Topic how to increase render distance in blender: Discover how to enhance your Blender projects by increasing render distance, a crucial technique for artists seeking to expand their visual horizons and push the limits of their creative work.
Table of Content
- Adjusting Render Distance
- Render Performance Optimization
- Advanced Techniques
- How can I increase render distance in Blender?
- YOUTUBE: 4K Blender Tutorial: How to Increase Draw Distance
- Render Performance Optimization
- Advanced Techniques
- Advanced Techniques
- Understanding Render Distance in Blender
- Adjusting Render Distance Settings
- Optimizing Blender Settings for Increased Render Distance
- Advanced Techniques for Render Distance Enhancement
- Utilizing Lighting and Shadows for Better Distance Rendering
- Geometry and Particles Optimization for Extended Render Distance
- Performance Tips for Smooth Rendering at Long Distances
- Common Questions and Solutions for Render Distance Issues
- Case Studies: Improving Render Distance in Blender Projects
- Future Developments in Blender for Render Distance
Adjusting Render Distance
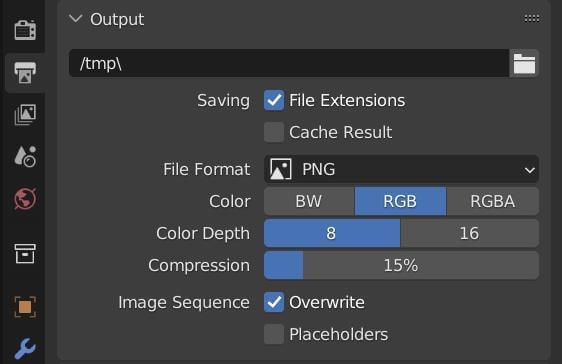
To adjust the render distance in Blender, navigate to the Render tab and locate the Distance option. By default, it is set to Auto, allowing Blender to determine the optimal render distance. You can manually set this to a specific value to control the visibility range of objects in your scene.
Related Tips
- Use the Ruler/Protractor tool to measure distances within your scene for precise adjustments.
- Lower game graphics settings or increase video card memory to improve render distance in game environments.
READ MORE:
Render Performance Optimization
Optimizing render performance while adjusting render distance can help maintain a balance between quality and efficiency.
Lighting and Bounces
- Disabling unnecessary caustics through the light paths section in render settings can save render time.
- Adjusting the number of light bounces can reduce calculations. Experiment with reducing the default settings by half for better performance.
Geometry and Particles
- Optimizing geometry by using instances and reducing complexity can enhance render performance.
- Limiting particle effects and utilizing vertex groups for efficient distribution can prevent performance issues.

Advanced Techniques
Blender offers advanced settings for fine-tuning render performance and quality, including adaptive sampling, denoising, and light path adjustments. Exploring these options can provide significant improvements to render distance visibility and overall scene quality.
| Feature | Description | Impact on Render |
| Adaptive Sampling | Adjusts sample counts based on noise levels, improving render times. | Reduces time by 10-30% |
| Denoising | Removes noise from renders, offering options for real-time and post-processing denoising. | Enhances image clarity |
| Light Path Settings | Controls the number of bounces for light rays, affecting scene realism and render time. | Balance between realism and efficiency |
Experimenting with these settings can help find the optimal balance for your specific project needs, enhancing render distance and scene quality in Blender.
How can I increase render distance in Blender?
To increase render distance in Blender, you can adjust the clipping distance settings of the camera. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Press \'n\' to open the properties panel.
- Go to the \'View\' tab.
- Locate the \'Clip Start\' and \'Clip End\' settings.
- Adjust the values of \'Clip Start\' and \'Clip End\' to increase the render distance.
- By increasing these values, you will extend the range at which geometry is visible to the camera during rendering.
By following these steps, you can effectively increase the render distance in Blender and adjust how far the camera can see the geometry in your scenes.
4K Blender Tutorial: How to Increase Draw Distance
Tutorial: Learn insider tips and tricks in this engaging tutorial video that will take your skills to the next level. Watch and master new techniques in a fun and educational way! Render: Immerse yourself in the world of stunning visual effects in this captivating render video. Explore the magic of digital artistry and witness how creativity comes to life on screen.
Blender How To Increase Render Distance
With the Blender How To Increase Render Distance, you will learn how to adjust the settings of your Blender software to increase ...
Render Performance Optimization
Optimizing render performance while adjusting render distance can help maintain a balance between quality and efficiency.
Lighting and Bounces
- Disabling unnecessary caustics through the light paths section in render settings can save render time.
- Adjusting the number of light bounces can reduce calculations. Experiment with reducing the default settings by half for better performance.
Geometry and Particles
- Optimizing geometry by using instances and reducing complexity can enhance render performance.
- Limiting particle effects and utilizing vertex groups for efficient distribution can prevent performance issues.

_HOOK_
Advanced Techniques
Blender offers advanced settings for fine-tuning render performance and quality, including adaptive sampling, denoising, and light path adjustments. Exploring these options can provide significant improvements to render distance visibility and overall scene quality.
Experimenting with these settings can help find the optimal balance for your specific project needs, enhancing render distance and scene quality in Blender.

Advanced Techniques
Blender offers advanced settings for fine-tuning render performance and quality, including adaptive sampling, denoising, and light path adjustments. Exploring these options can provide significant improvements to render distance visibility and overall scene quality.
| Feature | Description | Impact on Render |
| Adaptive Sampling | Adjusts sample counts based on noise levels, improving render times. | Reduces time by 10-30% |
| Denoising | Removes noise from renders, offering options for real-time and post-processing denoising. | Enhances image clarity |
| Light Path Settings | Controls the number of bounces for light rays, affecting scene realism and render time. | Balance between realism and efficiency |
Experimenting with these settings can help find the optimal balance for your specific project needs, enhancing render distance and scene quality in Blender.