Topic how to render an image in blender: Discover the art of rendering in Blender with our step-by-step guide, designed to elevate your 3D images from concept to photorealistic masterpieces, whether you"re a beginner or a seasoned pro.
Table of Content
- Basic Steps to Render an Image
- Choosing a Render Engine
- Rendering Tips
- Advanced Rendering Features
- Conclusion
- Choosing a Render Engine
- Rendering Tips
- Advanced Rendering Features
- What is the process of rendering an image in Blender?
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: How to Render an Image in Blender Tutorial
- Rendering Tips
- Advanced Rendering Features
- Conclusion
- Advanced Rendering Features
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Blender Rendering
- Choosing the Right Render Engine
- Basic Steps to Render an Image
- Improving Render Quality with Lighting and Materials
- Rendering Animations in Blender
- Advanced Rendering Features and Techniques
- Optimizing Render Times
- Common Rendering Issues and Solutions
- Conclusion: Enhancing Your Rendering Skills
Basic Steps to Render an Image
- Press F12 to render a still image or Ctrl+F12 to render an animation.
- Alternatively, navigate to the render menu and select \"Render Image\" or \"Render Animation\".
- After rendering, go to Image > Save As to save your rendered image.

READ MORE:
Choosing a Render Engine
Blender supports multiple rendering engines like Eevee and Cycles, each offering unique capabilities and settings for different visual outcomes.
Eevee vs. Cycles
- Eevee is Blender\"s real-time render engine, ideal for quick previews and less complex rendering tasks.
- Cycles is a ray-tracing render engine that produces more photorealistic images but requires more time to render.

Rendering Tips
- Experiment with lighting and materials to achieve more realistic effects.
- Adjust camera angles and perspectives for dynamic compositions.
- Use high-resolution textures for detailed surfaces.
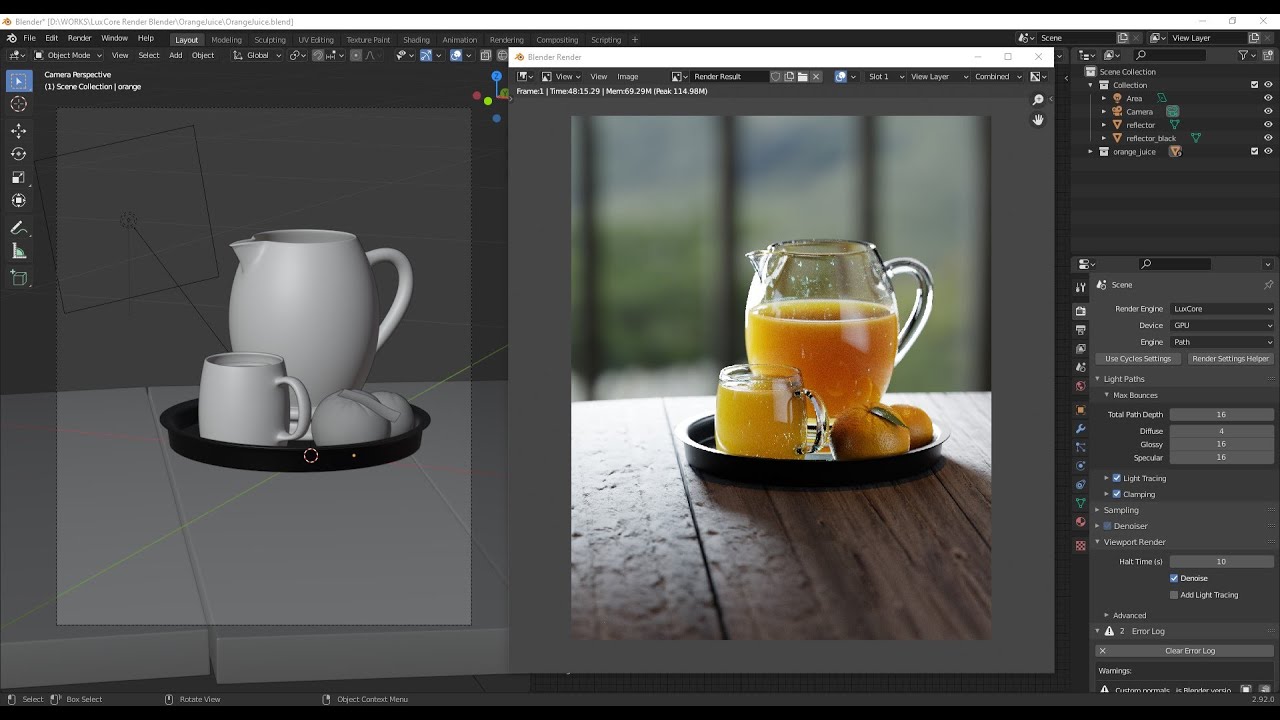
Advanced Rendering Features
Blender also offers advanced features like image sequencing for animations, background image rendering, and 360-degree image rendering, enabling users to create complex and immersive visuals.
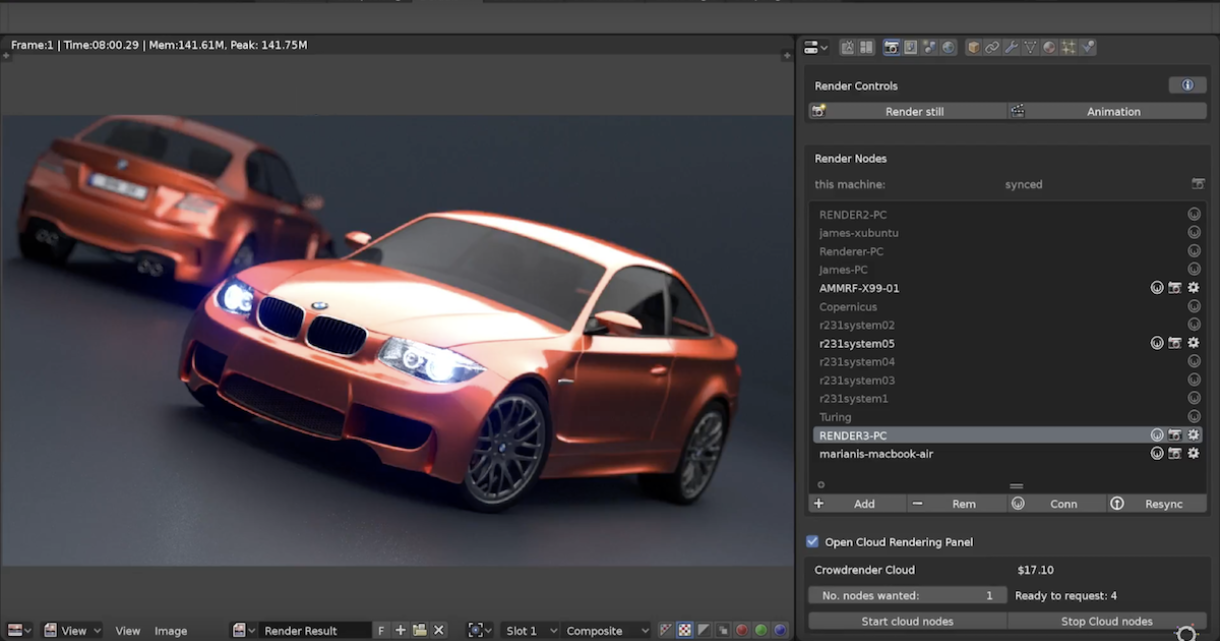
Conclusion
Rendering in Blender is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical prowess. By understanding the basics and experimenting with advanced features, users can unlock the full potential of their 3D models.

_HOOK_
Choosing a Render Engine
Blender supports multiple rendering engines like Eevee and Cycles, each offering unique capabilities and settings for different visual outcomes.
Eevee vs. Cycles
- Eevee is Blender\"s real-time render engine, ideal for quick previews and less complex rendering tasks.
- Cycles is a ray-tracing render engine that produces more photorealistic images but requires more time to render.

Rendering Tips
- Experiment with lighting and materials to achieve more realistic effects.
- Adjust camera angles and perspectives for dynamic compositions.
- Use high-resolution textures for detailed surfaces.

Advanced Rendering Features
Blender also offers advanced features like image sequencing for animations, background image rendering, and 360-degree image rendering, enabling users to create complex and immersive visuals.
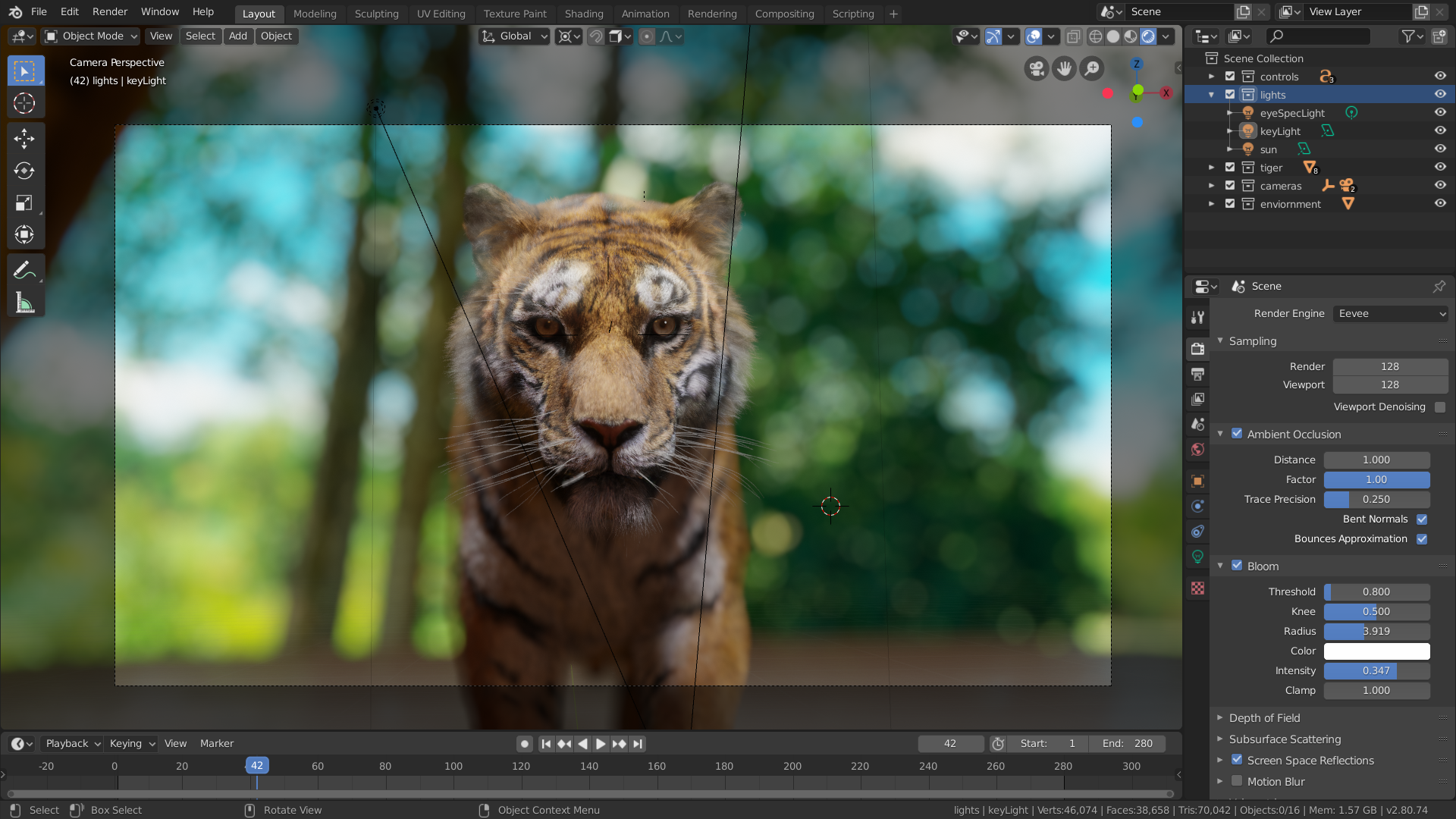
What is the process of rendering an image in Blender?
To render an image in Blender, follow these steps:
- Open Blender and import the 3D model you want to render.
- Set up the camera angle and lighting to achieve the desired composition for your image.
- Go to the \"Render\" tab located at the top of the interface.
- Click on the \"Render Image\" button to start the rendering process.
- Wait for Blender to render the image based on the settings you have chosen.
- Once the rendering is complete, you can save the image by going to \"Image\" > \"Save As Image\" and selecting the desired format and location.
Conclusion
Rendering in Blender is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical prowess. By understanding the basics and experimenting with advanced features, users can unlock the full potential of their 3D models.
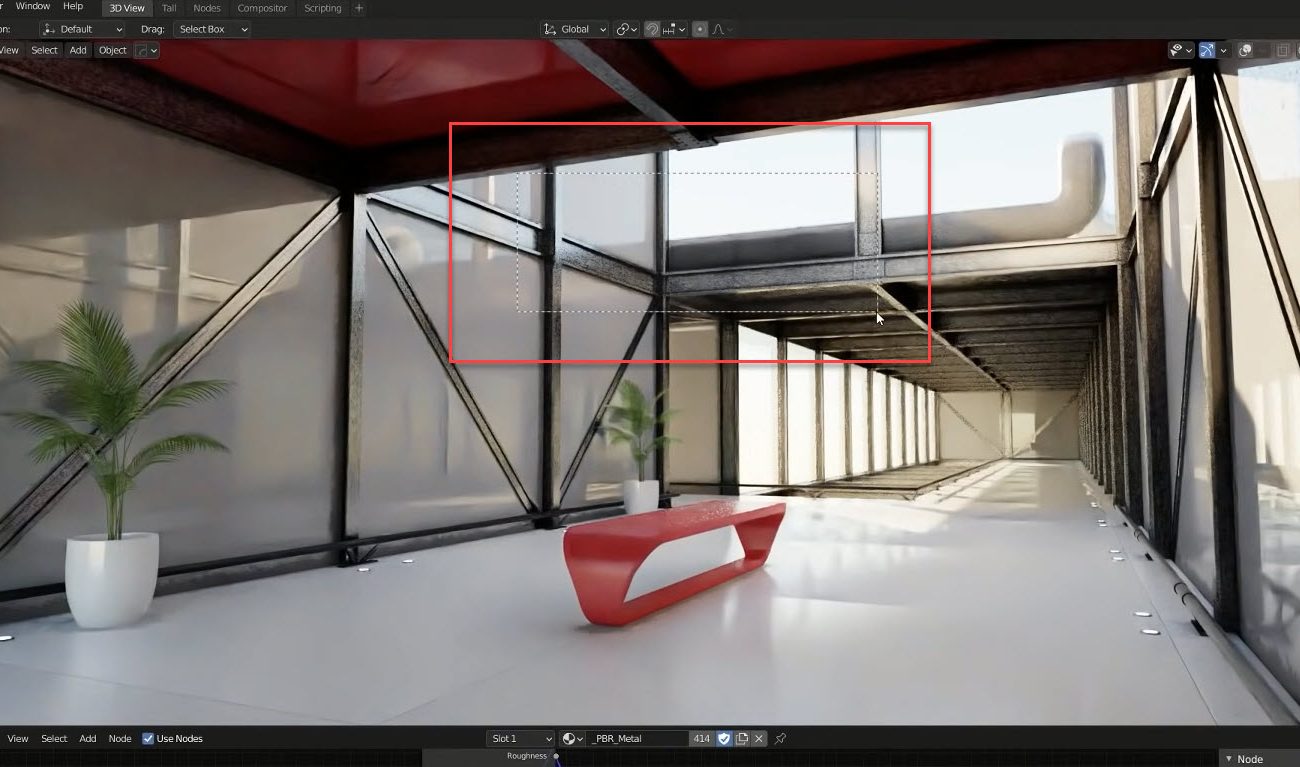
_HOOK_
How to Render an Image in Blender Tutorial
Rendering: Dive into the mesmerizing world of rendering and witness how digital art comes to life with breathtaking visuals and vibrant colors. Let your imagination soar as you explore the endless creative possibilities in this captivating video. Tutorial: Learn and master new skills with this engaging tutorial that breaks down complex concepts into easy-to-follow steps. Whether you\'re a beginner or an expert, this video is designed to enhance your knowledge and fuel your passion for learning.
How to Render an Image in Blender 4.0 Tutorial
Blender Tutorial for Beginners - In this tutorial, https://youtu.be/0RFkyiyYOHc , I show you how you can render an image in Blender ...
Rendering Tips
- Experiment with lighting and materials to achieve more realistic effects.
- Adjust camera angles and perspectives for dynamic compositions.
- Use high-resolution textures for detailed surfaces.
Advanced Rendering Features
Blender also offers advanced features like image sequencing for animations, background image rendering, and 360-degree image rendering, enabling users to create complex and immersive visuals.
Conclusion
Rendering in Blender is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical prowess. By understanding the basics and experimenting with advanced features, users can unlock the full potential of their 3D models.
Advanced Rendering Features
Blender also offers advanced features like image sequencing for animations, background image rendering, and 360-degree image rendering, enabling users to create complex and immersive visuals.
Conclusion
Rendering in Blender is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical prowess. By understanding the basics and experimenting with advanced features, users can unlock the full potential of their 3D models.
_HOOK_
Conclusion
Rendering in Blender is a multifaceted process that combines creativity with technical prowess. By understanding the basics and experimenting with advanced features, users can unlock the full potential of their 3D models.
Introduction to Blender Rendering
Blender rendering transforms your 3D models into stunning images or animations, bridging the gap between digital sculpture and visual art. It\"s a crucial final step that brings your creative vision to life. Whether you\"re a hobbyist or a professional, mastering rendering in Blender opens up a world of visual storytelling possibilities.
Rendering in Blender can be as simple or complex as your project requires. From quick previews using the Eevee engine to photorealistic images with Cycles, Blender\"s versatility caters to a wide range of artistic needs. Key to successful rendering is not just about hitting \"Render\"; it\"s about understanding how different settings and engines affect the final outcome.
- Press F12 for a still image or Ctrl+F12 for an animation to begin the rendering process.
- Navigate through the render menu to choose \"Render Image\" or \"Render Animation\" for more control over the rendering process.
- Save your rendered image from the Image menu, ensuring your artwork is ready for presentation or further post-processing.
Choosing the right render engine—Eevee for real-time rendering and Cycles for ray-traced photorealism—is crucial. Each engine has its strengths, with Eevee offering speed and efficiency, while Cycles provides depth and realism.
Understanding rendering is just the beginning. As you dive deeper, exploring lighting, materials, and camera angles, you\"ll discover how to enhance the mood, realism, and impact of your 3D creations. Blender\"s advanced features, such as volumetric effects, depth of field, and motion blur, further enrich your renderings, making them truly stand out.
Whether you\"re crafting a simple model or an intricate scene, rendering in Blender is your gateway to showcasing your work in its best light. With practice and experimentation, you\"ll learn to manipulate the myriad of settings to achieve your desired visual effect, making every render a step forward in your 3D art journey.
Choosing the Right Render Engine
Blender offers multiple render engines, each with unique features and strengths, tailored to different types of projects and artistic visions. Understanding the differences between these engines is crucial for achieving optimal results in your renders.
- Eevee: Blender\"s real-time render engine, ideal for fast previews and less resource-intensive projects. Eevee provides good quality outputs with significantly shorter render times compared to Cycles. It is well-suited for animations and scenes where real-time feedback is important.
- Cycles: A ray-tracing render engine known for its ability to produce photorealistic images. Cycles use a physically based path tracer for rendering, offering high-quality results at the cost of longer render times. It is perfect for projects where realism and detail are paramount.
- Workbench: Primarily used for layout, modeling, and quick previews without the need for photorealistic rendering. It offers a solid color or basic shaded views which are great for artistic planning or technical checks.
Choosing the right engine depends on your project\"s needs:
- For quick iterations and design work, Eevee is recommended.
- If your goal is high-quality visualizations or animations with realistic lighting and materials, Cycles should be your go-to.
- For modeling, sculpting, or technical previews, the Workbench engine provides the necessary tools without the overhead of complex rendering features.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each engine will help you streamline your workflow and produce stunning visuals, whether you\"re crafting a simple concept or a complex scene.
Basic Steps to Render an Image
Rendering an image in Blender is a straightforward process that allows you to turn your 3D models into beautiful, photorealistic images or animations. Here are the basic steps to render an image in Blender:
- Set up your Scene: Before you start rendering, ensure your 3D model is complete and your scene is set up with the correct camera angle. Add any lighting, materials, and textures needed to achieve the desired look for your render.
- Choose your Render Engine: Blender comes with several render engines, such as Eevee and Cycles. Eevee is a real-time render engine that provides faster results, while Cycles is a ray-traced render engine that produces more photorealistic images but takes longer. Select the engine that best suits your project\"s needs.
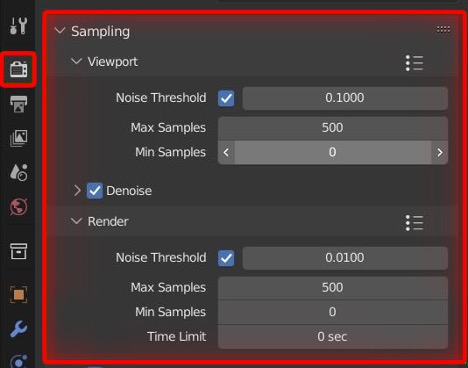
- Configure Render Settings: Go to the Render Properties panel to adjust settings like resolution, aspect ratio, and output format. You can also tweak sampling rates for Cycles to balance between render quality and time.
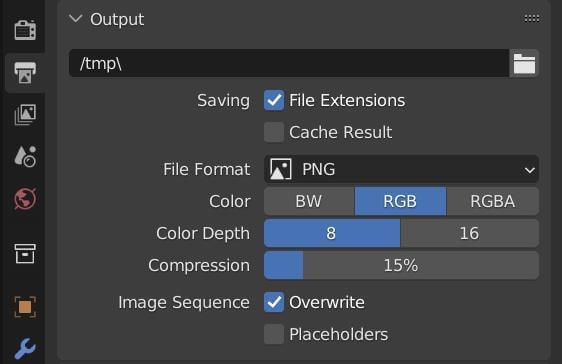
- Set the Output Path: Specify where you want to save your rendered image. You can choose the file format (e.g., PNG, JPEG) at this stage as well.
- Preview your Render: Use the Render Preview mode to get an idea of how your final image will look. This can help you make any necessary adjustments before performing the final render.
- Render the Image: Once you are satisfied with your setup, click on the Render button in the Render Properties panel or use the shortcut F12. Blender will start rendering the final image based on your settings.
- Save the Render: After rendering is complete, don\"t forget to save your image. You can do this from the Image Editor by selecting Image > Save As and choosing your desired location and format.
By following these steps, you can render stunning images in Blender. Remember, practice and experimentation with different settings and techniques are key to mastering the art of rendering.
Improving Render Quality with Lighting and Materials
Enhancing the render quality in Blender involves a strategic approach to lighting and materials. These elements are crucial for bringing realism and depth to your scenes. Follow these steps to elevate the quality of your renders:
- Understand Lighting Basics: Start by exploring different lighting techniques. Three-point lighting is a classic approach that provides a balanced and professional look. Experiment with key, fill, and back lights to achieve the desired mood and depth.
- Use HDRI for Environmental Lighting: High Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI) can drastically improve the realism of your scene by providing rich, natural lighting. It captures a wider range of light and dark tones, offering a more dynamic scene illumination.
- Optimize Material Properties: Blender’s material editor allows you to create lifelike textures and surfaces. Pay attention to the Specularity, Roughness, and Bump Mapping settings to add realism to your materials. Realistic textures can significantly enhance the final render.
- Incorporate Subsurface Scattering (SSS): For materials like skin, wax, or marble, use subsurface scattering to simulate light passing through a translucent object. This adds a level of realism to organic and semi-transparent materials.
- Experiment with Volumetric Lighting: Volumetric lighting adds atmospheric depth to a scene, especially useful for creating rays of light, fog, or mist. It can add a dramatic effect and greatly enhance the mood of your render.
- Utilize Global Illumination: Global illumination (GI) simulates the way light bounces off surfaces, providing a more realistic lighting model. It helps in achieving softer, more diffuse lighting in your scenes.
- Refine with Post-Processing: Blender’s compositor offers powerful post-processing tools. Use them to adjust the contrast, saturation, and brightness, or to add effects like glare or bloom to increase the visual appeal of your render.
Remember, improving render quality is an iterative process. Experiment with different settings and techniques to find what works best for your scene. Regularly reviewing and adjusting lighting and materials will lead to stunning, lifelike renders.
_HOOK_
Rendering Animations in Blender
Rendering animations in Blender involves several steps to ensure your final product is of high quality and visually appealing. This guide will walk you through the process from setting up your animation to the final render.
- Prepare Your Scene: Before rendering, make sure your animation is fully set up. This includes all the objects, animations, camera angles, and lighting. Double-check the animation timeline to ensure everything moves as expected.
- Choose the Right Render Engine: Blender offers several render engines like Eevee and Cycles. Eevee is faster and suitable for real-time rendering, while Cycles is more physically accurate, better for final productions but slower.
- Set Render Properties: In the Render Properties tab, select your render engine and adjust settings like resolution, frame rate, and the start and end frames for your animation. This is crucial for defining the quality and length of your animation.
- Adjust Lighting and Materials: Good lighting and high-quality materials can significantly enhance your animation. Spend time fine-tuning the materials for each object and setting up the lighting to achieve the desired mood and realism.
- Optimize Performance: Animations can be resource-intensive. Use techniques like simplifying geometry, reducing subsurface modifiers, and using proxies for complex objects to improve render times without compromising too much on quality.
- Rendering: Once everything is set up, go to the Render menu and select Render Animation. Blender will then render each frame of your animation, which can take a significant amount of time depending on the complexity and length of the animation.
- Post-Processing: After rendering, you may want to post-process your animation in Blender’s Compositor or an external video editing software. This can include color correction, adding effects, or stitching together different scenes.
Rendering animations in Blender is a rewarding process that allows you to bring your creations to life. With patience and practice, you can produce stunning animations that showcase your skills and creativity.
Advanced Rendering Features and Techniques
To elevate the quality of your renders in Blender, understanding and utilizing advanced rendering features and techniques is essential. These advanced strategies help in achieving photo-realistic results, enhancing the visual appeal of your projects. Here’s how to leverage these advanced features:
- High Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI) for Lighting: Use HDRI maps for lighting your scenes. HDRI provides more realistic lighting by capturing a wider range of light and dark shades, mimicking real-world lighting conditions.
- Ray Tracing for Realism: Blender\"s Cycles engine uses ray tracing to simulate the way light interacts with objects. Enable features like caustics, reflections, and soft shadows to add realism to your renders.
- Subsurface Scattering (SSS): For materials like skin, wax, or marble, subsurface scattering simulates light penetrating the surface. This feature is crucial for achieving realistic-looking materials.
- Volumetric Rendering: Create complex phenomena like smoke, fire, fog, or clouds with volumetric rendering. This technique calculates light’s interaction with particles in a volumetric medium.
- Node-Based Compositing: Use Blender’s node-based compositor for post-processing effects. This allows for the combination of different rendered elements, adjustment of colors, adding of effects like blurs or glows, and much more.
- Adaptive Sampling: Reduce render times without compromising on quality by using adaptive sampling. This feature automatically adjusts the number of samples in areas of the image that require less detail, focusing computational power where it\"s needed most.
- Multi-Layer EXR Output: For complex compositing and post-production work, output your renders in Multi-Layer EXR format. This retains high dynamic range data and separates elements into layers for greater flexibility in post-processing.
- Render Passes and Layers: Utilize render passes and layers to isolate different elements of your scene. This technique allows for more control in post-processing, making it easier to adjust or enhance specific components of your render.
- Denoisers: Use denoisers to clean up noise in your renders, especially in low-light conditions or when using high ISO values. Blender includes built-in denoisers that can dramatically improve image quality.
By integrating these advanced rendering features and techniques into your workflow, you can push the boundaries of what\"s possible in Blender, creating stunning, high-quality images and animations that stand out.
Optimizing Render Times
Rendering complex scenes in Blender can be time-consuming, but with the right techniques, you can significantly reduce render times without compromising on quality. Here are some effective strategies to optimize your rendering process:
- Reduce Sample Counts: Lower the number of samples in your render settings. Experiment to find the lowest number that still produces acceptable quality, especially for previews or less crucial elements.
- Simplify the Scene: Remove or simplify unnecessary geometry, textures, and effects. Use modifiers like Decimate to reduce polygon counts where high detail is not needed.
- Optimize Light Sources: Excessive or complex lighting can increase render times. Use fewer light sources and consider baking lighting for static scenes to speed up the process.
- Use Render Regions: If you\"re working on a specific part of your scene, use the Render Region feature to render only that portion. This can significantly reduce render times during the development phase.
- Adjust Tile Size: For CPU rendering, smaller tile sizes (like 32x32) can be faster, whereas for GPU rendering, larger tiles (such as 256x256) are more efficient. Experiment with tile sizes to find the best option for your setup.
- Enable Denoising: Use Blender’s built-in denoising features to allow for lower sample rates by cleaning up noise in post-processing, which can drastically reduce render times.
- Use Simplified Materials: Complex shaders and materials can increase render times. Where possible, use simpler materials or consider baking textures to reduce computational load.
- Render Layers and Compositing: Render complex scenes in layers or passes and composite them together in post-processing. This allows for more control and can often be faster than rendering everything in a single pass.
- Optimize Output Settings: Render at a lower resolution during testing and only use high resolutions for final outputs. Also, consider the file format; some formats are quicker to write to disk than others.
- Hardware Upgrades: While not always an option, upgrading your hardware (more RAM, a faster CPU, or a better GPU) can have a significant impact on reducing render times.
By applying these strategies, you can optimize your Blender render times effectively, allowing for a more efficient workflow and faster turnaround on projects.
Common Rendering Issues and Solutions
When working with Blender, users might encounter various rendering issues that can affect the quality and efficiency of their projects. Identifying and resolving these common problems is key to a smooth rendering process. Here are some typical issues and their solutions:
- Long Render Times: Optimize your scene by reducing the resolution, simplifying the geometry, and using less complex materials. Consider using Blender\"s Simplify option and adaptive sampling to speed up render times.
- Noisy Renders: Increase the number of samples for your render or use the Denoise feature in Blender. Adjusting light paths and reducing the complexity of materials can also help reduce noise.
- Materials or Textures Not Showing: Ensure that all materials and textures are correctly linked and not missing. Check the UV maps and texture paths to ensure they are correctly set up.
- Fire or Smoke Not Rendering: Make sure the domain for your smoke or fire simulation is correctly set up. Check the material settings for the domain and ensure the use of the correct shader, such as the Principled Volume shader.
- Rendering Artifacts: Artifacts can be caused by issues with geometry, normals, or overlapping faces. Clean up your mesh, recalculate normals, and remove any duplicate vertices to solve this issue.
- Unexpected Shadows or Dark Areas: This could be due to incorrect light setup or shadow settings. Adjust your light sources, increase the size of the light source for softer shadows, or tweak the shadow settings in your render settings.
- Animations Not Rendering Correctly: Ensure all keyframes are set correctly and that the animation timeline is configured to include all frames. Also, verify that the frame rate is correctly set for your project.
- Crashes During Rendering: This may be due to insufficient system resources. Try lowering the render resolution, closing other applications to free up memory, or rendering in smaller sections using the Render Region feature.
By addressing these common rendering issues with the provided solutions, you can improve the quality of your renders and enjoy a more efficient workflow in Blender.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Enhancing Your Rendering Skills
Mastering rendering in Blender is a journey that combines both the art of visualization and the science of technical settings. Improving your rendering skills not only enhances the visual quality of your projects but also makes the process more efficient and enjoyable. Here are steps to continually enhance your rendering skills:
- Practice Regularly: The key to mastering any skill is consistent practice. Experiment with different rendering techniques, settings, and challenges to broaden your experience.
- Stay Updated: Blender is continuously evolving, with new features and improvements being added regularly. Stay updated with the latest versions and explore new functionalities to stay ahead.
- Explore Different Render Engines: While Blender comes with its own powerful render engines, exploring third-party render engines can provide new perspectives and tools that might be better suited for certain projects.
- Learn from the Community: Blender has a vast and supportive community. Participate in forums, watch tutorials, and collaborate with other artists to learn new tips and tricks.
- Focus on Lighting and Composition: Good lighting and composition are fundamental to a great render. Spend time understanding and applying principles of lighting and composition to elevate your renders.
- Understand Materials and Textures: Realism in rendering often comes down to how well materials and textures are used. Dive deep into creating and manipulating materials to achieve more lifelike results.
- Utilize Post-Processing: Post-processing is a powerful tool to enhance your renders. Use Blender’s compositor or external software to adjust colors, add effects, and refine your images.
- Challenge Yourself: Take on projects that push your limits. Trying complex scenes or animations can uncover new learning opportunities and improve your problem-solving skills.
- Share Your Work: Sharing your work with others can provide valuable feedback. Use critiques to refine your techniques and approach to rendering.
In conclusion, enhancing your rendering skills in Blender is a continuous process of learning, practicing, and experimenting. Embrace the journey, and you will find yourself creating stunning visuals that bring your ideas to life. Remember, every render is a step forward in your path to becoming a more skilled and confident artist.
Embark on your journey to mastering Blender rendering with our comprehensive guide, and unlock the potential to create stunning visuals. Let each step enhance your skills, transforming your creative visions into breathtaking realities.
_HOOK_