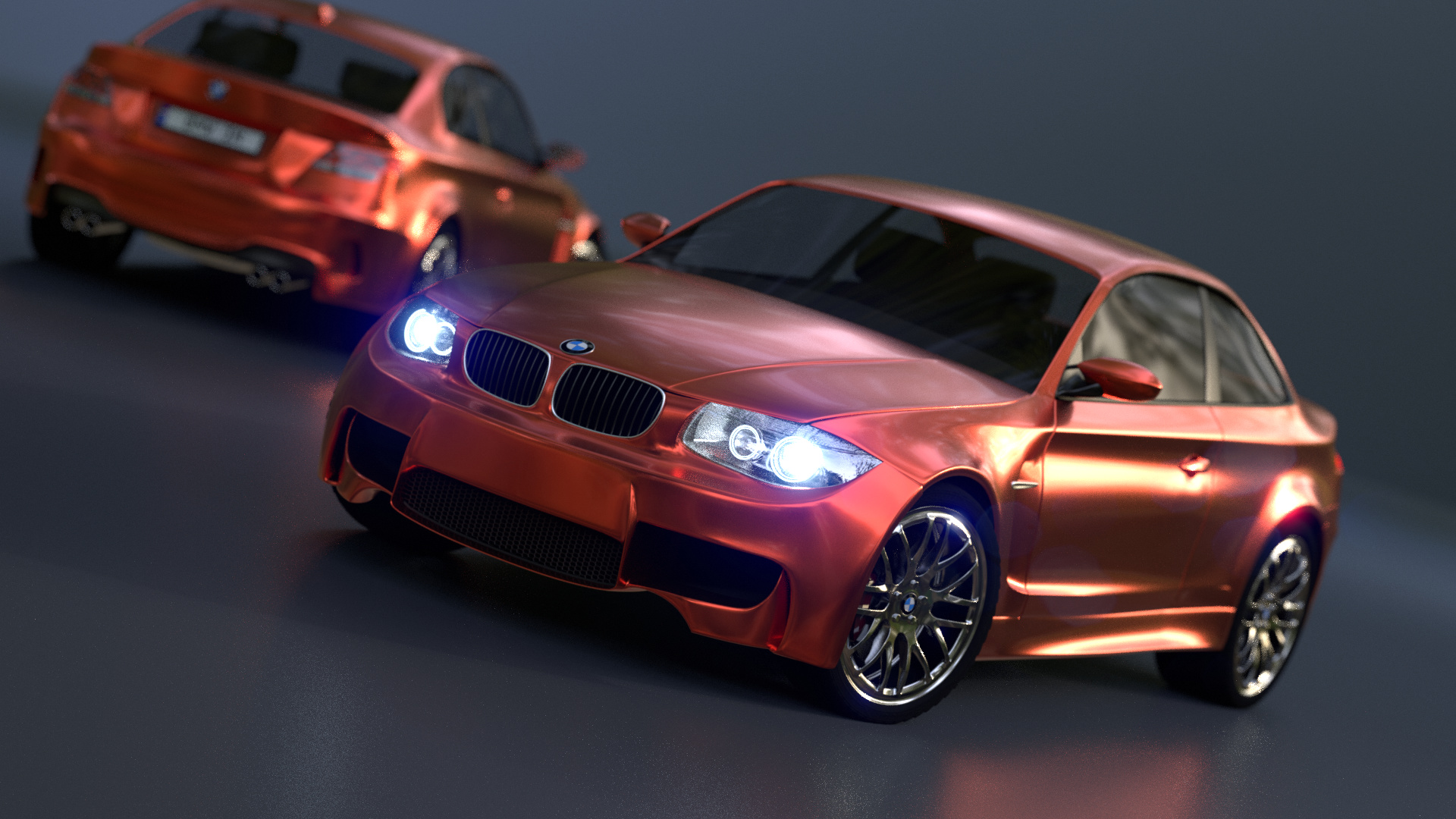
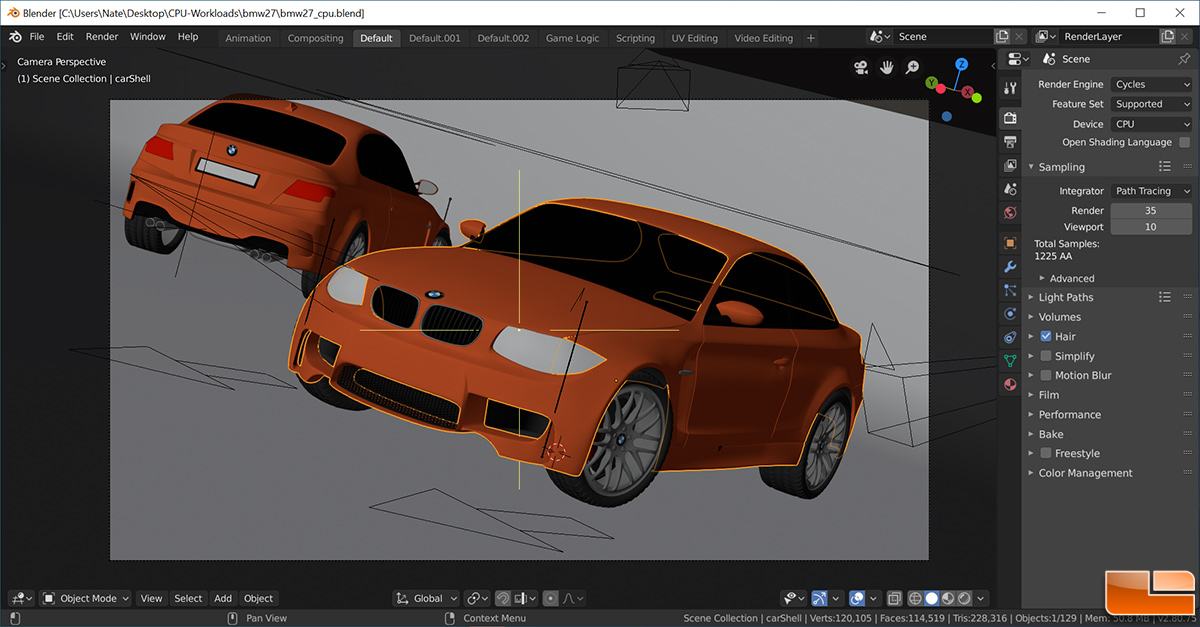
Topic blender render test: Discover the transformative power of Blender render tests, a pivotal tool for artists and developers seeking to elevate their 3D rendering skills and optimize their creative workflows.
Table of Content
- Blender Benchmark
- Performance Testing
- Rendering Techniques
- What are the best practices for conducting a thorough Blender render test?
- YOUTUBE: Blender classroom test RTX 3060 CUDA
- Performance Testing
- Rendering Techniques
- Rendering Techniques
- Introduction to Blender Render Tests
- Understanding Blender Benchmark and Performance Metrics
- Exploring Blender\"s Rendering Capabilities
- Comparative Analysis of CPU vs. GPU Rendering in Blender
- Optimization Tips for Efficient Blender Rendering
- Advanced Rendering Techniques in Blender
- Community Contributions and Open Data Insights
- Future Trends in Blender Rendering Technologies
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Conclusion and Resources for Further Learning
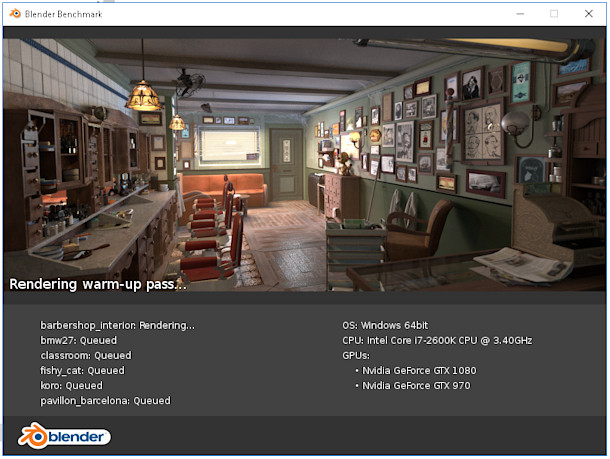
Blender Benchmark
The Blender Benchmark platform allows users to measure the performance of their system through downloadable packages that render several production files. This initiative emphasizes transparency and privacy, utilizing only free and open-source software.
Open Data Platform
- Collects, displays, and queries hardware and software performance test results.
- Encourages community participation in sharing performance data.
READ MORE:
Performance Testing
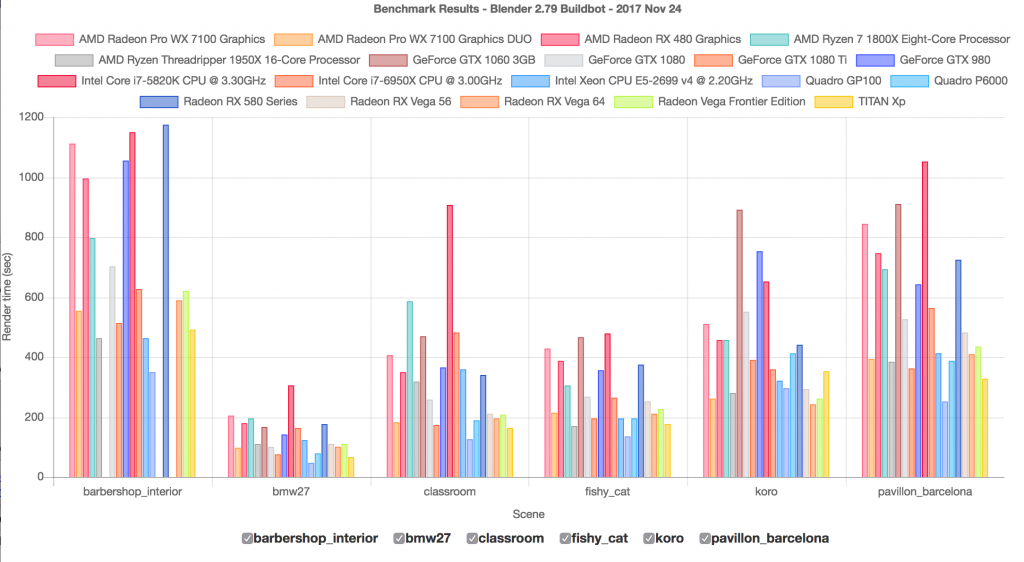
Performance tests reveal insights into the efficiency of rendering processes, highlighting the importance of powerful hardware for tasks such as 3D graphics rendering, CAD design, and 3D animation. The benchmark includes tests for both CPU and GPU render times, emphasizing the need for a balanced system.
Updated Scores and Features
- Blender 4.0 introduces new features and more demanding render tests, showcasing the evolution of rendering technology.
- Comparative tests between different Blender versions highlight improvements and the impact of hardware configurations on render times.
Rendering Techniques
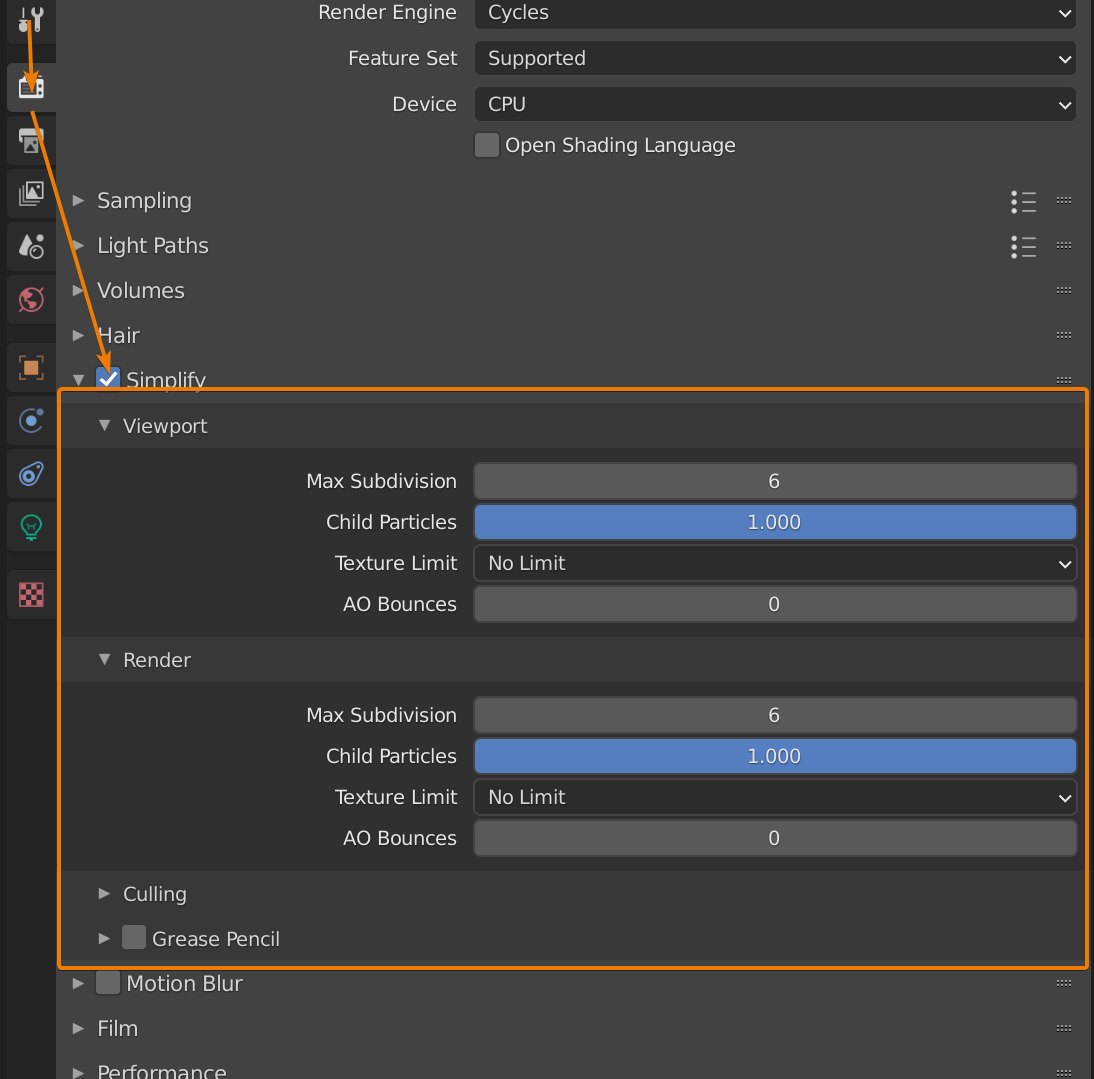
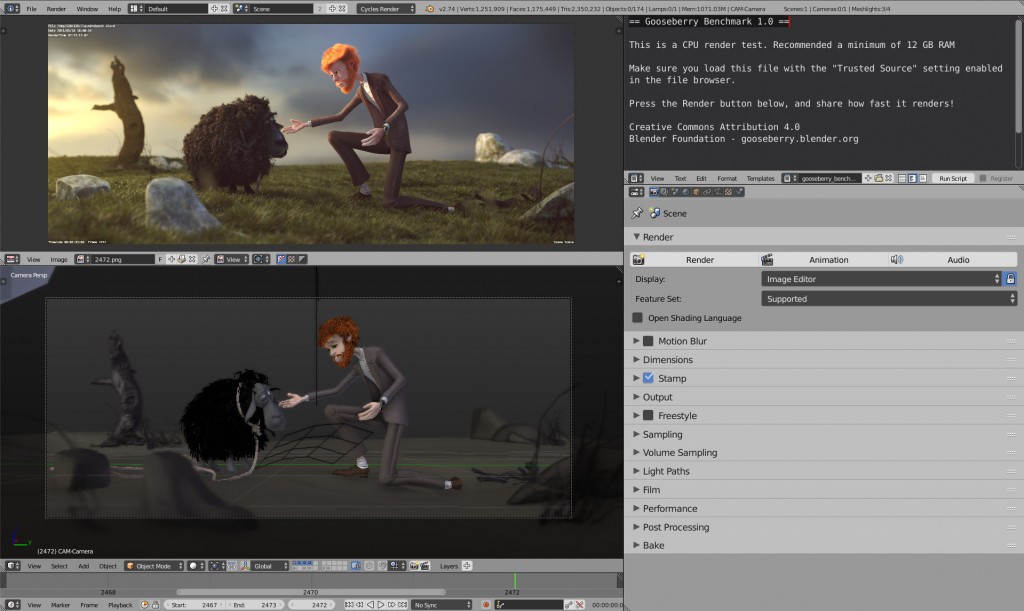
Blender supports a variety of rendering techniques, including hybrid (CPU+GPU) rendering, which demonstrates different performance benefits depending on the hardware setup. The development of photorealistic renders using Blender showcases its capability to produce high-quality visual content.
Optimization Tips
- Strategies for reducing render times, such as adjusting render settings and optimizing hardware configurations.
- The importance of selecting the right render engine and settings for specific project requirements.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| GPU Rendering | Utilizes the graphics processor for rendering tasks. | Speeds up render times for complex scenes. |
| CPU Rendering | Leverages the central processing unit. | Provides compatibility with a wide range of hardware. |
| Hybrid Rendering | Combines CPU and GPU processing power. | Optimizes resource usage for faster renders. |
What are the best practices for conducting a thorough Blender render test?
When conducting a thorough Blender render test, it\'s important to follow some best practices to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some steps to guide you through the process:
- Prepare your scene: Start by setting up a scene that represents the type of project you typically work on. Include complex models, textures, lighting, and effects to test the full capabilities of Blender\'s rendering engine.
- Optimize your scene: Before running the test, make sure to optimize your scene by removing any unnecessary elements that might impact the rendering performance. Use appropriate shaders and textures to streamline the process.
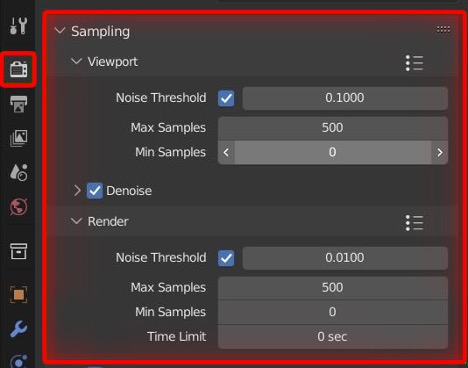
- Set rendering parameters: Configure the rendering settings according to your requirements. Adjust parameters such as resolution, samples, light bounces, and render engine options to achieve the desired output quality.
- Run the test: Start the rendering process and monitor the progress closely. Note the time taken to complete the rendering and analyze the visual quality of the output.
- Compare results: Compare the rendered image with previous tests or benchmark results to evaluate the performance improvement or degradation. Pay attention to details such as noise levels, shadow accuracy, and texture clarity.
- Iterate if necessary: If the results are not satisfactory, make adjustments to your scene or rendering settings and run the test again. Iterate this process until you achieve the desired balance between quality and speed.
Blender classroom test RTX 3060 CUDA
CUDA: Discover the power of CUDA in this fascinating video, showcasing the incredible speed and efficiency it brings to computing tasks. See how CUDA can revolutionize your workflow and enhance your computing experience! Benchmark: Dive into the world of benchmarking with this insightful video, as experts demonstrate how it can optimize your system\'s performance. Learn how benchmarking can help you make informed decisions for better computing results.
RTX 4070 Ti is INSANE! Blender 3D Benchmark Test BMW Classroom Barbershop
i will test the Nvidia RTX 4070 Ti on different Demo Files in Blender 3.4 Sometimes i stream when i\'m Blendering ...
Performance Testing
Performance tests reveal insights into the efficiency of rendering processes, highlighting the importance of powerful hardware for tasks such as 3D graphics rendering, CAD design, and 3D animation. The benchmark includes tests for both CPU and GPU render times, emphasizing the need for a balanced system.
Updated Scores and Features
- Blender 4.0 introduces new features and more demanding render tests, showcasing the evolution of rendering technology.
- Comparative tests between different Blender versions highlight improvements and the impact of hardware configurations on render times.

_HOOK_
Rendering Techniques
Blender supports a variety of rendering techniques, including hybrid (CPU+GPU) rendering, which demonstrates different performance benefits depending on the hardware setup. The development of photorealistic renders using Blender showcases its capability to produce high-quality visual content.
Optimization Tips
- Strategies for reducing render times, such as adjusting render settings and optimizing hardware configurations.
- The importance of selecting the right render engine and settings for specific project requirements.
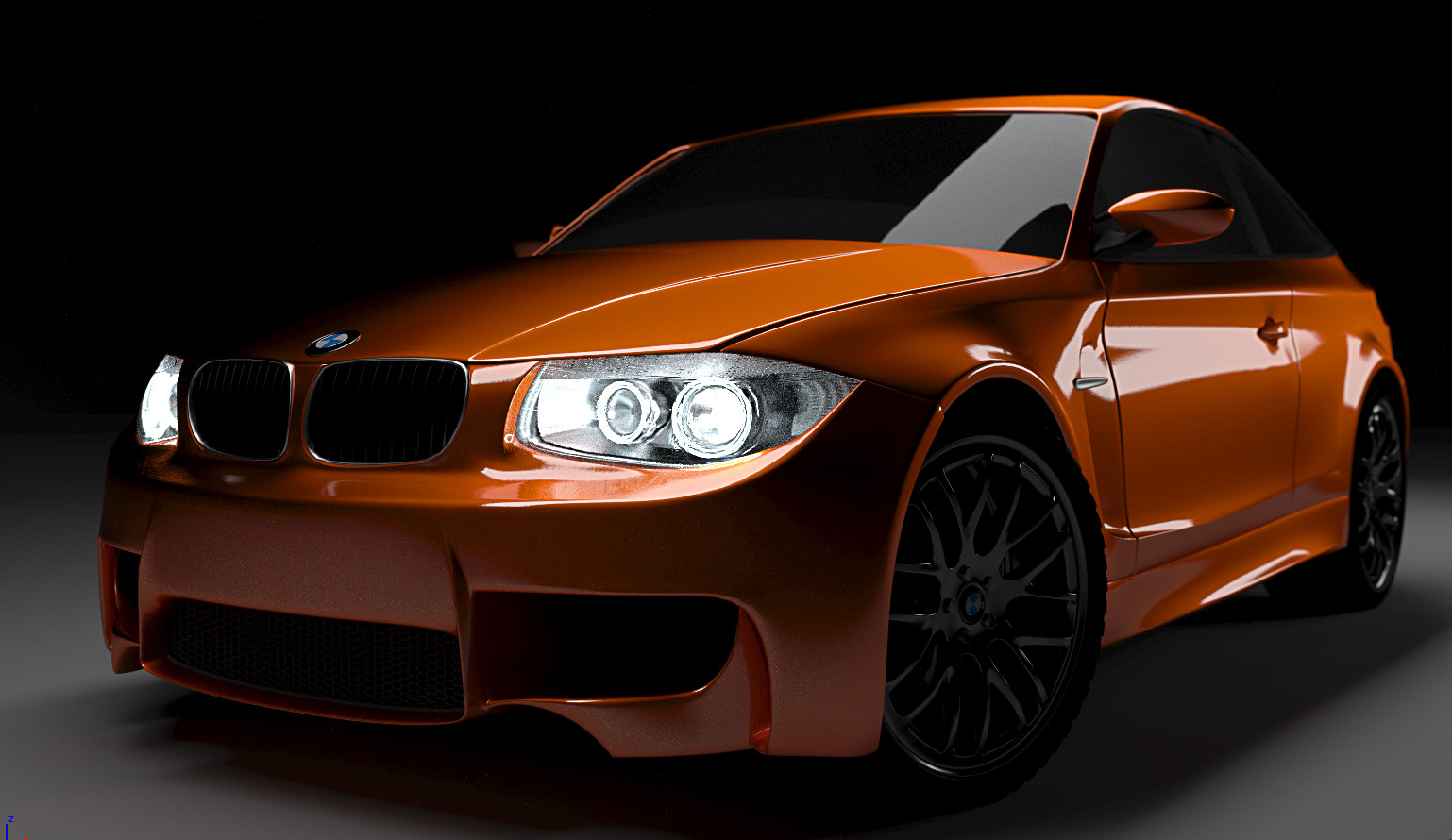

Rendering Techniques
Blender supports a variety of rendering techniques, including hybrid (CPU+GPU) rendering, which demonstrates different performance benefits depending on the hardware setup. The development of photorealistic renders using Blender showcases its capability to produce high-quality visual content.
Optimization Tips
- Strategies for reducing render times, such as adjusting render settings and optimizing hardware configurations.
- The importance of selecting the right render engine and settings for specific project requirements.
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| GPU Rendering | Utilizes the graphics processor for rendering tasks. | Speeds up render times for complex scenes. |
| CPU Rendering | Leverages the central processing unit. | Provides compatibility with a wide range of hardware. |
| Hybrid Rendering | Combines CPU and GPU processing power. | Optimizes resource usage for faster renders. |