Topic blender camera animation tutorial: Unlock the secrets of dynamic 3D storytelling with our Blender Camera Animation Tutorial, designed to elevate your animations from good to breathtaking. Start your journey to mastery today!
Table of Content
- How to precisely animate cameras in Blender for desired behavior?
- Understanding Basic Camera Controls and Keyframing
- Advanced Camera Movement Techniques for Dynamic Animation
- Camera Tracking and Focus for Enhanced Visual Storytelling
- Creating Smooth Camera Movements for Product Visualization
- Animating Cameras for Explainer Videos and Animated Infographics
- Mastering 360-Degree Camera Animations in Blender
- YOUTUBE: Quick Smooth Camera Movements Tutorial in Blender
- Applying Constraints for More Complex Camera Animations
- Utilizing Blender\"s Graph Editor for Fine-Tuning Animations
- Integrating Camera Animation with Scene Composition
- Exporting Your Camera Animation for Final Production
How to precisely animate cameras in Blender for desired behavior?
To precisely animate cameras in Blender for desired behavior, you can follow these steps:
- Open Blender and make sure you have a camera in your scene. If not, you can add a camera by pressing Shift + A and selecting Camera from the menu.
- Select the camera by right-clicking on it in the 3D viewport.
- Go to the Timeline window or the Dope Sheet window. If you don\'t have either of these windows open, you can add them by clicking on the \"+\" icon at the top right corner of the main viewport and selecting the desired window type.
- In the Timeline or Dope Sheet window, set the current frame to the starting point of your camera animation.
- Press I while the camera is still selected to bring up the Insert Keyframe menu.
- Select Location, Rotation, and Scale to insert keyframes for the camera\'s position, rotation, and scale at the current frame.
- Move the current frame to the desired ending point of your camera animation.
- Adjust the position, rotation, and scale of the camera in the 3D viewport.
- Press I again to insert keyframes for the camera at the current frame.
- Repeat steps 7-9 for any additional keyframes you want to add.
- To preview your camera animation, go to the Timeline or Dope Sheet window and press Play or use the timeline scrubber to navigate through the animation.
By following these steps, you can precisely animate cameras in Blender and achieve the desired behavior for your camera movements.
READ MORE:
Understanding Basic Camera Controls and Keyframing
Mastering Blender\"s camera controls and keyframing is foundational for creating engaging 3D animations. This section will guide you through the essential steps to get started.
- Selecting and Positioning the Camera: Initially, learn how to select the camera object and maneuver it within your scene to achieve the desired viewpoint. Use the \"G\" key to grab and move, and the \"R\" key to rotate.
- Understanding Camera Properties: Familiarize yourself with the camera\"s properties panel. Here, you can adjust focal length, depth of field, and other settings that influence the visual output of your camera.
- Inserting Keyframes: Keyframes are crucial for animation. To create movement, you must insert keyframes at different points in your timeline for the camera\"s position and rotation. This is done by moving the camera to your desired location, then pressing \"I\" and selecting \"Location\", \"Rotation\", or \"LocRot\" if you wish to keyframe both at the same time.
- Animating the Camera: With keyframes set, play back your timeline to see the camera animate through the scene. Experiment with moving the keyframes closer or further apart to adjust the speed of the camera\"s movement.
- Using the Graph Editor: For more control over the animation, open the Graph Editor. Here you can refine the interpolation between keyframes, smoothing out or sharpening the camera\"s movement as needed.
By understanding these basic controls and mastering keyframing, you\"re well on your way to producing compelling camera animations in Blender. Remember, practice is key to developing your skills in 3D animation.

Advanced Camera Movement Techniques for Dynamic Animation
Enhance your Blender animations by mastering advanced camera movement techniques. This section delves into sophisticated methods to create cinematic and dynamic animations.
- Dolly Zoom: Create a dramatic effect by simultaneously zooming in with the camera lens while moving the camera away from the subject, or vice versa. This technique, also known as the Vertigo effect, adds tension and depth to your scenes.
- Camera Tracking: Keep your subject in focus while the camera moves around it. Use the \"Track To\" constraint to lock the camera\"s focus on a moving object, adding a professional touch to your animations.
- Path Animation: For smooth, curved camera movements, attach your camera to a path. Use a Bezier curve to define the camera\"s trajectory and animate its movement along the path for elegant, sweeping shots.
- Handheld Camera Effect: Add realism to your scenes with a handheld camera effect. Use slight, random movements to simulate the look of a camera being held, adding life and realism to your animations.
- Depth of Field: Manipulate the camera\"s depth of field settings to focus on the subject while blurring the background or foreground. This technique is key for directing viewers\" attention and creating a cinematic look.
Implementing these advanced techniques can significantly elevate the quality of your animations, making them more engaging and visually appealing. Experiment with these methods to discover the best ways to convey your creative vision through dynamic camera movements.
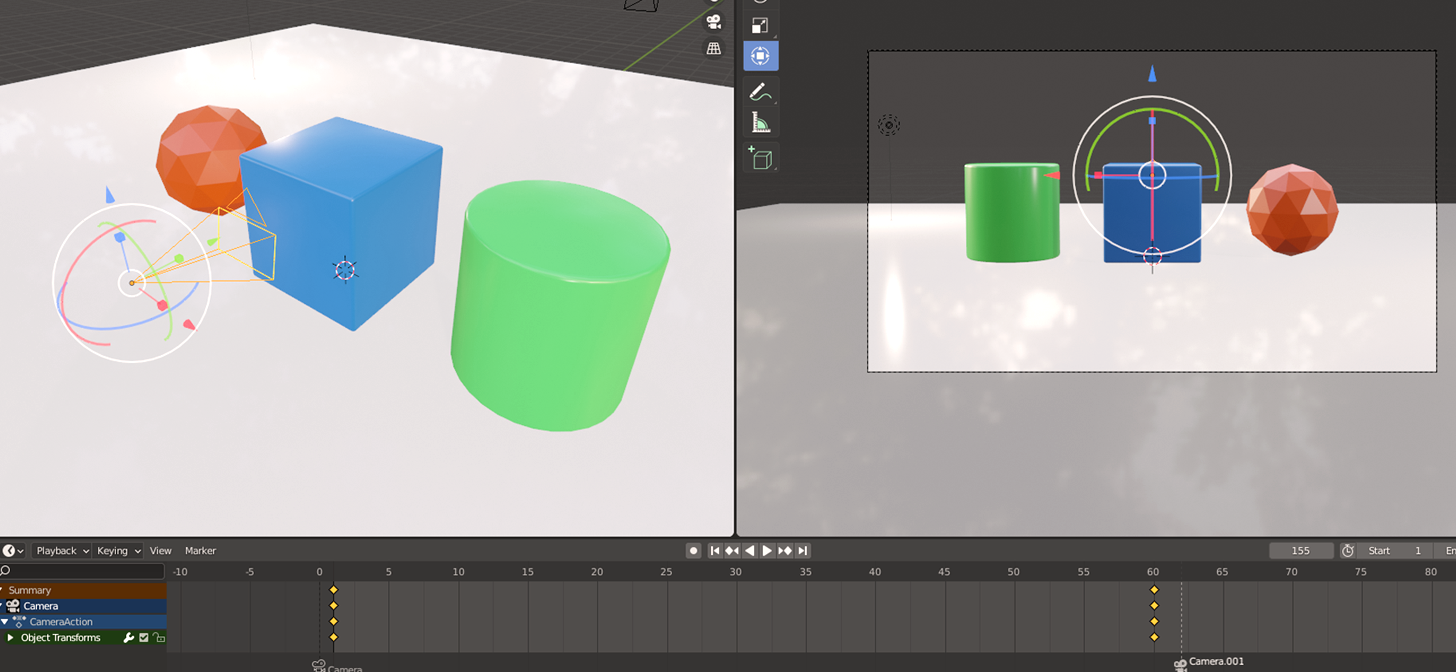
Camera Tracking and Focus for Enhanced Visual Storytelling
Utilizing camera tracking and focus effectively can transform your animations, adding depth and narrative power. This section covers techniques to enhance your storytelling through thoughtful camera work.
- Tracking Shots: To follow a character or object smoothly through a scene, use tracking shots. This involves moving the camera to keep the subject in the frame, creating a sense of motion and engagement.
- Focus Pull: A focus pull, or rack focus, shifts the viewer\"s attention from one subject to another by changing the focus point. This technique is great for highlighting details or changing narrative focus within a shot.
- Locking Focus: For scenes where the subject moves but you want it to remain sharply in focus, use a \"Track To\" constraint on the camera. This keeps the camera aimed at your subject, ensuring they remain in focus regardless of movement.
- Depth of Field (DoF): Adjust the depth of field to control the focus range within your scene. A shallow DoF can make a subject stand out by blurring the background and foreground, while a deep DoF keeps more of the scene in focus.
- Animating Focus: Animate the camera’s focus distance and DoF settings to dynamically change what is in focus throughout a shot. This can be used to guide the viewer’s eye or create interesting transitions.
By mastering these techniques, you can direct your audience\"s attention with precision, enhancing the storytelling impact of your animations. Experimentation and practice with these methods will lead to more engaging and visually compelling narratives.

Creating Smooth Camera Movements for Product Visualization
Smooth camera movements are crucial for showcasing products in their best light. This section provides step-by-step guidance to achieve professional-grade camera animations in Blender for product visualization.
- Plan Your Shots: Begin by planning your shots. Decide on the angles and movements that best showcase your product\"s features. Sketching a storyboard can be helpful.
- Set Up Your Scene: Ensure your product is properly modeled and textured. Lighting plays a significant role in product visualization, so set up your scene with appropriate lighting to highlight the product’s best features.
- Use a Curve Path: For smooth camera movements, consider attaching your camera to a curve path. This allows for fluid, consistent motion that can be easily controlled and adjusted for pacing.
- Adjust Camera Speed: The speed of your camera’s movement can significantly impact the viewer\"s perception of your product. Use the Graph Editor to fine-tune the speed, ensuring it is neither too fast to miss details nor too slow to lose viewer interest.
- Implement Depth of Field: Depth of field can draw attention to specific features of your product while softly blurring out the rest. This technique helps in creating a focal point and adds a professional touch to your visualizations.
- Preview and Refine: Preview your animations frequently. This step is crucial for making adjustments early on. Check for smoothness in movement and ensure that the camera paths align with your visualization goals.
- Rendering Settings: Finally, choose appropriate rendering settings to achieve high-quality visuals. Consider rendering in higher resolutions with sufficient samples to ensure your product looks its best.
By following these steps, you can create smooth and appealing camera movements that enhance your product visualizations, making them more engaging and visually striking to your audience.

_HOOK_
Animating Cameras for Explainer Videos and Animated Infographics
Camera animation plays a pivotal role in creating engaging explainer videos and animated infographics. This section guides you through techniques to make your visual stories more dynamic and informative.
- Storyboard Your Concept: Start with a clear storyboard. This will guide the camera movements and ensure they contribute effectively to the narrative, highlighting key points and data.
- Employ Dynamic Camera Moves: Use pans, zooms, and tilts to guide the viewer\"s attention. Dynamic moves can emphasize important information or transition between topics smoothly.
- Focus on Composition: Pay attention to composition in each shot. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing can all be used to make each frame as informative and visually appealing as possible.
- Integrate Camera Tracking: Tracking movements can follow an object or highlight a pathway through an infographic, making complex information easier to digest.
- Utilize Depth of Field: Use depth of field to blur out less important elements, focusing the viewer’s attention on the key parts of your explainer video or infographic.
- Experiment with Angles: Different angles can evoke different emotions or highlight aspects of your information in unique ways. Don\"t be afraid to experiment with high, low, or angled shots to find what works best for your story.
- Synchronize with Your Audio: For explainer videos, synchronize your camera movements with voiceover or music. This can enhance the impact of your message and keep viewers engaged.
By mastering these camera animation techniques, you can create explainer videos and animated infographics that are not only visually captivating but also effectively communicate your message.

Mastering 360-Degree Camera Animations in Blender
Creating 360-degree camera animations in Blender opens up new vistas for showcasing environments, products, or scenes in a comprehensive and immersive way. Follow these steps to master this technique.
- Setup Your Scene: Ensure your 3D model or scene is fully prepared before starting the camera animation process. This includes textures, lighting, and any environmental effects.
- Create a Camera Path: Use a Bezier circle to define the path around your object or scene. This acts as a track for the camera to move along, ensuring a smooth 360-degree rotation.
- Attach Camera to Path: Select your camera, then shift-select the path. Use Ctrl+P to parent the camera to the path, choosing the \"Follow Path\" option to make the camera follow the curve automatically.
- Adjust Camera Orientation: To ensure your camera is always pointing towards the center of your scene or object, apply a \"Track To\" constraint to the camera. Set your target as the central object or an Empty placed at your scene\"s center.
- Animate the Path: With the camera attached to the path, animate the camera\"s movement around the path using keyframes on the path\"s evaluation time or offset factor in the \"Follow Path\" constraint settings.
- Refine Movement: Use the Graph Editor to adjust the animation curve, ensuring a consistent speed throughout the animation or adding ease-in and ease-out effects for a more dynamic presentation.
- Preview and Render: Regularly preview your animation by scrubbing through the timeline or using the playback feature. Once satisfied, adjust your render settings for a 360-degree view and render your animation.
This approach to 360-degree camera animation in Blender can dramatically enhance your presentations, allowing viewers to fully engage with your digital environment or product from every angle.
Quick Smooth Camera Movements Tutorial in Blender
If you\'re looking for a comprehensive and easy-to-follow tutorial, this video is just for you! Learn step-by-step instructions and valuable tips on the topic at hand and enhance your skills in no time. Don\'t miss out on this educational and enlightening video!
3 Killer Blender Camera Tricks for Animations
Discover some brilliant tricks that will revolutionize the way you approach the subject. This video is packed with little-known hacks and clever shortcuts that will amaze you. Prepare to be blown away as you witness these innovative tricks! Watch now and unlock a world of possibilities.
Applying Constraints for More Complex Camera Animations
Blender\"s constraint system offers powerful tools for creating more complex and dynamic camera animations. This section walks you through the steps to leverage constraints for enhancing your camera work.
- Track To Constraint: Use the \"Track To\" constraint to make the camera automatically point towards a target object. This is ideal for focus pulls or ensuring the subject remains in frame during movement.
- Follow Path Constraint: Attach your camera to a path with the \"Follow Path\" constraint for smooth, predefined movements. This can be used for intricate camera paths that are difficult to achieve manually.
- Limit Location and Rotation: Apply \"Limit Location\" and \"Limit Rotation\" constraints to restrict the camera\"s movement and rotation. This is useful for simulating real-world camera operation limits.
- Camera Rigging: Create a camera rig using multiple constraints for advanced control. For example, a rig can allow for simultaneous tracking, dollying, and crane movements.
- Damped Track Constraint: For a more subtle effect than \"Track To\", use \"Damped Track\" to point the camera towards a target. This allows for smoother transitions in focus.
- Locking Camera to a Character: For animations involving characters, use constraints to lock the camera\"s focus to the character as they move through the scene, ensuring they always remain in view.
By mastering these constraint-based techniques, you can create sophisticated camera animations that bring your Blender projects to life. Experiment with different constraints to discover new creative possibilities for your animations.

Utilizing Blender\"s Graph Editor for Fine-Tuning Animations
The Graph Editor in Blender is a powerful tool for fine-tuning animations, offering precise control over the interpolation and timing of keyframes. This section guides you through its effective use to enhance your camera animations.
- Accessing the Graph Editor: Switch to the Animation screen layout and select the Graph Editor from the editor type menu. This displays the animation curves for the selected object.
- Understanding F-Curves: Each animated property has its own F-Curve, representing the change in value over time. Analyze these curves to understand the motion\"s dynamics.
- Adjusting Keyframes: Move keyframes within the Graph Editor to adjust the timing of animations. This can help in synchronizing camera movements with other elements in the scene.
- Modifying Interpolation: Change the interpolation type between keyframes by selecting them and pressing T. Choose from options like Linear, Bezier, or Constant to change how values transition.
- Editing Handles: For Bezier interpolation, manipulate the handles of each keyframe to adjust the easing in and out of camera movements. This can make transitions smoother or more dynamic.
- Adding Modifiers: Use the Add Modifier menu to apply non-destructive transformations to F-Curves, such as noise, cycles, or limits. This is useful for creating complex, repetitive, or random movements without manual keyframing.
- Preview and Refine: Regularly preview your animation by playing it back in the viewport. Use the Graph Editor in conjunction with the Dope Sheet to ensure precise timing and smooth motion.
Mastering the Graph Editor enables animators to fine-tune animations with a level of precision and creativity that is not possible through the Timeline or Dope Sheet alone. Spend time experimenting with its features to fully leverage its potential in your projects.
Integrating Camera Animation with Scene Composition
Integrating camera animation with scene composition is crucial for creating visually compelling and narrative-driven animations. This section explores how to harmonize camera movements with the elements of your scene for maximum impact.
- Visual Storytelling: Start with a clear narrative or message. Use camera movements to guide the viewer\"s eye and emphasize key components of your story, ensuring that each shot contributes to the overall narrative.
- Planning Your Shots: Before animating, plan your shots carefully. Consider the angle, composition, and movement of the camera in relation to the scene elements. Storyboards and pre-visualization can be invaluable tools here.
- Rule of Thirds: Apply the rule of thirds to frame your shots. Positioning important elements along these lines or their intersections can create more engaging and balanced compositions.
- Depth and Layering: Use camera movements to reveal depth and layers in your scene. Dolly or track shots can unveil foreground, midground, and background elements sequentially, adding depth to your story.
- Focus and Depth of Field: Manipulate focus and depth of field in tandem with camera movement. This can highlight important scene elements or shift attention smoothly between subjects.
- Motion and Emotion: The speed and smoothness of camera movements can evoke emotions. Slow, smooth pans can create a calm, reflective atmosphere, while quick, sharp movements can build tension or excitement.
- Continuity: Ensure continuity between shots. Camera movements should flow naturally from one scene to the next, maintaining spatial and narrative coherence.
By carefully integrating camera animation with scene composition, you can create more dynamic and emotionally resonant animations. This approach not only enhances the visual appeal of your work but also deepens the viewer\"s engagement with your narrative.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Exporting Your Camera Animation for Final Production
Finalizing and exporting your camera animation in Blender is a crucial step towards integrating it into your final project. This section outlines the process to ensure your animation is ready for final production.
- Final Checks: Review your animation thoroughly. Check for any visual glitches, ensure all movements are smooth, and confirm that the timing aligns with your project\"s requirements.
- Resolution and Frame Rate: Set your output resolution and frame rate according to your project\"s standards. Higher resolutions are preferable for detailed visuals, while the frame rate should match the medium where it will be displayed.
- Rendering Settings: Adjust your rendering settings for optimal quality. Consider factors like sampling, light bounces, and shadow quality. Render a few test frames to ensure the settings meet your expectations.
- Output Format: Choose an appropriate output format for your animation. For editing in video software, formats like AVI or MOV are recommended. For web use, consider exporting as an MP4 or WebM.
- Batch Rendering: For longer animations, consider using batch rendering to minimize the risk of interruptions. This can be done by rendering your animation in segments or by using cloud rendering services.
- Post-Production: After rendering, your animation may require post-production work. This includes color correction, compositing, and adding any final effects in video editing software.
- Export and Integration: Once post-production is complete, export your final animation. Ensure it\"s in the correct format and resolution for its final use, whether it be film, television, web, or interactive media.
By following these steps, you can ensure your Blender camera animation is polished and ready for incorporation into your final production, helping to bring your creative vision to life.
Embark on a journey to master Blender camera animations with our comprehensive guide. Unlock the full potential of your 3D projects, bringing your visions to life with dynamic and captivating animations that engage and inspire viewers.