Topic linux blender install: Discover the seamless process of installing Blender on Linux with our comprehensive guide, tailored for artists and designers seeking to unleash their creative potential on a robust platform.
Table of Content
- How to install Blender on Linux?
- Downloading Blender
- Installation Methods
- Launching Blender
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- Installation Methods
- YOUTUBE: Installing Blender on Linux
- Launching Blender
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- Launching Blender
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- Troubleshooting
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Blender for Linux Users
- System Requirements for Blender on Linux
- Downloading Blender from the Official Website
- Installing Blender on Linux via Package Manager
- Installing Blender with Snap Package
- Using Flatpak to Install Blender
- Launching Blender on Linux
- Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
- Updating Blender to the Latest Version
- Extending Blender with Add-ons and Plugins
- Resources for Learning Blender on Linux
- Conclusion: Getting Started with Blender
How to install Blender on Linux?
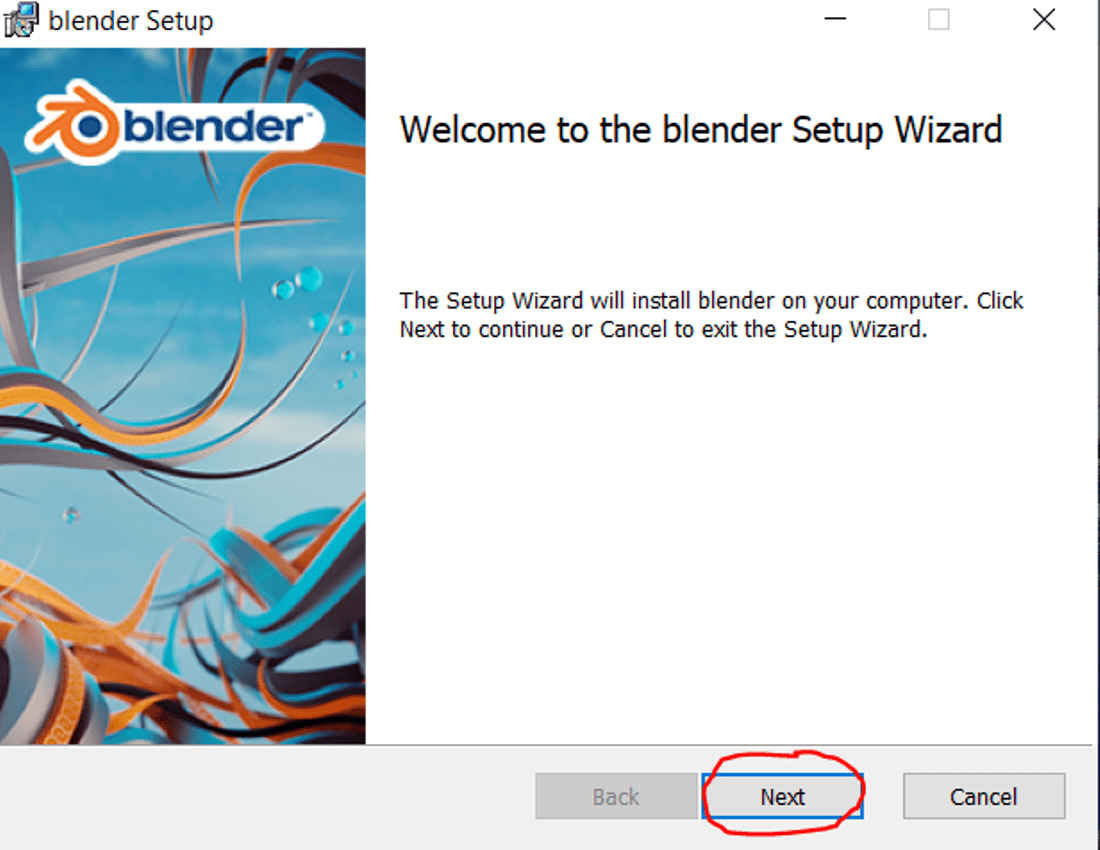
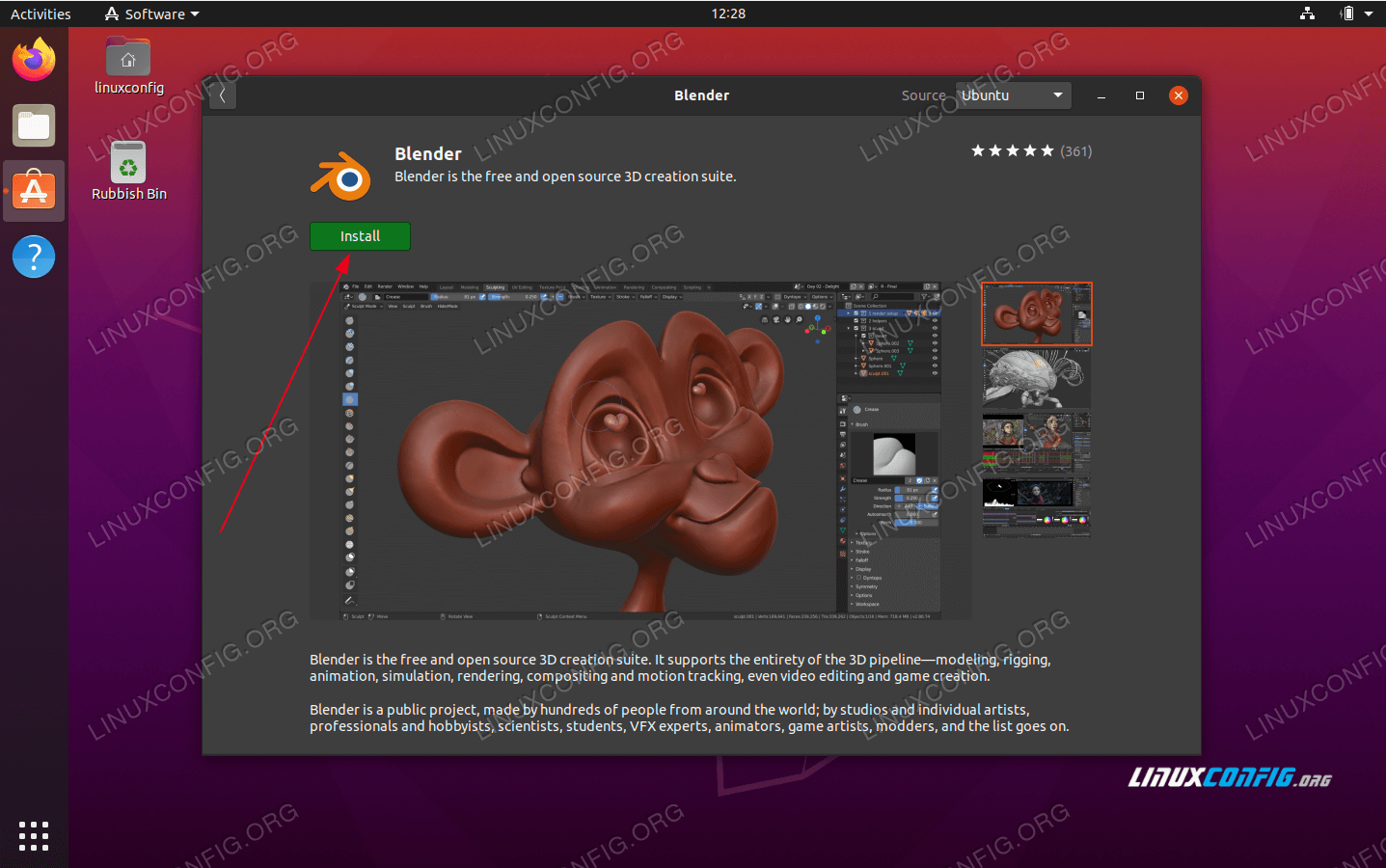
To install Blender on Linux, follow these steps:
- Visit the official Blender website at blender.org/download.
- Download the Linux version of Blender suitable for your architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Once the download is complete, navigate to the directory where the downloaded file is located.
- Decompress the downloaded file to the desired location on your system. This can be done using the following command in the terminal:
tar xjf blender-*.tar.bz2 -C /opt/- Now, you can run Blender by executing the following command in the terminal:
/opt/blender-*/blender- Alternatively, you can create a desktop shortcut for Blender by creating a .desktop file in
/usr/share/applications/with the following contents:
| Name: | Blender |
| Exec: | /opt/blender-*/blender |
| Icon: | /opt/blender-*/blender.svg |
READ MORE:
Downloading Blender
First, visit the official Blender website to download the latest version of Blender for Linux. Choose the package that suits your distribution, and download the tarball file.
Installation Methods
Via Package Manager
- Open your terminal.
- For Debian-based systems, use sudo apt-get install blender.
- For Fedora or similar, use sudo dnf install blender.
Via Snap Package
- Ensure Snap is installed on your system.
- Install Blender by running sudo snap install blender --classic in the terminal.
Via Flatpak
- Install Flatpak if it\"s not already installed.
- Add the Flathub repository with flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo.
- Install Blender using flatpak install flathub org.blender.Blender.

Launching Blender
After installation, you can launch Blender directly from your terminal by typing blender, or through your system\"s application menu.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues during the installation, ensure your system is up to date, and check the official Blender documentation for troubleshooting tips.

_HOOK_
Conclusion
Blender is a versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. With these steps, you can easily install Blender on your Linux system and start creating stunning 3D artwork.
Installation Methods
Via Package Manager
- Open your terminal.
- For Debian-based systems, use sudo apt-get install blender.
- For Fedora or similar, use sudo dnf install blender.
Via Snap Package
- Ensure Snap is installed on your system.
- Install Blender by running sudo snap install blender --classic in the terminal.
Via Flatpak
- Install Flatpak if it\"s not already installed.
- Add the Flathub repository with flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo.
- Install Blender using flatpak install flathub org.blender.Blender.

Installing Blender on Linux
Discover the power and flexibility of Linux, the operating system that empowers users to customize and control their digital experience like never before. Watch the video to learn how Linux can enhance your computing journey!
Installing Blender on Linux
Discover the power and flexibility of Linux, the operating system that empowers users to customize and control their digital experience like never before. Watch the video to learn how Linux can enhance your computing journey!
Launching Blender
After installation, you can launch Blender directly from your terminal by typing blender, or through your system\"s application menu.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues during the installation, ensure your system is up to date, and check the official Blender documentation for troubleshooting tips.

Conclusion
Blender is a versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. With these steps, you can easily install Blender on your Linux system and start creating stunning 3D artwork.
_HOOK_
Launching Blender
After installation, you can launch Blender directly from your terminal by typing blender, or through your system\"s application menu.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues during the installation, ensure your system is up to date, and check the official Blender documentation for troubleshooting tips.
Conclusion
Blender is a versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. With these steps, you can easily install Blender on your Linux system and start creating stunning 3D artwork.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues during the installation, ensure your system is up to date, and check the official Blender documentation for troubleshooting tips.
Conclusion
Blender is a versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. With these steps, you can easily install Blender on your Linux system and start creating stunning 3D artwork.
_HOOK_
Conclusion
Blender is a versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. With these steps, you can easily install Blender on your Linux system and start creating stunning 3D artwork.
Introduction to Blender for Linux Users
Blender is an open-source 3D creation suite that offers a broad spectrum of functionalities in 3D pipeline including modeling, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing, and motion tracking. For Linux users, Blender provides a powerful platform for 3D design and animation, compatible with various Linux distributions. This section aims to guide you through the benefits of using Blender on Linux, the prerequisites for a smooth installation, and how to navigate the initial setup to kickstart your creative projects.
- Why Choose Blender for Linux: Blender\"s compatibility with Linux offers a stable and efficient environment for professional-grade 3D projects, leveraging the power and flexibility of Linux operating systems.
- System Requirements: Before installing Blender on Linux, ensure your system meets the minimum requirements to run Blender smoothly, including a compatible graphics card, sufficient RAM, and a modern processor.
- Advantages of Blender on Linux: Blender on Linux stands out for its performance, cost-effectiveness, and the strong community support that fosters learning and collaboration among users.
Getting started with Blender on Linux not only opens up a world of professional 3D design possibilities but also integrates seamlessly into the Linux ecosystem, making it an ideal choice for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
System Requirements for Blender on Linux
For Linux users keen on using Blender, understanding the system requirements is crucial to ensure a smooth experience. Blender is designed to be compatible with a broad range of Linux distributions, but certain minimum system specifications must be met for optimal performance.
- Operating System: Most recent GNU/Linux distributions with glibc 2.28 or newer are supported.
- Processor: A 64-bit dual core 2Ghz CPU with SSE4.2 support is the minimum requirement, but an eight-core 64-bit CPU is recommended for better performance.
- Memory: At least 8 GB of RAM is required, with 16 GB or more recommended for handling complex projects.
- Graphics: A Graphics card with 2 GB RAM is the minimum requirement. For optimal performance, a dedicated GPU with CUDA compute capability 5.0 or higher and 8 GB VRAM is recommended. Blender supports NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel graphics.
- Display: A Full HD display with a 24-bit color depth is recommended for the best visual experience.
- Input Devices: A three-button mouse and a graphics tablet for sculpting and painting tasks are recommended for an efficient workflow.
Meeting these requirements will not only ensure Blender runs smoothly on your Linux system but also enhances your 3D modeling, animation, and rendering projects with faster processing and improved graphics performance.
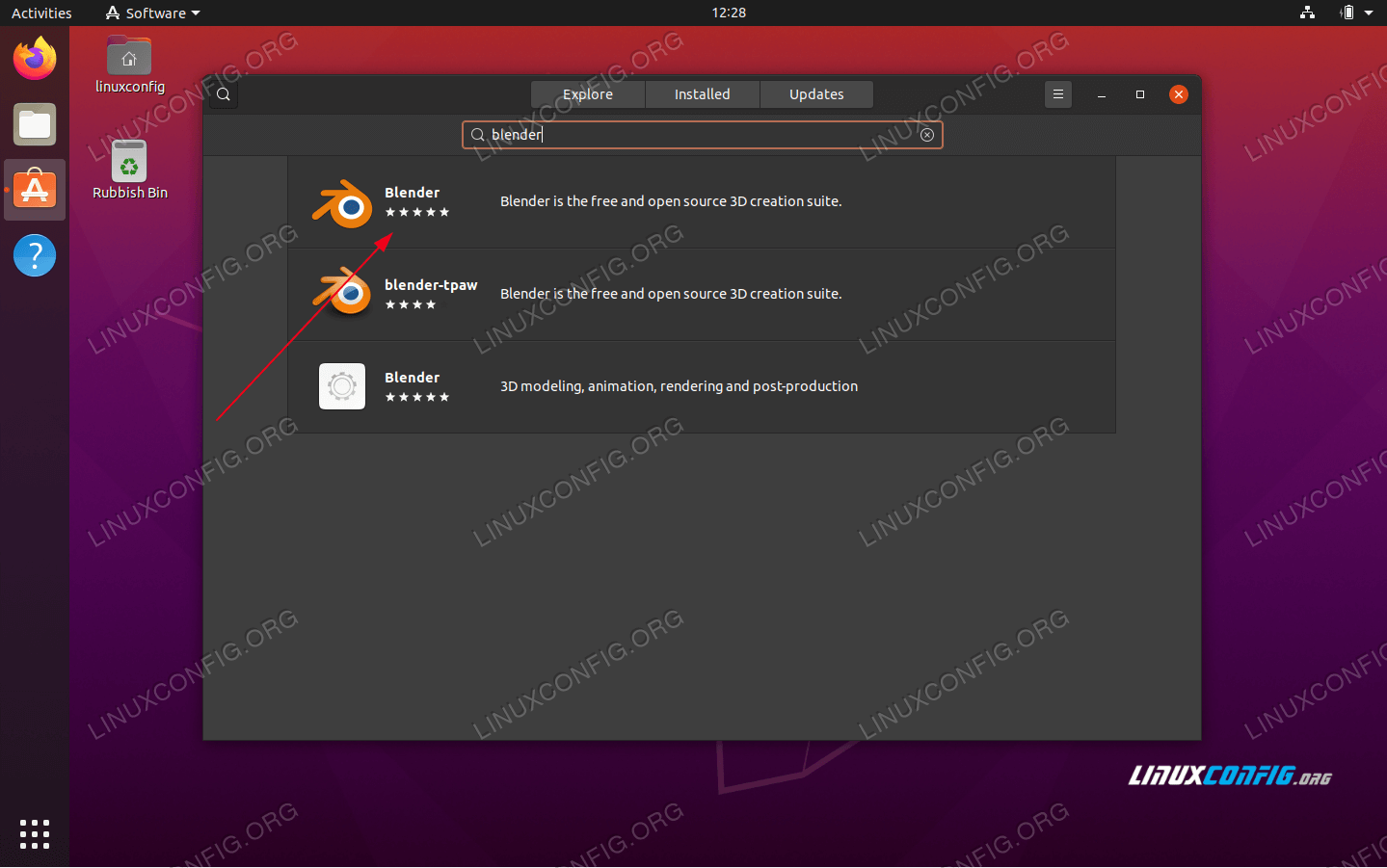
Downloading Blender from the Official Website
To ensure you\"re getting the most stable and secure version of Blender, downloading it directly from the official website is highly recommended. Here\"s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Navigate to the Blender official website at https://www.blender.org/download/.
- On the download page, you will see options for different operating systems. Select the version appropriate for Linux.
- Blender offers both LTS (Long Term Support) versions and the latest releases. Choose the version that best suits your needs. The LTS version is recommended for users who value stability over having the latest features.
- Click on the \"Download\" button for the version you\"ve chosen. The website might automatically detect your operating system and suggest the correct version for you.
- Once the download is complete, you will have a file with a \".tar.xz\" extension. This is a compressed file containing Blender.
After downloading Blender, the next step is to install it on your Linux system. There are several methods to install Blender on Linux, including using your distribution\"s package manager, Snap, or Flatpak. The method you choose may depend on your Linux distribution and your personal preference.
By downloading Blender directly from the official website, you ensure that you have the most up-to-date and secure version of the software, allowing you to start creating with confidence.
Installing Blender on Linux via Package Manager
Installing Blender on Linux using the package manager is a straightforward process that varies slightly depending on your Linux distribution. Here\"s a general guide to get you started:
- Open your terminal. You can typically do this by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T on your keyboard.
- Before installing new software, it\"s a good practice to update your package list. Enter the command sudo apt-get update and press Enter. You might need to enter your password.
- Now, install Blender by entering the command sudo apt-get install blender. Press Enter to execute the command.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation. This might include confirming the installation by pressing Y when prompted.
Note: The above steps are generally applicable to Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu. If you\"re using a different distribution, the package management commands might vary. For instance, you might use dnf for Fedora or zypper for openSUSE. Always ensure you\"re using the command appropriate for your distribution.
Once installed, you can launch Blender from your terminal by typing blender and pressing Enter, or you can find it in your application menu, depending on your desktop environment.
Using your distribution\"s package manager to install Blender ensures that it integrates well with your system, making it easy to manage updates and dependencies.
_HOOK_
Installing Blender with Snap Package
For Linux users, Snap packages offer a convenient and distribution-agnostic way to install Blender. Follow these steps to install Blender using Snap:
- Ensure Snap is installed on your Linux distribution. Snap is installed by default on Ubuntu 20.04 and later. For other distributions, you may need to install Snap first. You can check if Snap is installed by running snap version in your terminal.
- If Snap is not installed, you can install it by following the instructions specific to your Linux distribution. For example, on Debian-based systems, you can use sudo apt update followed by sudo apt install snapd.
- Once Snap is installed and running, you can install Blender by opening your terminal and typing sudo snap install blender --classic. The --classic flag is necessary because it allows Blender to access system files and resources like your graphics hardware, which are needed for full functionality.
- Wait for the installation to complete. This process can take a few minutes, depending on your internet connection speed.
After installation, you can start Blender by typing blender in your terminal or by finding Blender in your application menu, depending on your desktop environment.
Using Snap to install Blender not only simplifies the installation process across different Linux distributions but also ensures that you automatically receive updates to Blender, keeping your software up to date with the latest features and security patches.
Using Flatpak to Install Blender
Flatpak is a software utility for software deployment, application virtualization, and package management that provides a sandbox environment to run applications in isolation from the rest of the system. It\"s available across multiple Linux distributions and is perfect for installing Blender. Here\"s how you can install Blender using Flatpak:
- First, ensure that Flatpak is installed on your system. If it\"s not already installed, you can typically install it via your distribution\"s package manager. For example, on Fedora, you would use sudo dnf install flatpak, and on Ubuntu, sudo apt install flatpak.
- Next, you need to enable the Flathub repository, which is the primary repository of Flatpak applications. You can do this by running flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo in your terminal.
- Once Flathub is enabled, you can install Blender by running flatpak install flathub org.blender.Blender.
- Follow the prompts in your terminal to complete the installation. This process may take some time as it downloads Blender and the necessary runtime environments.
After installation, you can run Blender via Flatpak by executing flatpak run org.blender.Blender in your terminal. Alternatively, you might find Blender in your application menu, depending on your desktop environment.
Using Flatpak to install Blender not only simplifies the installation process across different Linux distributions but also isolates Blender from other system software, reducing potential conflicts and ensuring that Blender runs with its required dependencies.
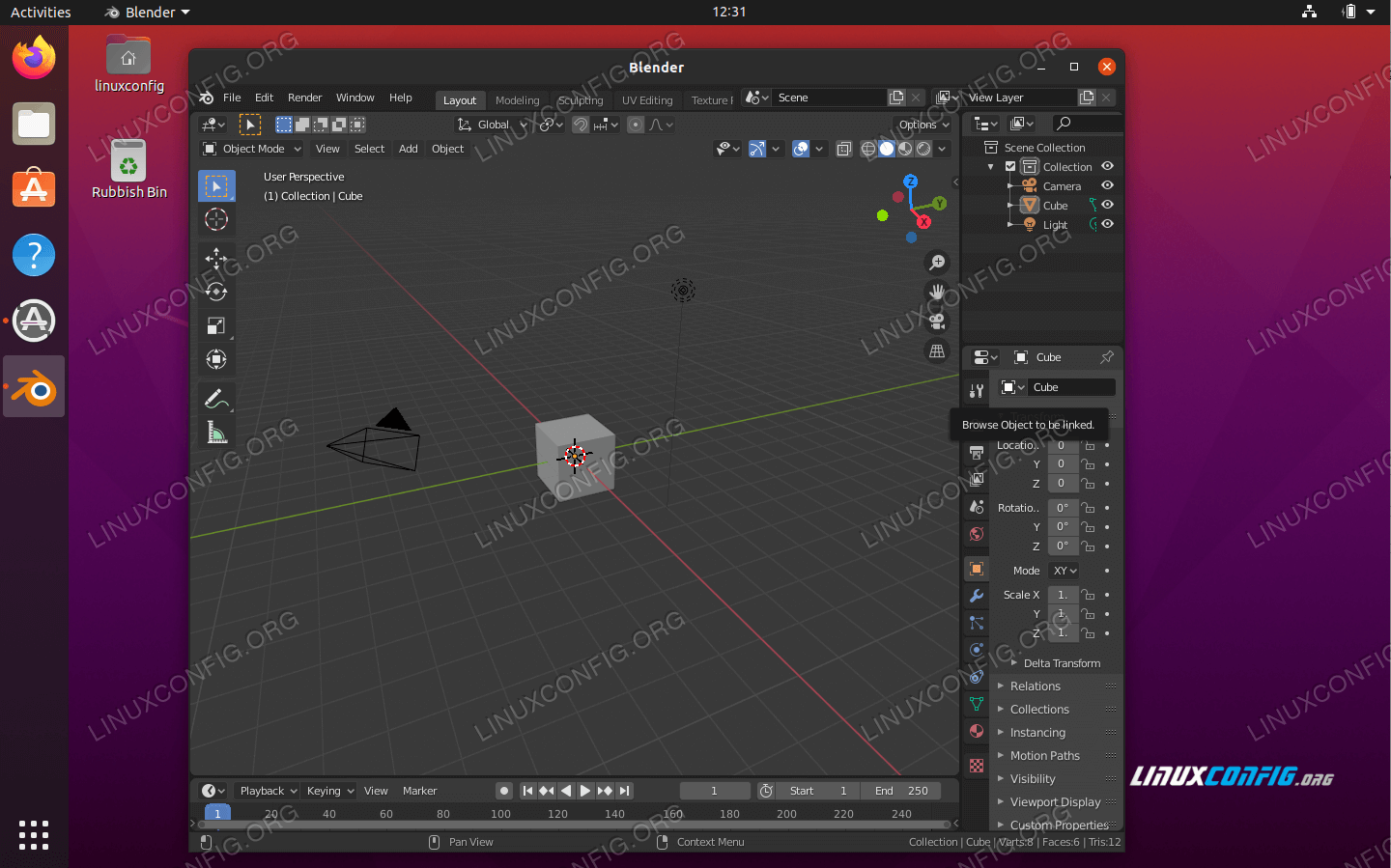
Launching Blender on Linux
After successfully installing Blender on your Linux system, launching it is the final step to begin your 3D modeling, animation, or rendering projects. Here are the common methods to launch Blender on Linux, catering to different installation methods:
- Using the Application Menu: If you installed Blender through a package manager, Snap, or Flatpak, it should appear in your desktop environment\"s application menu. Simply navigate to the menu, search for Blender, and click on it to launch.
- Through the Terminal: For installations via package manager, Snap, or directly from a tarball, you can also launch Blender by opening a terminal and typing blender, then pressing Enter. If installed via Snap, use snap run blender, and for Flatpak, use flatpak run org.blender.Blender.
- Creating a Shortcut: If you downloaded Blender directly from the official website and extracted it, you can launch Blender by navigating to the extracted folder and double-clicking the Blender executable. For convenience, you can create a shortcut to this executable on your desktop or application menu.
- From the File Manager: You can also navigate to the directory where Blender is installed using your file manager and double-click the Blender executable to start the program. This method works for tarball installations and manual downloads from the official website.
Once launched, Blender will open with its default screen, ready for you to start your projects. For first-time users, it might be helpful to explore the user interface or follow some introductory tutorials to get accustomed to the Blender workflow and its powerful features.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Encountering issues during the installation of Blender on Linux is not uncommon. However, most problems have straightforward solutions. Below are some common issues and their resolutions:
- Dependency Errors: If you\"re facing dependency errors during installation, ensure your system is up to date. Run sudo apt-get update and sudo apt-get upgrade on Debian-based systems, or the equivalent on other distributions, before trying to install Blender again.
- Snap and Flatpak Issues: For problems related to Snap or Flatpak installations, make sure Snap or Flatpak is correctly installed and up to date. For Snap, use sudo snap refresh, and for Flatpak, use flatpak update.
- Graphics Driver Issues: Blender requires up-to-date graphics drivers to function correctly. If Blender fails to start or displays poorly, check your graphics drivers and update them if necessary. For NVIDIA and AMD GPUs, this may involve installing proprietary drivers from the manufacturer.
- Permission Denied: If you\"re encountering a \"Permission Denied\" error when launching Blender, it\"s likely an issue with the executable permissions. Navigate to the Blender directory and run chmod +x blender to make the Blender executable runnable.
- Missing Libraries: Blender may fail to start if certain libraries are missing. This is common with tarball installations. Run Blender from the terminal to see which libraries are missing and install them using your package manager.
For issues not listed here, checking the official Blender forums and community support channels can be incredibly helpful. The Blender community is active and supportive, and chances are, someone has faced and solved your issue before.
Updating Blender to the Latest Version
Keeping Blender up-to-date ensures you have access to the latest features, improvements, and bug fixes. Here’s how to update Blender on Linux:
- Check the Current Version: Open Blender and go to Help > About Blender to check your current version.
- Visit the Official Blender Website: Go to https://www.blender.org/download/ to find the latest version of Blender.
- Download the Latest Version: Choose the Linux version and download the appropriate package for your system (e.g., .tar.xz file).
- Extract the Downloaded File: Use your file manager or the command line to extract the downloaded package. For command line, you can use tar -xf blender-x.x.x-linux64.tar.xz.
- Remove the Old Version (Optional): To avoid confusion, you may want to remove the old version of Blender. This step is optional and depends on your installation method.
- Run Blender: Navigate to the extracted folder and run Blender directly from there. You can create a desktop shortcut or a menu entry for easy access.
- Using a Package Manager (For Package Manager Installs): If you installed Blender via a package manager like APT or DNF, you can update Blender using the same tool. For example, sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade blender on Debian/Ubuntu systems.
- Using Snap or Flatpak: If you installed Blender through Snap or Flatpak, updates would typically be handled automatically. You can manually check for updates with snap refresh blender or flatpak update org.blender.Blender.
Remember, it’s important to back up your Blender settings and customizations before updating, especially if you’re performing a manual update.
_HOOK_
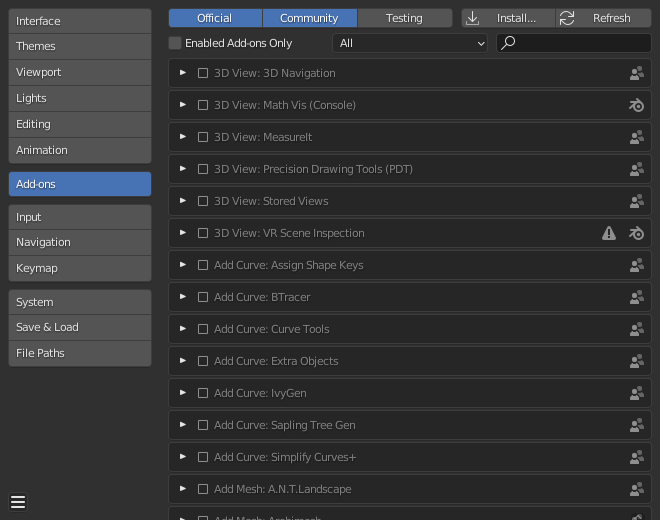
Extending Blender with Add-ons and Plugins
Blender\"s functionality can be greatly extended through the use of add-ons and plugins. Whether you\"re looking to improve your workflow, add new capabilities, or customize your environment, here\"s how you can install and manage these extensions on Linux:
- Access Blender Preferences: Start Blender and navigate to Edit > Preferences. In the Preferences window, switch to the Add-ons tab.
- Installing Add-ons: You can install add-ons in Blender either by downloading them from the internet or using the ones bundled with Blender. To install a downloaded add-on, click on the Install button in the top right corner of the Add-ons tab, navigate to the downloaded file (usually a .zip file), select it, and click Install Add-on.
- Enabling Add-ons: After installation, the add-on will appear in the list but will be disabled by default. Find the add-on you\"ve installed using the search bar or by browsing the list, and enable it by checking the box next to its name.
- Configuring Add-ons: Some add-ons come with configurable options. Once an add-on is enabled, if it has configurable settings, a Preferences button will appear next to its enable checkbox. Click this to adjust the add-on\"s settings to your liking.
- Updating Add-ons: For add-ons downloaded from external sources, you\"ll need to manually check for updates by visiting the original download page. To update, download the latest version and repeat the installation process to overwrite the old version. For bundled add-ons, updates are managed through Blender updates.
- Using Add-ons: Once installed and enabled, the add-on will integrate into Blender\"s interface. Depending on the add-on, new panels, menus, or tools will become available. Refer to the add-on\"s documentation for specific usage instructions.
- Recommended Add-ons: Explore Blender\"s extensive collection of add-ons for animation, modeling, rendering, and more. Popular add-ons include Node Wrangler for shader editing, BoolTool for boolean operations, and Auto-Rig Pro for character rigging.
For a vast selection of add-ons, both free and paid, visit the official Blender Marketplace or community forums. Remember to only download add-ons from reputable sources to avoid security risks.
Resources for Learning Blender on Linux
Blender offers a wealth of resources for both new and experienced users to learn and enhance their skills. Below are some of the most valuable resources available for Linux users:
- Official Blender Tutorials: The Blender website provides official tutorials that cover everything from the basics to advanced techniques. These tutorials are a great starting point for beginners.
- Blender Guru: A popular YouTube channel known for its high-quality tutorials and the famous \"Donut\" beginner tutorial series. It\"s an excellent resource for users of all levels.
- CG Cookie: Offers a mix of free and premium Blender tutorials that range from beginner to advanced levels, covering various aspects of Blender.
- Blender Artists Community: An online forum where Blender users from around the world share their knowledge, ask questions, and showcase their work.
- Blender Stack Exchange: A Q&A site for people who use Blender to create 3D graphics, animations, or games. It\"s a great place to find answers to specific questions.
- Books and eBooks: There are several books and eBooks available that cater to learning Blender. They range from introductory texts to advanced guides on specific aspects of Blender.
- Blender Network: Connect with professionals and enthusiasts in the Blender community. It\"s also a place to find Blender-related jobs and collaborations.
- Blender Cloud: Subscription service offering access to training videos, production assets, and exclusive content from Blender Foundation\"s open projects.
These resources, combined with practice and experimentation, can significantly enhance your Blender skills and knowledge, making the journey of learning Blender on Linux both productive and enjoyable.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Getting Started with Blender
Embarking on your Blender journey on Linux marks the beginning of an exciting adventure in 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. Here are some concluding thoughts to help you get started:
- Explore Blender\"s Interface: Spend some time familiarizing yourself with Blender\"s interface. It might seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes intuitive.
- Start Simple: Begin with simple projects to understand the basics of modeling, lighting, and texturing. Gradually move on to more complex tasks as you gain confidence.
- Utilize Resources: Make the most of the plethora of online tutorials, forums, and communities. Blender\"s official website and YouTube channels like Blender Guru offer invaluable guidance for learners at all levels.
- Practice Regularly: Like any software, proficiency in Blender comes with regular practice. Dedicate time to experimenting with different features and techniques.
- Contribute to the Community: Blender has a vibrant community. Sharing your work, seeking feedback, and helping others are great ways to learn and grow.
- Keep Updated: Blender is constantly evolving. Stay updated with the latest versions and features to make the most of what Blender has to offer.
With patience and perseverance, you\"ll find Blender to be an incredibly powerful tool for your creative projects. Happy blending!
Embrace the power of Blender on Linux to unlock your creative potential. With our comprehensive guide, diving into 3D modeling and animation has never been easier or more accessible. Start your Blender journey today!