Topic blender character animation tutorial: Dive into the world of 3D animation with our Blender Character Animation Tutorial, designed to guide beginners and intermediates through the exciting process of bringing characters to life. Start your creative journey today!
Table of Content
- What are some tutorials for character animation in Blender?
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface and Setup
- Beginning with Blender Animation: Key Principles and Simple Projects
- Rigging Your Character: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Animating Your Character: From Basic Movements to Complex Actions
- Advanced Techniques: Facial Animation and Lip Syncing
- Working with Physics and Simulation in Animation
- YOUTUBE: Master Animation in 25 Minutes with Blender Tutorial
- Lighting and Rendering Your Animated Scene
- Utilizing Blender\"s Graph Editor for Precise Animation Control
- Animation Tips and Tricks: Enhancing Realism and Expression
- Learning Resources: Where to Find Further Guidance and Inspiration
What are some tutorials for character animation in Blender?
There are several tutorials available for character animation in Blender. Here are some options:
- Blender Character Animation Tutorial: This YouTube tutorial provides a step-by-step guide on how to animate a character in Blender. It covers topics such as rigging, posing, and keyframe animation.
- Character Animation in Blender: Introduction and Rigging: In this tutorial, you will learn the basics of character animation in Blender. It includes an introduction to rigging and demonstrates how to create a simple rig for your character.
- Get started with Character Animation in Blender: This tutorial offers a more in-depth approach to character animation in Blender. It covers rigging, animation techniques, and advanced topics such as facial animation and lip syncing. The tutorial is available on Gumroad.
- Blender Tutorial Archives: The official Blender website provides a collection of tutorial archives that cover various aspects of animation, including character animation. You can find step-by-step guides and video tutorials to help you learn and improve your character animation skills.
These tutorials should give you a good starting point to learn character animation in Blender. Remember to practice and experiment with different techniques to enhance your skills.
READ MORE:
Understanding Blender\"s Interface and Setup
Blender\"s interface might seem daunting at first, but it\"s designed to streamline the animation process. This section will help you get comfortable with the layout and basic functionalities to kickstart your character animation projects.
- Workspace Overview: Blender\"s default screen is divided into several editors, like the 3D Viewport, Timeline, and Outliner. Familiarize yourself with these areas as they are essential for animation.
- Customizing the Interface: Learn how to adjust the interface to suit your workflow. Blender allows you to resize, split, and join windows to create a personalized workspace.
- Navigating the 3D Viewport: Mastering viewport navigation is crucial. Practice zooming, panning, and rotating the view to examine your scene from any angle.
- Object Mode and Edit Mode: Understand the difference between these two primary modes. Object Mode is for positioning and transforming whole objects, while Edit Mode lets you modify the individual vertices, edges, and faces of a mesh.
- Using the Properties Panel: The Properties Panel is where you\"ll find options for modifying object properties, material settings, and physics simulations. It\"s a critical area for adding detail and realism to your animations.
- Introduction to Keyframes: Keyframes are the backbone of animation in Blender. Learn how to insert them in the Timeline to define the start and end points of your animation.
As you become more familiar with Blender\"s interface and tools, you\"ll find that what once seemed complex becomes second nature. The key is to practice regularly and not be afraid to experiment with different features to see what they do.

Beginning with Blender Animation: Key Principles and Simple Projects
Starting your journey into Blender animation requires understanding its key principles. This section introduces fundamental concepts and guides you through simple projects to build your skills.
- Understanding Animation Basics: Animation in Blender involves creating a sequence of frames that simulate motion. Learn about keyframes, interpolation, and timing to start animating.
- Simple Animation Project - The Bouncing Ball: Begin with a classic animation exercise. Animate a bouncing ball to grasp the basics of movement, squash and stretch, and anticipation.
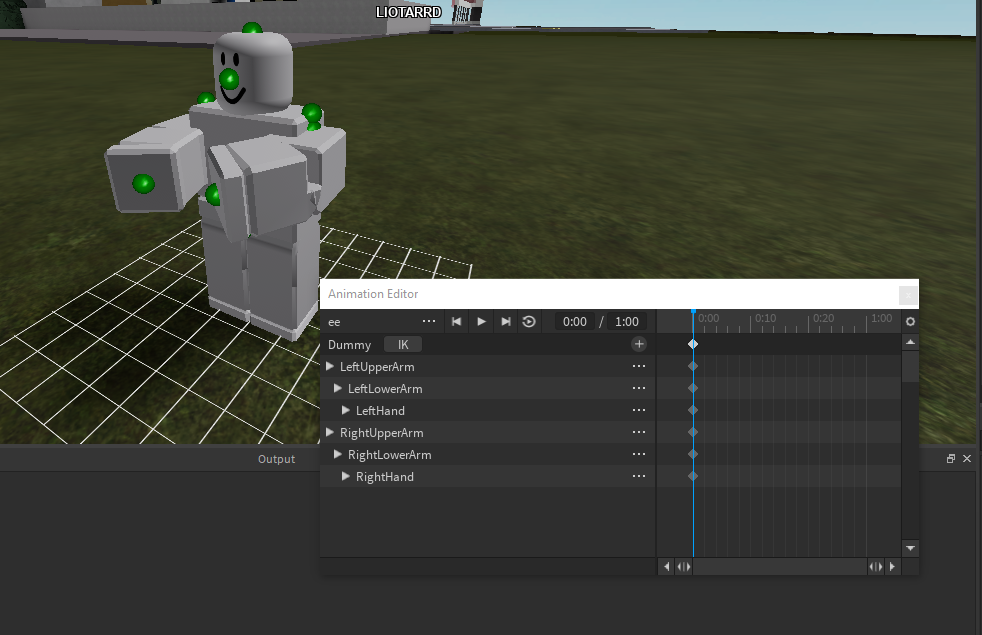
- Rigging Your First Character: Rigging is preparing your model for animation. Start with a simple character rig to understand bone creation, parenting, and automatic weights.
- Walk Cycle Fundamentals: A walk cycle is a crucial skill in character animation. Practice by animating a basic walk cycle, focusing on leg and arm movements to create believable motion.
- Facial Expressions and Lip Sync: Learn to animate facial expressions using shape keys for emotion and mouth movements for speech, starting with simple phrases or emotions.
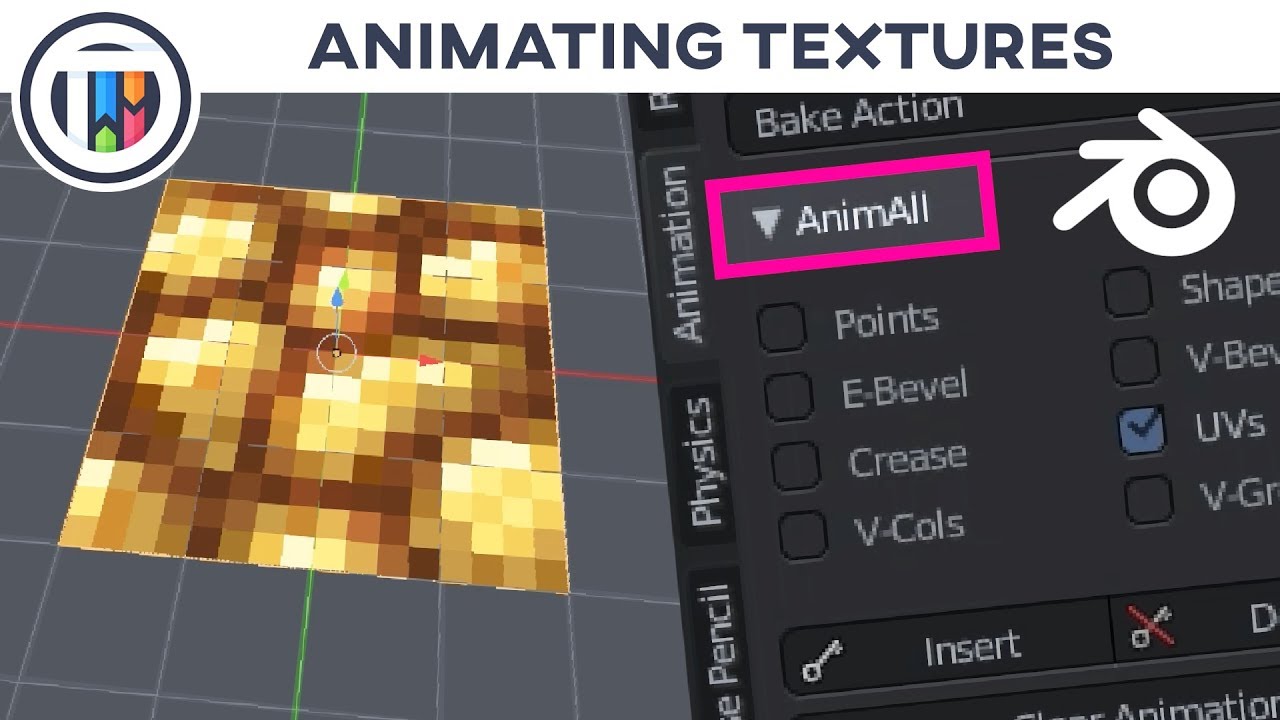
- Utilizing the Graph Editor: The Graph Editor is a powerful tool for refining animations. Understand how to use it to smooth out motions and add nuances to your animations.
These initial steps are designed to build a solid foundation in Blender animation. By starting small and gradually increasing complexity, you\"ll develop the skills and confidence to tackle more advanced projects.

Rigging Your Character: A Step-by-Step Guide
Rigging is the process of creating a skeleton for your character so it can move. This guide breaks down the rigging process in Blender, ensuring you can animate your characters effectively.
- Preparing Your Model: Before rigging, ensure your character model is complete. This means the mesh is closed, and there are no unnecessary vertices.
- Creating the Armature: Armature is Blender’s term for a skeleton. Start by adding bones to your model, beginning with the main parts like the spine, then arms and legs. Each bone controls a part of the model.
- Positioning Bones: Position bones accurately inside your model. This step is crucial for natural movement. Use front, side, and top views for precise placement.
- Editing Bones: In Edit Mode, adjust the length and orientation of the bones to match your character\"s anatomy. Parent bones where necessary, such as making the arm bones children of the spine bone.
- Automatic Weights: With your armature in place, parent your mesh to the armature using the \"With Automatic Weights\" option. Blender will attempt to calculate how much each bone influences parts of the mesh.
- Weight Painting: After automatic weighting, some areas may not deform as expected. Use Weight Painting to manually adjust the influence of each bone over the mesh.
- Adding Inverse Kinematics (IK): IK simplifies the animation process by allowing you to move a chain of bones by manipulating only the last bone in the chain. This is particularly useful for limbs.
- Testing the Rig: Pose your character in various positions to test the rig. Adjust weights and bone constraints as needed to ensure natural movement.
Rigging is a meticulous process that requires patience and practice. Once mastered, it provides a strong foundation for character animation, allowing for more expressive and dynamic movements.

Animating Your Character: From Basic Movements to Complex Actions
Once your character is rigged, the next step is to bring it to life through animation. This section covers the essentials of character animation, from basic movements to more complex actions, ensuring your characters move believably and expressively.
- Starting with Simple Actions: Begin by animating simple actions like walking or waving. Focus on the key poses that define the action, known as \"keyframes\". This helps in understanding timing and spacing.
- Animating a Walk Cycle: A walk cycle is a fundamental exercise in character animation. It involves creating a loopable sequence where the character takes a step with each foot. Pay attention to the cycle\"s phases: contact, down, passing, and up.
- Adding Secondary Actions: Secondary actions, such as a character looking around or adjusting their clothing while walking, add realism and depth. Integrate these after the primary action is smooth and believable.
- Facial Expressions and Lip Sync: Use shape keys (also known as blend shapes) to animate facial expressions. For lip-syncing, match mouth shapes (phonemes) to the audio to make your character speak naturally.
- Working with the Graph Editor: Use the Graph Editor to refine animations. Adjusting the curves allows for smoother transitions between keyframes and can help fix any mechanical movements.
- Incorporating Physics and Simulations: Blender\"s physics engine can add realism to your animations. Use cloth simulation for dynamic clothing movement, or rigid body physics for interactions between objects.
- Complex Actions and Interaction: For more complex actions, like a character picking up an object, ensure your character\"s movements are coordinated with the object. Parenting and constraints can be used for interaction.
- Final Touches: Review your animation for any sliding, popping, or unnatural movements. Adding details like eye blinks or breathing can greatly enhance believability.
Character animation is a blend of art and science. Through practice and experimentation, you\"ll develop a keen eye for movement and timing, enabling you to produce engaging and lifelike animations.

_HOOK_
Advanced Techniques: Facial Animation and Lip Syncing
Creating convincing facial animations and syncing lip movements to speech are advanced skills that can significantly enhance character believability. This section explores techniques to master these complex aspects of character animation in Blender.
- Understanding Morph Targets (Shape Keys): Learn how to use Blender\"s shape keys to create facial expressions. Shape keys allow for the deformation of mesh into different poses, essential for animating mouth movements, blinks, and other facial expressions.
- Creating a Phoneme Set: For lip-syncing, develop a set of key mouth shapes (phonemes) that correspond to different sounds. This library of shapes can be mixed and matched to produce accurate lip movements in sync with dialogue.
- Rigging for Facial Animation: Besides shape keys, facial rigs can include bones for jaw movement, eyebrow raising, and other subtle facial motions. Combining bone rigs with shape keys offers a versatile approach to facial animation.
- Animating Eye Movements: Eyes are the window to the soul and play a crucial role in conveying emotion. Learn techniques for animating eye direction and blinks to add life to your characters.
- Syncing Dialogue: Use Blender\"s audio features to import voice tracks. Then, animate your character\"s mouth shapes to match the dialogue, adjusting timing to ensure synchronization with the audio.
- Using Drivers for Automation: Drivers can automate aspects of facial animation, such as making the eyelids follow the eyes\" vertical movement. This reduces manual keyframing and creates more natural animations.
- Expression Mixing: To achieve nuanced expressions, blend multiple shape keys. This technique allows for a wide range of emotions and reactions, making your characters more expressive and dynamic.
- Practicing with Lip Sync Tools: Experiment with Blender add-ons and tools designed to facilitate lip-syncing, which can automate the matching of phonemes to audio files, speeding up the animation process.
Facial animation and lip-syncing are advanced skills that add depth and realism to character animation. Through careful observation, practice, and the use of Blender\"s powerful tools, animators can create expressive, lifelike characters.

Working with Physics and Simulation in Animation
Blender offers robust tools for incorporating physics and simulations into your animations, adding realism and complexity with relative ease. This section will guide you through the process of integrating dynamic simulations into your projects.
- Introduction to Physics Simulations: Understand Blender\"s physics engine capabilities, including rigid body dynamics, fluid simulations, cloth physics, and particle systems. Each system has its settings and applications for different effects.
- Creating Cloth Simulations: Learn how to apply cloth physics to objects. This is particularly useful for animating clothing on characters or flags waving in the wind. Explore settings like stiffness, damping, and collision to achieve realistic results.
- Rigid Body Dynamics: Rigid body simulation allows non-deforming objects to interact under the laws of physics. Use this for animations involving collisions, falling objects, and stacking.
- Fluid Dynamics for Realistic Water and Smoke: Fluid simulations can create realistic water, smoke, and fire effects. Dive into the settings for viscosity, flow, and obstacles to craft convincing fluid animations.
- Working with Particle Systems: Particle systems can simulate complex phenomena like rain, snow, or even hair. Understand how to emit particles from objects, control their behavior, and use forces like wind or gravity.
- Soft Body Simulations: Soft body physics is perfect for animating deformable objects like jelly, balloons, or flesh. Adjust parameters such as pressure and bending to simulate soft materials accurately.
- Integrating Simulations with Animation: Learn how to integrate your physics simulations seamlessly with character animations. This might include making a character interact with a simulated environment or wearing dynamically simulated clothing.
- Optimizing Simulations for Performance: Simulations can be computationally intensive. Explore techniques for optimizing your scenes, such as baking simulations and reducing particle counts, to maintain a smooth workflow.
By mastering Blender\"s physics and simulation tools, you can add a layer of realism and dynamism to your animations that breathes life into your scenes. Practice with these systems will allow you to create more engaging and visually stunning animations.

Master Animation in 25 Minutes with Blender Tutorial
Animation: Get ready to be mesmerized by this captivating video showcasing stunning animations that bring characters and stories to life. Be prepared to be amazed as you dive into an enchanting world of creativity and imagination!
Learn Rigging and Animation in Blender!
Rigging: Dive into the fascinating world of rigging in this awe-inspiring video. Witness the expertise and precision involved in creating realistic movements for characters and objects, as talented artists unleash their skills to make the impossible seem effortlessly achievable.
Lighting and Rendering Your Animated Scene
Lighting and rendering are crucial for bringing your animated scenes to life, adding depth, mood, and realism. This section explores how to effectively light your scenes and render them in Blender to achieve professional-quality results.
- Understanding Blender\"s Lighting System: Get familiar with Blender\"s lighting options, including point lights, spotlights, area lights, and sun lamps. Each light type offers different effects and uses, from soft diffused lighting to sharp, directed beams.
- Creating a Three-Point Lighting Setup: Learn the classic three-point lighting technique to add dimension and depth to your characters and scenes. This setup uses key light, fill light, and back light to highlight forms and minimize harsh shadows.
- Exploring HDRIs for Environmental Lighting: High Dynamic Range Images (HDRIs) can provide realistic environmental lighting with minimal setup. Discover how to use HDRIs to simulate outdoor or studio lighting conditions.
- Adjusting Materials and Textures: Lighting interacts with the materials and textures of your objects. Experiment with Blender\"s material settings to ensure your objects reflect, absorb, or diffuse light in realistic ways.
- Utilizing Blender\"s Render Engines: Compare Blender\"s render engines—Cycles and Eevee. Cycles offers physically-based rendering for photorealistic results, while Eevee is a real-time engine suitable for faster previews.
- Rendering Settings for Animation: Adjust rendering settings to balance quality and render time. Explore settings like sampling, resolution, and motion blur to enhance the final output without excessive rendering times.
- Post-Processing Effects: Use Blender\"s Compositor for post-processing effects. Enhance your rendered animation with color correction, glare, and bloom effects to add the finishing touches.
- Exporting Your Animation: Learn the best formats and settings for exporting your animation for various platforms, ensuring the highest quality playback on web, mobile, or broadcast.
By carefully planning your lighting and rendering, you can dramatically improve the visual impact of your animations. These steps provide a foundation for creating visually stunning scenes that captivate your audience.

Utilizing Blender\"s Graph Editor for Precise Animation Control
The Graph Editor in Blender is a powerful tool for fine-tuning animations with precision. It allows animators to adjust the interpolation and timing of keyframes beyond the capabilities of the Timeline. Mastering the Graph Editor can significantly enhance the quality and realism of your animations.
- Introduction to the Graph Editor: Begin by understanding the layout of the Graph Editor. Learn how to navigate the graph, select keyframes, and manipulate the bezier handles for smooth transitions.
- Adjusting Keyframe Interpolation: Explore the different interpolation types (like linear, bezier, and constant) to control how animations transition between keyframes. This is crucial for creating natural movements.
- Editing F-Curves: F-Curves represent the animation\"s velocity over time for each property. Adjust these curves to refine the speed and timing of your animations, adding realism to movements.
- Using Handles for Fine Control: Manipulate the handles of each keyframe on the F-Curve to create custom easing in and out. This level of control is essential for achieving lifelike animations.
- Working with Keyframe Modifiers: Blender\"s Graph Editor allows you to apply modifiers to keyframes, such as noise, cycles, or limits. These can automate repetitive tasks and add complexity to animations.
- Ghosting Animation Paths: Use the motion paths feature to visualize the trajectory of moving objects. This helps in anticipating and refining movements throughout the animation.
- Locking and Muting Channels: Learn how to lock or mute specific animation channels to focus on animating one property at a time, preventing accidental changes to other aspects of the animation.
- Batch Editing Keyframes: Discover techniques for selecting and editing multiple keyframes simultaneously, which is invaluable for adjusting the timing and flow of complex animations.
By integrating the Graph Editor into your animation workflow, you can achieve a higher level of precision and control, resulting in smoother, more dynamic animations that capture the essence of your characters and scenes.

Animation Tips and Tricks: Enhancing Realism and Expression
Animating characters in a way that captures realism and expression is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. This section shares essential tips and tricks to elevate your Blender animations, making them more lifelike and engaging.
- Observation Is Key: Start by observing real-life movements and expressions. Notice the subtleties in how people move, interact, and express emotions. Integrating these observations into your animations adds authenticity.
- Overlapping Action: Real movement is rarely uniform. Incorporate overlapping action by offsetting movements of different parts of the body to create more dynamic and fluid animations.
- Squash and Stretch: These principles give elasticity to your animations, adding weight and volume as characters move. Use them judiciously to maintain the character’s volume consistency.
- Anticipation and Follow-Through: Before any significant movement, add a small anticipation to prepare the viewer. Similarly, follow-through lets parts of the body continue moving after the main action has stopped, adding realism.
- Secondary Actions: Add minor actions that complement the primary action, like a character blinking or adjusting their stance. These add layers and richness to the scene.
- Facial Expressions: Conveying emotions through facial expressions is crucial. Pay attention to the eyes and eyebrows, as they are key in expressing feelings.
- Eye Direction: The direction where a character is looking can say a lot about their thoughts and intentions. Use eye direction to guide the audience\"s attention and add depth to storytelling.
- Timing and Spacing: Adjust the timing and spacing of keyframes for variations in speed and rhythm. This can dramatically impact the energy and mood of your animation.
- Using Reference Footage: Don\"t hesitate to use reference footage for complex actions or to understand movement dynamics better. This can be a powerful tool in achieving realistic animations.
By applying these tips and continuously practicing, you can significantly enhance the realism and expression in your character animations, bringing your Blender projects to life with greater impact and emotional depth.

_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Learning Resources: Where to Find Further Guidance and Inspiration
Advancing your skills in Blender character animation requires continuous learning and inspiration. Below is a compilation of valuable resources that offer in-depth tutorials, tips, and artistic inspiration to enhance your animation journey.
- Blender Official Tutorials: Start with Blender\"s own resources. The Blender Foundation offers comprehensive tutorials and documentation for users of all levels on their official website and YouTube channel.
- Online Courses and Workshops: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and CG Cookie provide structured courses ranging from beginner to advanced levels. These courses often include project-based learning and community support.
- YouTube Channels: Many experienced animators and educators share their knowledge on YouTube. Channels like Blender Guru, CG Geek, and Darrin Lile offer tutorials that cover a wide range of topics, including character animation.
- Blender Community and Forums: Engage with the Blender community through forums like Blender Artists and the Blender subreddit. These platforms are great for getting feedback, asking questions, and seeing what others are creating.
- Animation Books and Guides: Books like \"The Animator\"s Survival Kit\" by Richard Williams provide fundamental animation principles that are applicable in Blender. While not software-specific, the concepts are invaluable.
- Artistic Inspiration: Websites like ArtStation and Behance showcase professional and amateur work alike. Browsing through these can spark new ideas and help refine your artistic direction.
- Blender Add-ons and Tools: Explore the variety of add-ons available for Blender that can streamline your animation workflow. Blender Market and Gumroad are good places to start looking.
- Animation Challenges and Contests: Participating in challenges like the 11 Second Club can provide practice opportunities and expose you to the work of other animators.
By exploring these resources, you can deepen your understanding of Blender, stay updated with the latest tools and techniques, and continually find new sources of inspiration for your animation projects.
Embark on your Blender character animation journey with confidence and creativity. Harness the power of Blender to bring your visions to life, transforming ideas into animated realities. Let this guide be your first step towards mastering the art of animation.