Topic blender render engines: Explore the transformative power of Blender render engines, unlocking unparalleled creativity and efficiency in 3D visualization. Discover tools that elevate your projects, from photorealistic imagery to dynamic, real-time previews.
Table of Content
- Main Blender Render Engines
- Popular Third-Party Render Engines
- Choosing the Right Engine
- Popular Third-Party Render Engines
- Choosing the Right Engine
- Choosing the Right Engine
- What are the different render engines available in Blender and their respective strengths?
- YOUTUBE: All Blender Render Engines
- Introduction to Blender Render Engines
- Overview of Main Blender Render Engines
- Comparing Blender\"s Eevee and Cycles
- Insight into Third-Party Render Engines Compatible with Blender
- Advanced Features of Popular Third-Party Render Engines
- Factors to Consider When Choosing a Render Engine for Blender
- Impact of Render Engines on Workflow and Project Outcome
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Different Render Engines
- Future Trends in Blender Rendering Technologies
- Conclusion: Selecting the Best Render Engine for Your Needs
Main Blender Render Engines
- Eevee: Blender\"s real-time render engine, known for its speed and efficiency in delivering high-quality previews and final renders.
- Cycles: A ray-tracing render engine that provides stunning ultra-realistic images, supporting both CPU and GPU rendering.
- Workbench: Simplified for quick previews and technical visualization, focusing on speed and efficiency.

READ MORE:
Popular Third-Party Render Engines
- LuxCoreRender: An open-source unbiased render engine, celebrated for its accuracy and realism in light simulation.
- Redshift: A biased GPU render engine, favored for its speed and the quality of its renders, suitable for high-end production work.
- Octane Render: Known for its real-time rendering capabilities, providing artists with immediate feedback on changes.
- V-Ray: Offers a blend of speed and quality, widely used in various industries for its versatility and photorealistic renders.
- Corona Renderer: Praised for its ease of use and realistic lighting, Corona integrates seamlessly with Blender, enhancing workflow efficiency.
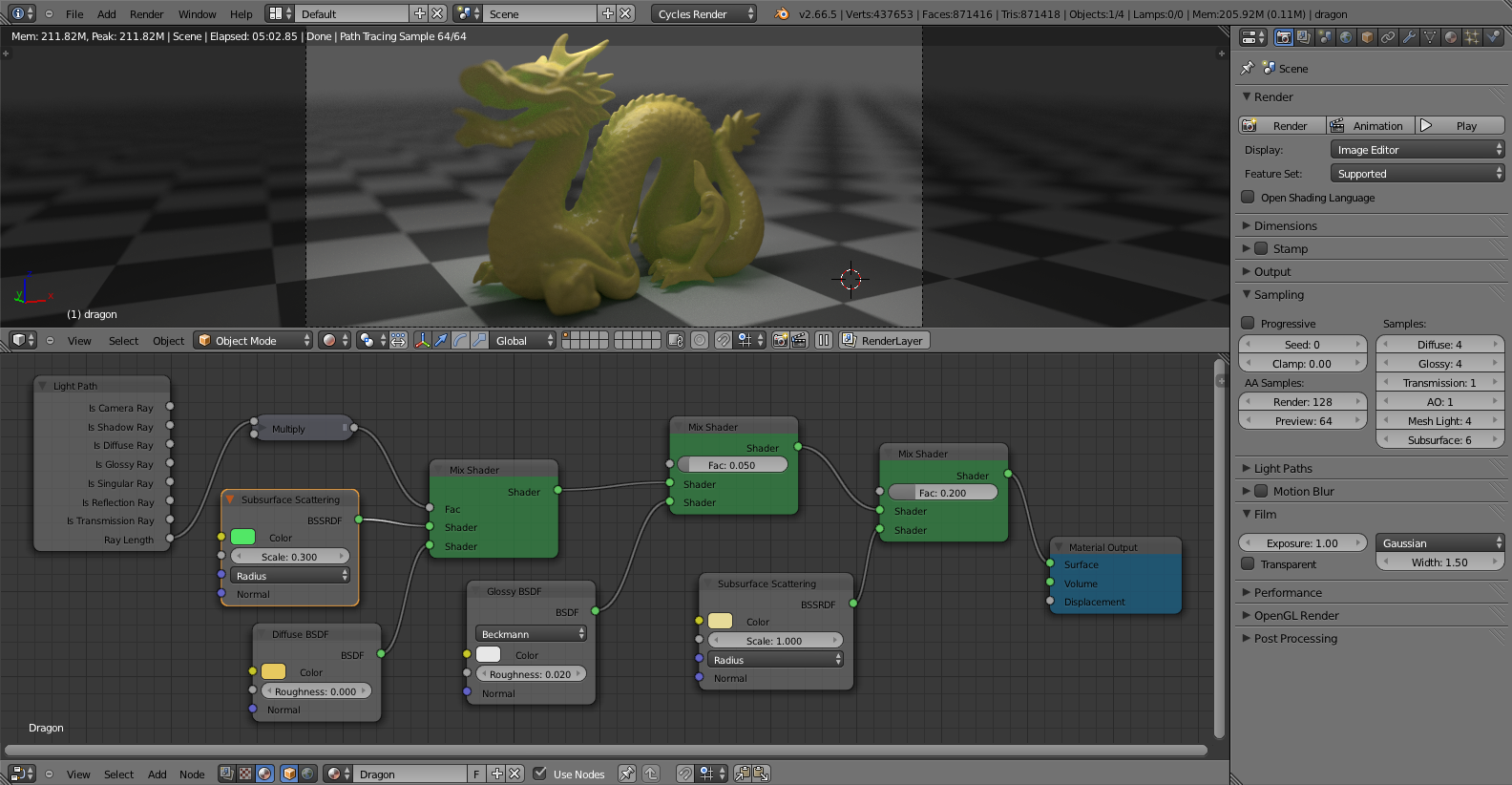
Choosing the Right Engine
Selecting the right render engine depends on project requirements, available resources, and desired output quality. Eevee and Cycles are powerful options for artists working within Blender\"s ecosystem, while third-party engines like Redshift and V-Ray offer specialized tools for complex projects.
Factors to Consider
- Rendering speed vs. quality balance
- Hardware capabilities and optimization
- Specific features such as real-time rendering or photorealism
- Project budget and engine affordability
In conclusion, Blender\"s versatility in supporting various render engines makes it a formidable tool for 3D artists and designers. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each engine, users can tailor their workflow to achieve the best results for their projects.

Popular Third-Party Render Engines
- LuxCoreRender: An open-source unbiased render engine, celebrated for its accuracy and realism in light simulation.
- Redshift: A biased GPU render engine, favored for its speed and the quality of its renders, suitable for high-end production work.
- Octane Render: Known for its real-time rendering capabilities, providing artists with immediate feedback on changes.
- V-Ray: Offers a blend of speed and quality, widely used in various industries for its versatility and photorealistic renders.
- Corona Renderer: Praised for its ease of use and realistic lighting, Corona integrates seamlessly with Blender, enhancing workflow efficiency.
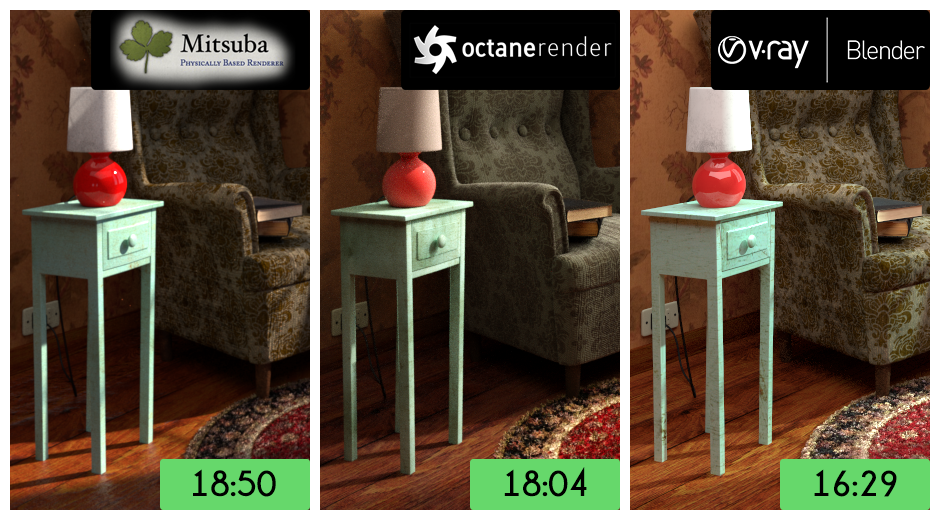

Choosing the Right Engine
Selecting the right render engine depends on project requirements, available resources, and desired output quality. Eevee and Cycles are powerful options for artists working within Blender\"s ecosystem, while third-party engines like Redshift and V-Ray offer specialized tools for complex projects.
Factors to Consider
- Rendering speed vs. quality balance
- Hardware capabilities and optimization
- Specific features such as real-time rendering or photorealism
- Project budget and engine affordability
In conclusion, Blender\"s versatility in supporting various render engines makes it a formidable tool for 3D artists and designers. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each engine, users can tailor their workflow to achieve the best results for their projects.

_HOOK_
Choosing the Right Engine
Selecting the right render engine depends on project requirements, available resources, and desired output quality. Eevee and Cycles are powerful options for artists working within Blender\"s ecosystem, while third-party engines like Redshift and V-Ray offer specialized tools for complex projects.
Factors to Consider
- Rendering speed vs. quality balance
- Hardware capabilities and optimization
- Specific features such as real-time rendering or photorealism
- Project budget and engine affordability
In conclusion, Blender\"s versatility in supporting various render engines makes it a formidable tool for 3D artists and designers. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each engine, users can tailor their workflow to achieve the best results for their projects.
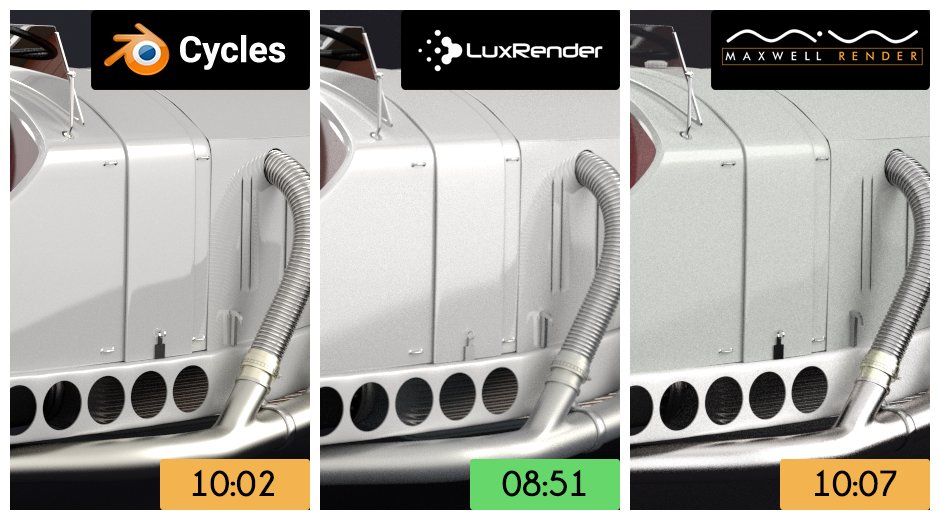
What are the different render engines available in Blender and their respective strengths?
- Cycles: Cycles is Blender\'s ray-trace based production render engine. It offers stunning ultra-realistic rendering and is known for its ability to create high-quality images with accurate lighting and shadows.
- Eevee: Eevee is Blender\'s real-time render engine. It is designed for fast rendering of interactive previews and animations. Eevee is best suited for projects that require quick feedback on changes and real-time visualization.
- EEG: Experimental Render Engine. This engine is still in development and is intended for testing new features and technologies. It may not be as stable or feature-rich as Cycles or Eevee, but it offers a glimpse into the future of Blender rendering.
All Blender Render Engines
Comparison: Discover the power of comparison in our engaging video, showcasing the benefits of evaluating options side by side. See how this simple tool can help you make informed decisions confidently. Top Picks: Explore our exclusive video featuring the top picks in technology for this year. From gadgets to gizmos, we\'ve handpicked the best of the best just for you. Tune in and stay ahead of the curve!
Introduction to Blender Render Engines
Blender is a versatile 3D creation suite that offers various render engines, each designed to meet specific visualization needs. From real-time rendering to photorealistic output, Blender\"s engines cater to a wide range of projects, enhancing creativity and productivity.
- Eevee: Blender\"s real-time engine, ideal for quick previews and animations, providing a balance between speed and quality.
- Cycles: A powerful, ray-tracing engine that excels in producing photorealistic images, supporting CPU and GPU rendering.
- Workbench: Focused on speed, this engine is perfect for modeling and technical visualization, offering a simplified rendering process.
In addition to these built-in engines, Blender supports third-party render engines, expanding the possibilities for artists and designers. These include:
- LuxCoreRender: An unbiased engine known for its realistic lighting and material simulation.
- Redshift: A GPU-accelerated renderer favored for its speed and efficiency in production environments.
- Octane Render and V-Ray: Both are renowned for their advanced lighting and shading capabilities, enabling stunning visual effects.
Choosing the right render engine depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the desired level of realism, render time constraints, and hardware capabilities. Each engine offers unique strengths, from Eevee\"s rapid real-time rendering to Cycles\" unrivaled quality for final production shots. Blender\"s flexibility in rendering options ensures that users can find the perfect match for their creative vision and workflow needs.

Best Render Engines for Blender
In today\'s video, we\'ll discuss some of the best engines to use with Blender. Try Out Drop & Render For Free Here: For ...
Overview of Main Blender Render Engines
Blender\"s render engines are pivotal in transforming 3D models into stunning visuals. This section provides a detailed overview of Blender\"s main render engines, highlighting their unique features and applications.
- Eevee: Blender\"s real-time engine, Eevee, is celebrated for its speed and versatility. Ideal for quick previews and animations, it offers a wide array of real-time rendering features, including PBR shaders and soft shadows, making it a favorite for interactive media and game development.
- Cycles: Cycles, Blender\"s fully ray-traced render engine, is known for its outstanding realism and photorealistic rendering capabilities. Utilizing both CPU and GPU rendering, Cycles excels in creating complex materials and lighting scenarios, preferred for high-quality visualizations and final renders.
- Workbench: The Workbench engine is designed for artists who need a fast and efficient way to visualize their models during the modeling stage. It provides a simplified, non-photorealistic render, perfect for quick studies, layout previews, and technical drawings.
Each engine caters to different aspects of the 3D rendering process, from real-time visualization with Eevee to the photorealistic capabilities of Cycles and the simplicity of Workbench. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each engine can help users select the most suitable one for their project\"s needs, whether it be rapid prototyping, animation, or high-fidelity visual effects.

Comparing Blender\"s Eevee and Cycles
Blender offers two primary render engines, Eevee and Cycles, each with distinct capabilities catering to different rendering needs. Understanding their differences is crucial for selecting the right engine for your project.
- Eevee: Eevee is Blender\"s real-time render engine, designed for speed and interactivity. It uses rasterization, similar to game engines, making it ideal for previews, animations, and projects requiring quick iterations. Eevee excels in delivering impressive results with less computational time, offering features like PBR shaders, soft shadows, and real-time viewport feedback.
- Cycles: Cycles is a path-tracing render engine known for its photorealism and accuracy in simulating real-world lighting conditions. It computes light bounces and interactions with materials in a physically accurate manner, making it suitable for high-quality stills and animations requiring intricate detail and realism. Cycles can utilize both CPU and GPU, offering flexibility based on the user\"s hardware setup.
When comparing Eevee and Cycles, consider the following:
- Rendering Speed: Eevee is significantly faster, providing real-time feedback, whereas Cycles, being a path-tracer, takes more time to render images, especially in complex scenes.
- Quality and Accuracy: Cycles offers higher photorealism through accurate light simulation, ideal for final renders. Eevee, while fast, may require additional tweaking to achieve similar levels of realism.
- Use Case: Eevee is preferred for animation and real-time projects, while Cycles is chosen for projects where ultimate realism and detail are paramount.
Ultimately, the choice between Eevee and Cycles depends on the project\"s requirements, including time constraints, desired quality, and the type of visuals needed. Many artists find using both engines in different stages of production beneficial, leveraging Eevee for layout and animation previews and Cycles for the final render.
_HOOK_
Insight into Third-Party Render Engines Compatible with Blender
Blender\"s flexibility is further enhanced by its compatibility with a range of third-party render engines, each offering unique features and benefits. These engines can provide advanced rendering capabilities, different visualization styles, and optimized workflows, catering to diverse project requirements.
- LuxCoreRender: An open-source unbiased renderer, known for its realistic light simulation and material accuracy. LuxCoreRender excels in producing photorealistic images with attention to light behavior and material properties.
- Redshift: A powerful GPU-accelerated renderer, Redshift is favored for its speed and efficiency. It\"s particularly suited for projects requiring complex shading networks and large datasets, delivering high-quality results in less time.
- Octane Render: Known for its real-time rendering capabilities, Octane Render leverages the GPU to provide instant visual feedback, facilitating a highly interactive design process. It\"s renowned for its photorealistic rendering, with a focus on lighting and materials.
- V-Ray: V-Ray is widely used across various industries for its versatility and photorealistic rendering quality. It offers a comprehensive set of lighting, shading, and rendering tools, making it suitable for everything from architectural visualization to VFX.
- Corona Renderer: Praised for its balance of simplicity and power, Corona Renderer delivers high-quality, photorealistic visuals with an intuitive setup. It\"s designed to streamline the rendering process, making photorealism more accessible.
These third-party engines integrate seamlessly with Blender, providing users with additional tools and options to achieve the desired outcome. Whether seeking realism, speed, or specific rendering techniques, there\"s a third-party engine that complements Blender\"s native capabilities, expanding the creative possibilities for artists and designers.

Advanced Features of Popular Third-Party Render Engines
The integration of third-party render engines into Blender significantly enhances its rendering capabilities. These engines offer advanced features that cater to a wide range of visualization needs, from photorealistic rendering to real-time previews. Below is an overview of the advanced features provided by some of the most popular third-party render engines compatible with Blender.
- LuxCoreRender: Offers accurate light simulation and material rendering, thanks to its physically based rendering (PBR) algorithms. It\"s known for its ability to handle complex lighting scenarios, including caustics and dispersion effects, with high efficiency.
- Redshift: A GPU-accelerated renderer that stands out for its rendering speed without compromising quality. It features out-of-core geometry and textures, allowing for the rendering of scenes larger than the available VRAM. Redshift also supports volumetric rendering for atmospheric effects.
- Octane Render: Known for its real-time rendering capabilities, Octane Render utilizes the GPU to achieve impressive speeds. It offers a deep pixel rendering feature, which captures detailed lighting and material information for complex compositing tasks.
- V-Ray: Provides a comprehensive suite of lighting, shading, and rendering tools for creating photorealistic imagery and animations. V-Ray\"s adaptive lights algorithm speeds up rendering in scenes with multiple light sources, making it efficient for complex indoor scenes.
- Corona Renderer: Focuses on ease of use and realism, offering an interactive rendering mode that updates the scene in real time. It includes advanced materials and lights, allowing for detailed and realistic renders with minimal setup.
These advanced features demonstrate the versatility and power of third-party render engines, providing Blender users with the tools to push the boundaries of 3D visualization. Whether working on architectural visualizations, animated films, or VFX, there\"s a render engine that fits the specific needs of any project.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Render Engine for Blender
Selecting the right render engine for your Blender projects involves weighing several important factors. Each engine offers distinct advantages, depending on your project\"s needs, workflow preferences, and the desired final output.
- Rendering Speed vs. Quality: Consider whether your priority is speed for real-time previews and animation (Eevee) or high-quality, photorealistic images (Cycles).
- Project Requirements: Assess the engine\"s suitability based on the project\"s complexity, such as the need for accurate lighting, materials, and textures.
- Hardware Capabilities: Determine if the engine leverages CPU, GPU, or both. GPU renderers like Redshift may deliver faster results but require a compatible graphics card.
- Feature Set: Look for specific features that are crucial for your work, such as volumetric rendering, particle systems, or advanced material options.
- Workflow Integration: Consider how well the engine integrates with Blender\"s workflow and whether it supports features like real-time viewport rendering.
- Community and Support: The availability of tutorials, forums, and user communities can be invaluable for troubleshooting and learning.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of third-party engines, which may require licenses, against the benefits they bring to your projects.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a render engine that best matches your creative goals, technical requirements, and budget, ensuring a smooth and efficient production process.
Impact of Render Engines on Workflow and Project Outcome
The choice of render engine significantly influences both the workflow of 3D artists and the outcome of projects. Each render engine integrated into Blender comes with its set of features, impacting the creative process and the final visual quality.
- Workflow Efficiency: Real-time render engines like Eevee can drastically reduce iteration times, allowing for immediate feedback and quicker decision-making. This is invaluable in fast-paced environments where time is of the essence.
- Visual Quality: Engines such as Cycles, known for their path-tracing capabilities, can achieve photorealistic results, enhancing the visual impact of projects. The choice of engine directly affects the realism and aesthetic appeal of the final render.
- Resource Management: The engine\"s hardware requirements can influence your workflow, with GPU-based engines offering speed but demanding significant GPU resources, whereas CPU-based rendering might be slower but more universally accessible.
- Feature Accessibility: Certain engines provide unique features (e.g., advanced material properties, volumetric effects) that can be crucial for achieving specific visual styles or effects, impacting the project\"s creative direction.
- Project Scope and Scale: The scalability of the render engine in handling large scenes or complex simulations without compromising performance is critical for large-scale projects, influencing timelines and project feasibility.
Ultimately, the impact of a render engine on Blender workflows and project outcomes is profound, affecting everything from the speed of production to the fidelity of the final images. By carefully selecting an engine that aligns with project requirements and team capabilities, artists can optimize their creative workflow and achieve their vision with greater efficiency and impact.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Different Render Engines
The application of Blender\"s render engines in real-world projects showcases their versatility and power. Below are case studies highlighting how different render engines have been utilized in various industries to achieve remarkable results.
- Architectural Visualization with Cycles: Architects and designers frequently use Cycles for its photorealistic lighting and material simulation, bringing architectural models to life with stunning realism and detail.
- Animation Production with Eevee: Animation studios leverage Eevee\"s real-time rendering capabilities to speed up the animation process, allowing for rapid iterations and previews, significantly reducing production times while still delivering high-quality visuals.
- Product Design with LuxCoreRender: Product designers opt for LuxCoreRender for its unbiased rendering qualities, capturing intricate details and realistic material properties, ideal for showcasing new product concepts.
- VFX and Cinematics with Redshift: The film and gaming industries utilize Redshift for its ability to handle complex shading networks and massive datasets efficiently, producing breathtaking visual effects and cinematics.
- Interior Design with Corona Renderer: Interior designers prefer Corona Renderer for its ease of use and realistic lighting simulation, enabling the creation of inviting and lifelike interior scenes.
These case studies illustrate the critical role render engines play in transforming creative concepts into vivid visual experiences across a broad spectrum of disciplines. By selecting the appropriate engine, professionals can optimize their workflows, achieve desired aesthetic goals, and push the boundaries of digital visualization.
_HOOK_
Future Trends in Blender Rendering Technologies
The landscape of Blender rendering technologies is continually evolving, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and user needs. The future promises even more dynamic changes, shaping how artists and designers create and render 3D content. Here are some emerging trends:
- Increased Real-time Rendering Capabilities: As hardware becomes more powerful, real-time rendering engines like Eevee are expected to offer quality closer to traditional ray-tracing, enabling more instantaneous feedback and interactive design processes.
- Greater Integration with AI and Machine Learning: AI technologies are set to enhance rendering workflows, offering smarter denoising, automatic optimization of scenes, and perhaps even stylistic adaptations of renders.
- Cloud-based Rendering Solutions: With the rise of cloud computing, more artists will likely leverage cloud-based rendering to access greater computational power, reducing the reliance on local hardware and accelerating project timelines.
- Advancements in Photorealism: Third-party engines and Cycles will continue to push the boundaries of photorealism, benefiting from research in light simulation and material science to produce even more lifelike images and animations.
- Expanded Support for VR and AR: Rendering technologies will evolve to better support VR and AR content creation, offering tools and features designed to streamline the production of immersive experiences.
These trends indicate a future where rendering in Blender becomes faster, more intuitive, and capable of producing even more stunning visuals. As technology progresses, Blender\"s rendering engines will likely offer unprecedented possibilities for creativity and innovation in 3D visualization.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Render Engine for Your Needs
Choosing the right render engine in Blender is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of your projects. Each engine, whether built-in like Cycles and Eevee or third-party options such as LuxCoreRender and Redshift, brings its strengths to the table. The best choice depends on a variety of factors, including the project\"s requirements, desired visual quality, and available hardware.
- Analyze Your Project Needs: Consider the complexity of your scenes, the level of realism required, and your timeline. Eevee might be perfect for quick previews and animations, while Cycles offers unparalleled realism for final renders.
- Consider Your Hardware: Your choice may be influenced by whether you have a powerful GPU, as some engines perform better with specific hardware configurations.
- Experiment and Evaluate: Don\"t hesitate to test different engines on parts of your project to see firsthand how they perform and what kind of results they deliver.
- Community and Support: The availability of resources, tutorials, and community support can also be a deciding factor, especially for complex projects or when learning a new engine.
In conclusion, the \"best\" render engine is the one that aligns most closely with your project goals, workflow preferences, and the final look you want to achieve. Blender\"s versatility in supporting multiple render engines ensures that there is always an option that fits your needs, empowering you to bring your creative visions to life with stunning results.
Embrace the power of Blender render engines to transform your creative visions into breathtaking realities. Explore, choose wisely, and leverage these engines to push the boundaries of digital art and visualization.