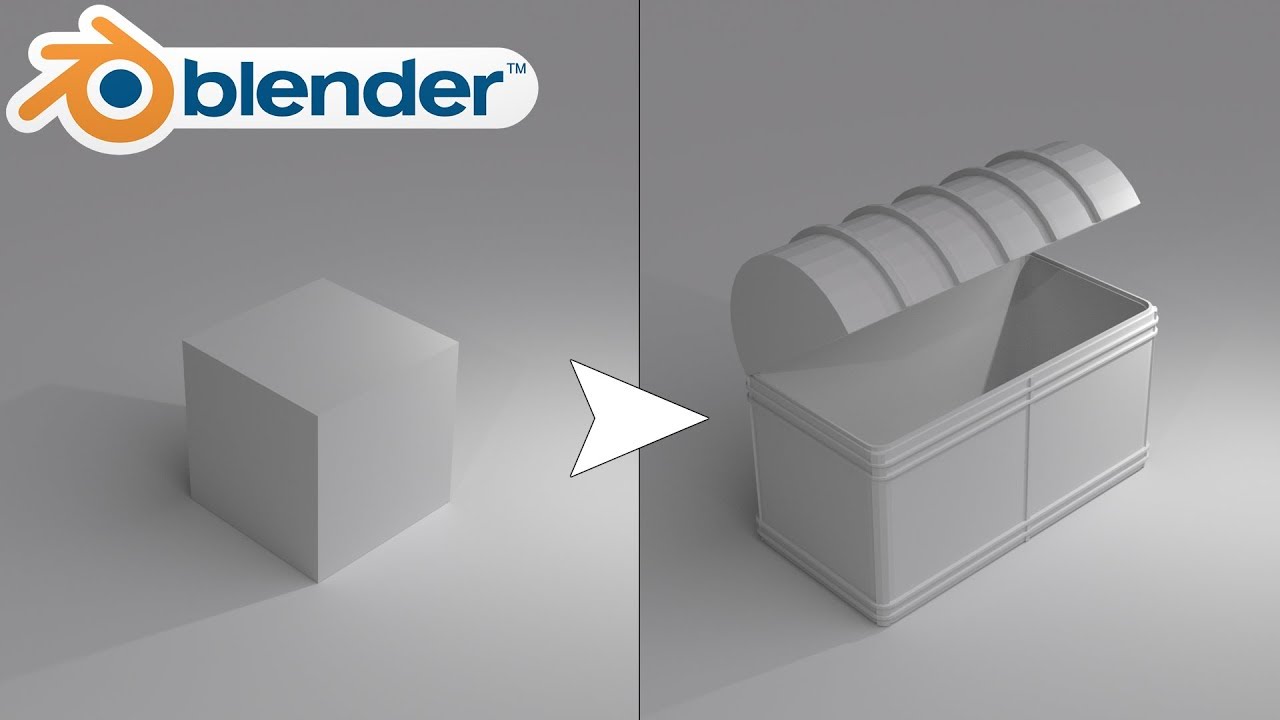
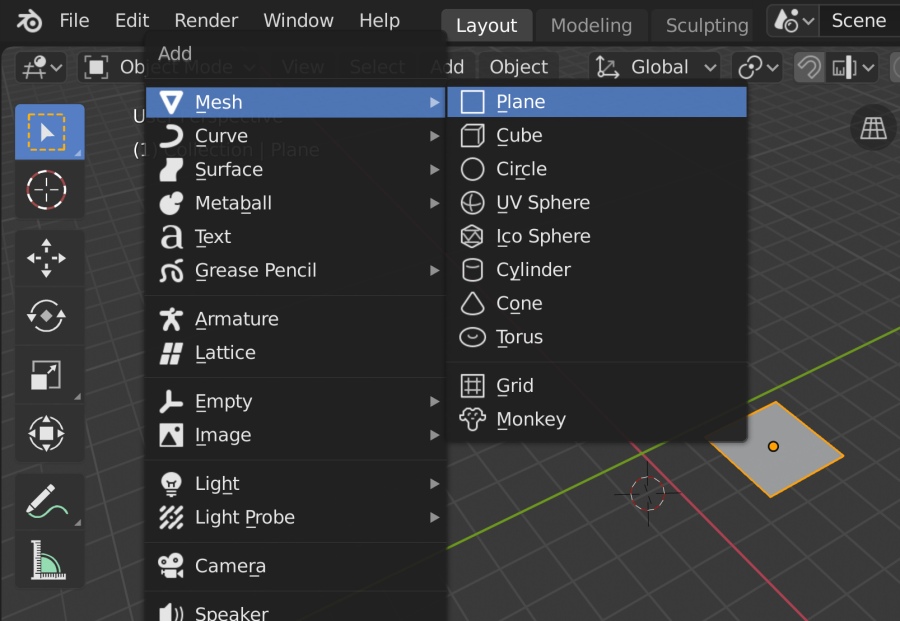
Topic 3d modeling blender tutorial: Discover the art of 3D modeling with our Blender tutorial, designed to guide beginners through the fundamentals and empower them to unleash their creative potential in the world of digital design.
Table of Content
- What are the best blender tutorials for learning 3D modeling in Blender?
- Beginner Tutorials
- Advanced Techniques
- Specialized Skills
- Resources for Continuous Learning
- Advanced Techniques
- Specialized Skills
- Resources for Continuous Learning
- Specialized Skills
- Resources for Continuous Learning
- YOUTUBE: Blender Tutorial for Complete Beginners Part 1
- Resources for Continuous Learning
- Introduction to Blender and 3D Modeling
- Getting Started with Blender for Beginners
- Step-by-Step Basic Modeling Tutorials
- Advanced Modeling Techniques and Tools
- Texturing and Rendering in Blender
- Creating Animations with Blender
- Specialized Modeling Topics: Sculpting, Rigging, and More
- Resources for Continuous Learning and Community Support
- Real-World Applications of Blender Skills
- Keeping Up with Blender Updates and Industry Trends
What are the best blender tutorials for learning 3D modeling in Blender?
Here are some of the best Blender tutorials for learning 3D modeling in Blender:
- Blender Project Website: This is the official website for Blender, where you can find a wealth of resources including tutorials, documentation, and community forums.
- Blender Guru on YouTube: Blender Guru offers a wide range of tutorials on various aspects of Blender, including 3D modeling. The tutorials are well-explained and perfect for beginners.
- Coursera Blender Courses: Coursera offers online courses on Blender, including 3D modeling tutorials taught by industry professionals. These courses provide a structured learning path for beginners.
- CG Cookie: CG Cookie is a platform that offers in-depth Blender tutorials, including courses specifically focused on 3D modeling. The tutorials cover a wide range of topics and are suitable for all skill levels.
By following these tutorials and practicing regularly, you can master 3D modeling in Blender and create stunning 3D artworks. Remember that practice is key to improving your skills in 3D modeling!
READ MORE:
Beginner Tutorials
- Getting Started with Blender: Learn the basics of the Blender interface and key concepts to start your 3D modeling journey.
- Modeling for Absolute Beginners: A step-by-step guide to familiarize yourself with 3D modeling fundamentals using Blender.
- Easy Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners: Dive into 3D modeling with an easy-to-follow tutorial designed for those new to Blender.

Advanced Techniques
- Morphing Techniques: Discover how to create impressive shape-shifting effects by morphing objects from one shape to another.
- Hard-Surface Modeling: Explore guides and tutorials to master hard-surface modeling capabilities in Blender.

Specialized Skills
- Low-Poly Tree Creation: Learn how to quickly create low-poly trees, perfect for game development and environmental design.
- NURBS Curves in 3D Modeling: Understand the use of NURBS curves and surfaces for more advanced modeling techniques.
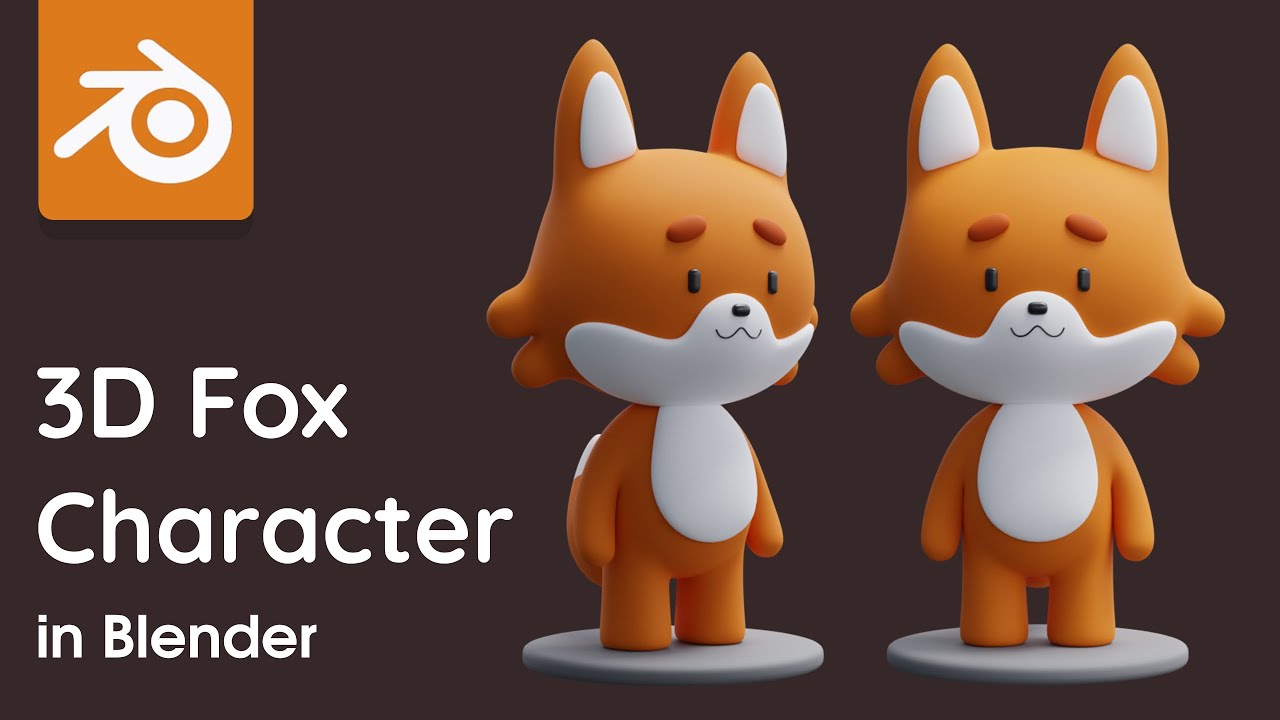
Resources for Continuous Learning
Blender\"s extensive community and online resources provide endless opportunities for learning and improvement. From official Blender tutorials to community-driven projects and courses, there\"s always something new to explore.
Further Exploration
- Check out Blender\"s official tutorials for both beginners and advanced users to stay updated with the latest features and tools.
- Engage with the Blender community through forums, online courses, and YouTube tutorials to gain insights and tips.
- Experiment with different projects and challenges to apply your skills in various contexts and build a diverse portfolio.

_HOOK_
Advanced Techniques
- Morphing Techniques: Discover how to create impressive shape-shifting effects by morphing objects from one shape to another.
- Hard-Surface Modeling: Explore guides and tutorials to master hard-surface modeling capabilities in Blender.

Specialized Skills
- Low-Poly Tree Creation: Learn how to quickly create low-poly trees, perfect for game development and environmental design.
- NURBS Curves in 3D Modeling: Understand the use of NURBS curves and surfaces for more advanced modeling techniques.

Resources for Continuous Learning
Blender\"s extensive community and online resources provide endless opportunities for learning and improvement. From official Blender tutorials to community-driven projects and courses, there\"s always something new to explore.
Further Exploration
- Check out Blender\"s official tutorials for both beginners and advanced users to stay updated with the latest features and tools.
- Engage with the Blender community through forums, online courses, and YouTube tutorials to gain insights and tips.
- Experiment with different projects and challenges to apply your skills in various contexts and build a diverse portfolio.

Specialized Skills
- Low-Poly Tree Creation: Learn how to quickly create low-poly trees, perfect for game development and environmental design.
- NURBS Curves in 3D Modeling: Understand the use of NURBS curves and surfaces for more advanced modeling techniques.
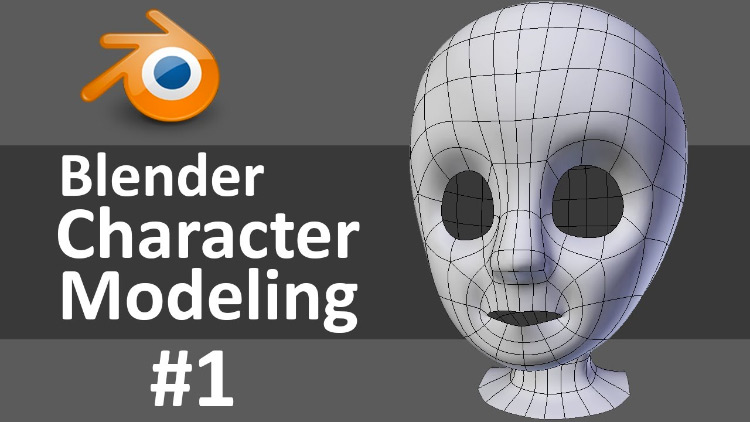
Resources for Continuous Learning
Blender\"s extensive community and online resources provide endless opportunities for learning and improvement. From official Blender tutorials to community-driven projects and courses, there\"s always something new to explore.
Further Exploration
- Check out Blender\"s official tutorials for both beginners and advanced users to stay updated with the latest features and tools.
- Engage with the Blender community through forums, online courses, and YouTube tutorials to gain insights and tips.
- Experiment with different projects and challenges to apply your skills in various contexts and build a diverse portfolio.

_HOOK_
Blender Tutorial for Complete Beginners Part 1
Basics: Dive into the world of the basics and unlock the fundamental knowledge that forms the foundation of any subject. This video simplifies complex concepts, making learning easy and enjoyable. Introduction: Start your journey with this comprehensive introduction to the topic. Gain valuable insights and a clear understanding of what to expect in the video ahead. Let this be the starting point of your educational adventure.
Blender 2.8 Beginner 3D Modeling Tutorial
This beginner Blender video demonstrates how to make a 3D model of a hammer. Blender version 2.8 beta was used for this ...
Resources for Continuous Learning
Blender\"s extensive community and online resources provide endless opportunities for learning and improvement. From official Blender tutorials to community-driven projects and courses, there\"s always something new to explore.
Further Exploration
- Check out Blender\"s official tutorials for both beginners and advanced users to stay updated with the latest features and tools.
- Engage with the Blender community through forums, online courses, and YouTube tutorials to gain insights and tips.
- Experiment with different projects and challenges to apply your skills in various contexts and build a diverse portfolio.

Introduction to Blender and 3D Modeling
Blender is a powerful, open-source software for 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and more. It offers a comprehensive suite of tools for professionals and hobbyists alike to bring their creative visions to life. This section introduces the fundamental concepts of 3D modeling and how Blender facilitates this creative process.
- Overview of Blender\"s Interface: Familiarize yourself with the user interface, including the 3D viewport, outliner, properties panel, and more.
- Basic 3D Modeling Concepts: Learn about vertices, edges, faces, and how they form the building blocks of 3D modeling.
- Getting Started with Blender: A step-by-step guide on installing Blender and setting up your first project.
- Navigation and Tools: Master Blender\"s navigation controls and discover essential tools for creating and editing 3D models.
- Creating Your First 3D Model: Follow a simple tutorial to create your first 3D model in Blender, covering the basics of modeling, texturing, and rendering.
Blender\"s extensive functionality doesn\"t stop at modeling; it also encompasses animation, sculpting, lighting, and rendering. As you progress through this guide, you\"ll uncover the depth of Blender\"s capabilities and how they can be applied to create stunning 3D artwork.
Getting Started with Blender for Beginners
Embarking on your 3D modeling journey with Blender opens a world of creative possibilities. This section is designed to help beginners navigate the initial steps of using Blender, ensuring a smooth transition into the world of 3D design.
- Installation and Setup: Begin by downloading Blender from the official website and follow the installation instructions to set up the software on your computer.
- Understanding the Blender Interface: Familiarize yourself with the Blender interface, learning about the workspace, navigation, and key tools.
- Basic Navigation: Master the basics of moving around in the 3D viewport, including zooming, panning, and rotating your view.
- First 3D Model: Dive into creating your first 3D model. Start with something simple, like a cube, and learn how to modify it with basic tools.
- Introduction to Modeling Tools: Explore the essential modeling tools available in Blender, such as extrude, scale, and rotate, to start shaping your creations.
- Materials and Texturing: Learn how to apply basic materials and textures to your models, giving them color and realism.
- Rendering Your First Scene: Discover how to set up and render your first scene, turning your 3D model into a stunning image.
- Where to Find Resources: Get to know the best places to find tutorials, assets, and community support as you continue learning Blender.
With patience and practice, you will start to feel comfortable navigating Blender\"s interface and tools. Remember, every expert was once a beginner. The key is to keep experimenting and learning. Happy modeling!
Step-by-Step Basic Modeling Tutorials
Embark on your 3D modeling journey in Blender with our comprehensive step-by-step tutorials designed for beginners. Blender, a powerful and free open-source software, offers an array of tools and features to bring your creative visions to life. Follow our beginner-friendly guide to master the basics of 3D modeling.
- Getting to Know Blender\"s Interface
- Start by familiarizing yourself with Blender\"s interface. Learn about the main areas including the 3D viewport, outliner, properties panel, and timeline. Understand how to navigate through the viewport, select objects, and use basic shortcuts to improve your workflow.
- Creating Your First 3D Model
- Begin your modeling journey by creating simple shapes. Learn how to add meshes, like cubes and spheres, to your scene. Discover the basics of transforming objects by moving, rotating, and scaling them to shape your first 3D model.
- Editing Meshes
- Dive deeper into Blender\"s modeling tools with edit mode. Explore vertex, edge, and face selections to modify your meshes with precision. Practice extruding, beveling, and using the loop cut tool to add detail to your models.
- Applying Modifiers
- Learn about Blender\"s powerful modifiers for non-destructive modeling. Experiment with modifiers like Subdivision Surface to smooth your models, Mirror for symmetrical designs, and Boolean for complex shapes. Understand how to apply and stack modifiers to enhance your creations.
- Materials and Texturing
- Bring your models to life with materials and textures. Discover how to add color and realism to your models by applying different materials. Learn the basics of UV unwrapping and texturing to give your creations a unique look.
- Lighting and Rendering
- Introduction to the fundamentals of lighting and rendering in Blender. Understand how to place lights in your scene to highlight your models and create mood. Learn the basics of rendering settings to produce high-quality images of your 3D creations.
With these tutorials, you\"ll build a solid foundation in Blender and 3D modeling. Practice regularly, experiment with different tools and techniques, and soon you\"ll be creating stunning 3D models of your own. Happy modeling!
Advanced Modeling Techniques and Tools
Mastering advanced modeling techniques and tools in Blender opens up a new realm of possibilities for 3D artists. This section explores some sophisticated strategies and tools to elevate your 3D modeling skills.
Hard Surface Modeling
- Bevel Modifier: Creates smooth edges and transitions between surfaces, essential for realistic mechanical parts.
- Boolean Operations: Combine or subtract mesh objects to create complex shapes with precision.
- Non-Destructive Workflow: Utilize modifiers to make changes that can be adjusted or reverted without altering the base mesh.
Subdivision Surface Modeling
Subdivision surface modeling enhances the smoothness and detail of your models. This technique divides the mesh into smaller faces, providing a smoother appearance. Key tools include:
- Subdivision Surface Modifier: Increases mesh density, smoothing out the appearance of the model.
- Control Loops: Add edge loops to control the sharpness of edges under subdivision.
Sculpting for Detail
Blender’s sculpting tools allow for intuitive shaping and detailing of organic models. Key aspects include:
- Dynamic Topology: Adds geometry dynamically as you sculpt, allowing for intricate detail.
- Brushes: A variety of brushes are available for different effects, such as creasing, smoothing, and texturing.
Retopology
Retopology is the process of creating a new, cleaner mesh over an existing detailed model. This is crucial for animation and game asset creation. Tools and techniques include:
- Shrinkwrap Modifier: Projects the new mesh onto the surface of the original, detailed model.
- Topology Guides: Use guides and snapping to ensure even distribution of vertices and optimal flow of edges.
Texturing and UV Unwrapping
After modeling, texturing and UV unwrapping are essential for bringing your model to life. Blender offers powerful tools for this, including:
- UV Editing Workspace: Provides a full suite of tools for unwrapping and editing UV maps.
- Texture Painting: Directly paint textures onto your 3D model in Blender’s 3D viewport.
Lighting and Rendering
The final step in showcasing your advanced models is through lighting and rendering. Blender’s Cycles and Eevee engines offer:
- Physically Based Rendering (PBR): For realistic materials and lighting.
- HDRI Lighting: Use HDRI images to provide realistic environmental lighting.
- Advanced Shaders: Utilize the node editor to create complex materials.
By mastering these advanced techniques and tools in Blender, you can create highly detailed, realistic models suitable for a variety of applications, from animation to game development. Continuous practice and exploration of Blender’s extensive feature set will further enhance your modeling skills.
_HOOK_
Texturing and Rendering in Blender
Texturing and rendering are critical phases in the 3D creation process, bringing vibrancy and realism to your models. This section delves into the steps and tools Blender offers for texturing your models and rendering them into stunning visuals.
UV Mapping and Texturing
UV mapping is the foundation of texturing, allowing you to lay out a model\"s surface in two dimensions for texturing.
- Unwrapping the Model: Start by marking seams on your model, then unwrap it to lay out the UV map in the UV/Image Editor.
- Texture Painting: Use Blender\"s texture paint tools to directly paint onto your model or its UV map, creating detailed textures.
- Image Textures: Apply image textures to your model using the shader editor, mapping them to the UV coordinates.
Shading and Materials
Shading and material application in Blender are accomplished through the Shader Editor, where you can create complex materials using nodes.
- Principled BSDF: A versatile shader for creating a wide range of materials with physical properties like roughness, metallic, and transparency.
- Node-based Materials: Combine various nodes to create intricate material effects such as subsurface scattering, reflection, and more.
Lighting Your Scene
Lighting is essential for setting the mood and realism of your scene.
- Three-Point Lighting: A classic technique that uses key, fill, and back lights to achieve depth and dimensionality.
- HDRI Lighting: Utilize High Dynamic Range Images (HDRI) to simulate realistic environmental lighting.
- Emissive Materials: Create materials that emit light to add glow effects to your scene.
Rendering with Cycles and Eevee
Blender offers two powerful rendering engines, Cycles and Eevee, each with its own advantages.
- Cycles: A path-tracing renderer for photo-realistic results. It simulates light in a physically accurate manner but can be more time-consuming.
- Eevee: A real-time renderer that offers faster results, suitable for interactive previews and less resource-intensive projects.
Post-Processing and Compositing
Enhance your renders with Blender\"s compositor for post-processing effects.
- Node-based Compositing: Use nodes to apply effects like blurs, color correction, and glare to your final render.
- Render Layers: Render your scene in layers to have more control over the final composition.
Through careful UV mapping, texturing, shading, and rendering, combined with effective lighting and post-processing, Blender allows you to transform your 3D models into lifelike or stylized works of art. Experimenting with these tools and techniques will enable you to achieve the exact look you desire for your projects.
Creating Animations with Blender
Blender is not only powerful for 3D modeling and rendering but also offers comprehensive tools for creating animations. Whether you\"re animating characters, objects, or creating dynamic simulations, Blender provides the functionality to bring your creations to life. Follow these steps to start animating in Blender.
Setting Up Your Scene
Begin by preparing your scene with the objects or characters you wish to animate. Ensure that your models are properly rigged if they require complex movements.
Understanding Keyframes
Keyframes are the cornerstone of animation in Blender. They define the start and end points of any movement, allowing Blender to interpolate the motion in between.
- Inserting Keyframes: Move your object to the desired starting position, and press I to insert a keyframe. Choose the property to keyframe, such as location, rotation, or scale.
- Animation Timeline: Use the timeline at the bottom of the Blender interface to navigate through your animation frames and insert additional keyframes as needed.
Animating with the Graph Editor
The Graph Editor allows for precise control over the interpolation of keyframes, enabling you to refine the speed and timing of your animations.
- Editing Curves: Each keyframed property is represented as a curve in the Graph Editor. Adjust these curves to smooth or sharpen the transitions between keyframes.
- Handling Interpolation: Blender offers various interpolation types, such as linear, bezier, and constant, each affecting how animation progresses between keyframes.
Dopesheet and the Action Editor
The Dopesheet provides an overview of all keyframes in your scene, while the Action Editor is used to create and manage reusable animation actions.
- Managing Actions: Create, duplicate, and assign actions to different objects or characters within your scene.
- Synchronizing Movements: Use the Dopesheet to align actions across multiple objects, ensuring coordinated movements.
Character Animation and Rigging
For character animation, Blender\"s rigging tools allow you to create a skeleton that can be animated with more natural movements.
- Armature and Bones: Build an armature system for your character, defining bones for limbs and other movable parts.
- Weight Painting: Define how the mesh of your character deforms in relation to the movement of the bones through weight painting.
Animating with Modifiers and Physics
Blender also allows for procedural animation through the use of modifiers and physics simulations.
- Cloth, Fluid, and Particle Simulations: Create dynamic animations that simulate real-world physics, such as cloth fluttering in the wind or liquid pouring into a container.
- Modifiers: Use modifiers like the Wave or Displace modifiers to add motion to objects without manual keyframing.
By mastering these tools and techniques, you can leverage Blender\"s full potential to create animations ranging from simple object movements to complex character animations. Remember, animation in Blender is an iterative process; practice and experimentation are key to achieving smooth, lifelike animations.
Specialized Modeling Topics: Sculpting, Rigging, and More
Delving into specialized modeling topics such as sculpting and rigging in Blender enhances the versatility and realism of your 3D projects. This section provides insights into these advanced techniques, empowering you to create more dynamic and detailed models.
Sculpting in Blender
Sculpting is a freeform modeling technique ideal for creating organic shapes and details.
- Dynamic Topology: Activate dynamic topology to add detail to your model dynamically as you sculpt, allowing for complex surface details without the need for a high initial polygon count.
- Sculpt Brushes: Utilize various brushes in Blender, such as the Grab, Crease, Smooth, and Clay strips, to mold your model with precision.
- Masking: Use masking to protect certain areas of your model from being altered while you sculpt other parts.
Rigging and Animation
Rigging is the process of creating a skeleton for a model so that it can be animated. Animation in Blender uses this rig to bring characters and objects to life.
- Armature: Create an armature (skeleton) that defines the movement points of the model.
- Weight Painting: Define how the vertices of the mesh move in relation to the bones of the armature through weight painting.
- Animation Principles: Apply key animation principles such as anticipation, squash and stretch, and secondary action to create believable motion.
Particle Systems and Simulations
Particle systems and physics simulations in Blender allow for the creation of complex dynamic scenes involving fluids, cloth, hair, and more.
- Hair and Fur: Use the particle system to add realistic hair or fur to characters and animals.
- Cloth Simulation: Simulate cloth physics to create realistic clothing and fabric movements.
- Fluid Dynamics: Create realistic liquid behaviors with Blender’s fluid simulation tools.
Environmental Modeling
Environmental modeling involves creating landscapes, architecture, and other large-scale scenes.
- Terrain Generation: Use Blender’s modifiers and sculpting tools to create realistic landscapes.
- Architectural Modeling: Utilize Blender’s precision modeling tools to create detailed architectural models.
- Environmental Effects: Add environmental effects such as fog, rain, and lighting to enhance the realism of your scenes.
Exploring these specialized modeling topics in Blender not only broadens your skill set but also opens up new creative possibilities for your projects. Whether sculpting intricate characters, rigging them for animation, or creating dynamic simulations, Blender provides a comprehensive toolkit for bringing your most ambitious 3D visions to life.
Resources for Continuous Learning and Community Support
The journey of mastering Blender and 3D modeling is ongoing, with continuous learning and community support playing a pivotal role. Here, we highlight key resources to aid your development and connect you with fellow enthusiasts.
Online Tutorials and Courses
Expand your skills through a variety of online platforms offering tutorials and courses tailored to all skill levels.
- Blender Official Tutorials: Start with the source! Blender’s official website hosts a plethora of tutorials covering basics to advanced topics.
- YouTube Channels: Numerous channels dedicated to Blender training, offering free tutorials, tips, and project walkthroughs.
- Udemy and Coursera: For a more structured learning path, consider enrolling in comprehensive courses available on these platforms.
Books and E-books
For those who prefer self-study, several books and e-books provide in-depth knowledge on Blender.
- \"Blender For Dummies\": An excellent start for beginners, covering the fundamentals of Blender.
- \"The Complete Guide to Blender Graphics\": More suited for intermediate to advanced users, focusing on graphics and animation.
Forums and Online Communities
Joining Blender forums and online communities can provide valuable support, feedback, and inspiration.
- Blender Artists Community: A vibrant forum where users share their work, ask questions, and offer advice.
- Reddit’s r/blender: A large community of Blender enthusiasts engaging in discussions, sharing projects, and helping each other.
Blender Conferences and Meetups
Attending Blender conferences and local meetups can enhance your learning through workshops, presentations, and networking with other professionals and hobbyists.
- Blender Conference: An annual event featuring workshops, talks, and showcases of outstanding work created with Blender.
- Local Blender Meetups: Search for Blender user groups in your area to connect with fellow 3D modeling enthusiasts locally.
By leveraging these resources, you can stay updated with the latest Blender features and techniques, enhance your skills, and become part of a global community of creators. Remember, the journey in 3D modeling is as much about the process and community as it is about the final product.
Real-World Applications of Blender Skills
Blender, with its comprehensive suite of 3D modeling, texturing, and animation tools, is not just for hobbyists. Professionals across various industries leverage Blender skills to enhance their work, innovate, and solve complex problems. Here’s how Blender skills are applied in the real world.
Video Game Development
Blender is instrumental in creating assets for video games, including characters, environments, and props. Its ability to export models in formats compatible with game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine makes it a valuable tool for indie developers and large studios alike.
Animation and Film
From pre-visualization to final production, Blender\"s animation tools are used to create animated features, short films, and visual effects. Its robust rendering engine supports the creation of visually stunning scenes.
Architectural Visualization
Architects and designers use Blender to bring their visions to life, creating detailed architectural renderings and virtual tours. This aids in the presentation, planning, and marketing of architectural projects.
Product Design and Prototyping
Designers in various fields, including furniture, automotive, and consumer electronics, use Blender for product design and prototyping. It allows for rapid visualization of new ideas and iterations.
Scientific Visualization
Researchers utilize Blender to visualize complex scientific data, from molecular biology to astrophysics. This helps in understanding data better, presenting findings, and educational purposes.
3D Printing
Blender is used to create and prepare models for 3D printing, offering tools for ensuring models are watertight and correctly scaled. This is valuable for prototyping, custom manufacturing, and art.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
As VR and AR technologies grow, Blender serves as a tool for creating immersive environments, interactive experiences, and simulations for education, training, and entertainment.
The versatility of Blender ensures that the skills acquired are not only relevant but also in demand across a broad spectrum of industries. Whether for professional advancement, personal projects, or academic pursuits, mastering Blender opens doors to countless opportunities.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Keeping Up with Blender Updates and Industry Trends
Staying current with Blender updates and industry trends is crucial for professionals and hobbyists alike. This evolving landscape offers new tools, techniques, and opportunities for growth. Here’s how you can stay informed and adaptable in the fast-paced world of 3D modeling.
Follow Blender’s Official Channels
Blender’s official website and social media channels are the primary sources for updates, release notes, and upcoming features.
- Blender.org: Official announcements, release notes, and development roadmaps.
- Twitter and Facebook: Quick updates, tips, and community highlights.
Participate in Online Communities
Online forums and social media groups are excellent for discussions on updates, troubleshooting, and sharing experiences.
- Blender Artists Forum: A place to engage with other users and find out how they adapt to new updates.
- Reddit’s r/blender: A community for sharing news and discussing Blender’s features and industry trends.
Subscribe to Industry Blogs and Newsletters
Many websites and blogs provide insights into Blender and the broader 3D modeling industry, offering tutorials, reviews, and trend analyses.
- CG Cookie Blog: Offers tutorials and articles on Blender and general 3D modeling trends.
- BlenderNation: Daily news, tutorials, art, and interviews from the Blender community.
Attend Workshops and Conferences
Conferences, both virtual and in-person, present opportunities to learn from industry professionals and see how Blender is being used in cutting-edge projects.
- Blender Conference: An annual event showcasing new developments and user projects.
- Local Meetups: Joining local Blender user groups can provide insights into how others are using Blender in various industries.
Continuous Learning
Advancements in technology and changes in industry standards require a commitment to ongoing education.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and Blender Cloud offer courses that are updated regularly to reflect the latest trends and techniques.
- Tutorials: Stay current by following tutorial creators who focus on the latest Blender features and workflows.
By actively engaging with these resources, you can ensure that your Blender skills remain relevant and that you’re well-informed about the latest in 3D modeling, animation, and rendering technologies. Embracing continuous learning and community engagement are key to navigating the ever-changing landscape of 3D art and design.
Embark on a transformative journey into the world of 3D modeling with Blender, where creativity meets endless possibilities. Whether you\"re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide is your gateway to mastering Blender and bringing your visions to life.