Topic blender vs fusion 360: Discover the strengths and differences between Blender and Fusion 360, two leading 3D modeling tools, to empower your creative and engineering projects with the best software choice.
Table of Content
- What are the main differences between Blender and Fusion 360?
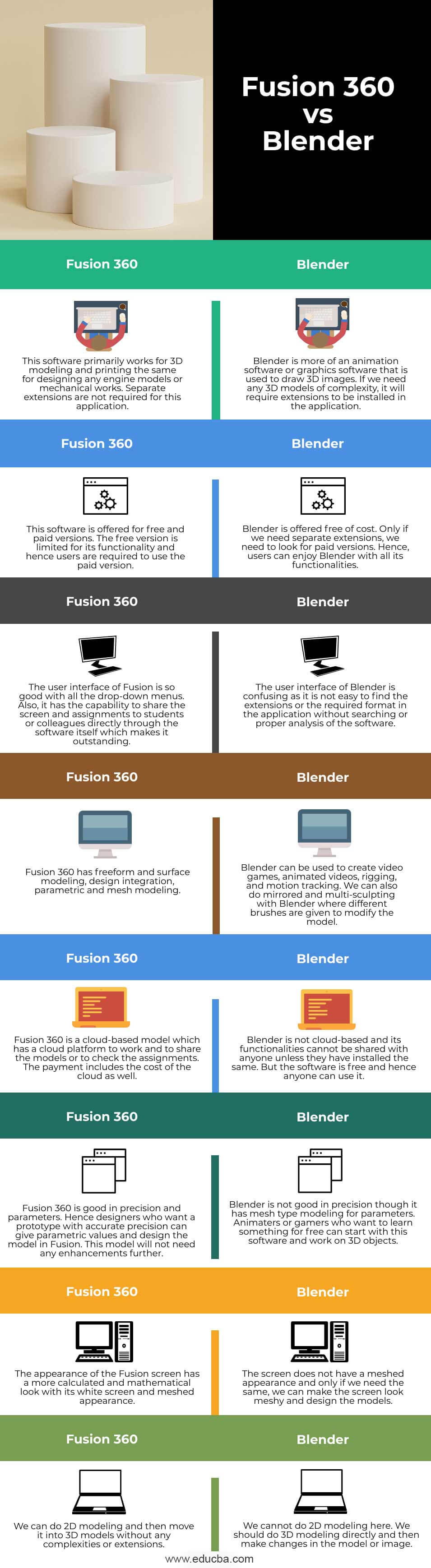
- Overview of Blender and Fusion 360
- Core Functionalities and Features
- User Interface and Experience
- 3D Modeling and Design Capabilities
- Support for Add-ons and Extensions
- YOUTUBE: Fusion 360 vs Blender: Best 3D Modeling Software for Beginners
- Application in Professional and Hobbyist Projects
- Compatibility and System Requirements
- Learning Curve and Community Support
- Cost, Licensing, and Availability
- Pros and Cons: A Comparative Summary
- Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
What are the main differences between Blender and Fusion 360?
The main differences between Blender and Fusion 360 can be summarized as follows:
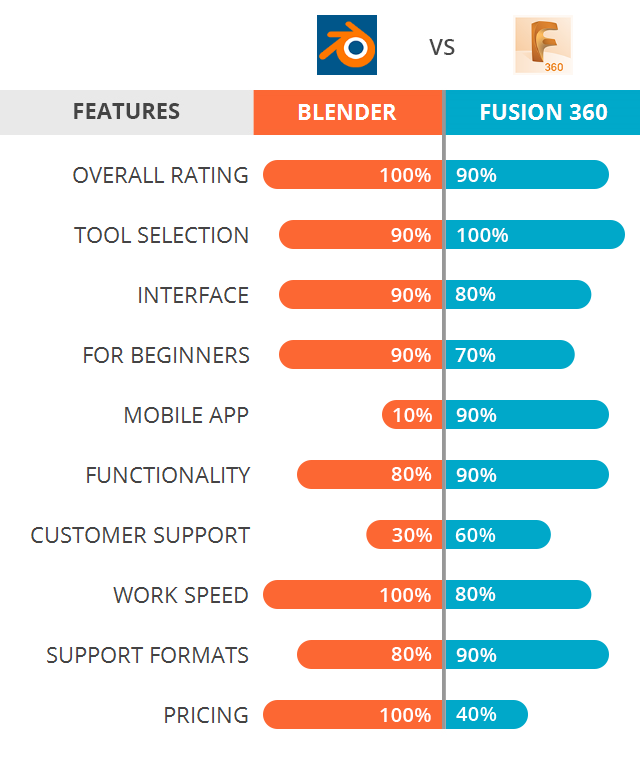
- Learning Curve: Blender has a steeper learning curve compared to Fusion 360, making it more involved and less intuitive for beginners.
- Functionality: Fusion 360 is primarily a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, specifically designed for engineering and manufacturing purposes. It offers advanced tools for parametric modeling, simulation, and collaboration. Blender, on the other hand, is a comprehensive 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software used for a wide range of purposes including visual effects, game development, and character animation.
- User Interface: Fusion 360 has a cleaner and less cluttered user interface, utilizing a familiar CAD ribbon-style menu that is easier for beginners to navigate. Blender, however, has a more complex and customizable interface with a wider range of features.
- 3D Printing: Fusion 360 is known for its strong capabilities in 3D printing design. It offers tools specifically tailored for 3D printing, making it easier to create objects that are ready for production. While Blender can also be used for 3D printing, it may require more manual adjustments and settings to ensure print readiness.
Ultimately, the choice between Blender and Fusion 360 depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you primarily require CAD functionality and ease of use for engineering purposes, Fusion 360 may be the better option. However, if you are looking for a more comprehensive and flexible software that covers a wide range of 3D modeling and animation tasks, Blender can be the preferred choice.
READ MORE:
Overview of Blender and Fusion 360
Blender and Fusion 360 are two of the most powerful and versatile 3D modeling software options available, catering to a wide range of creative and engineering needs. Both offer robust features but are tailored for different types of users and applications.
- Blender: An open-source 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software, ideal for artists and designers who require a comprehensive toolset for creating detailed 3D content, visual effects, and animations. It is well-suited for game development, film production, and digital art projects.
- Fusion 360: A cloud-based 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE tool developed by Autodesk, designed primarily for product design and manufacturing. It offers an integrated platform for CAD modeling, simulation, and collaboration, making it a favorite among engineers and product designers for its precision and professional-grade features.
While Blender excels in artistic and creative applications, Fusion 360 is renowned for its engineering and technical capabilities. The choice between Blender and Fusion 360 depends on the specific needs of the project, whether it\"s for artistic creation or engineering design.

Core Functionalities and Features
Both Blender and Fusion 360 offer a rich set of functionalities and features, making them powerful tools in their respective domains. Here\"s a breakdown of their core offerings:
- Blender:
- Comprehensive 3D modeling tools for creating, editing, and texturing models.
- Advanced animation features including rigging, skinning, and motion tracking.
- Realistic rendering capabilities with Cycles and Eevee engines.
- Simulation tools for fluids, smoke, fire, and soft body dynamics.
- Video editing and composition tools integrated into the software.
- Extensive library of add-ons and plugins for extended functionality.
- Fusion 360:
- Parametric and direct modeling to quickly iterate on design ideas.
- Simulation tools for testing the functionality and strength of designs.
- CAM integration for CNC machining workflows.
- PCB design integration for electronics projects.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools to share and review designs with team members.
- Generative design capabilities to explore design alternatives and optimize for material or cost.
While Blender is celebrated for its versatility in creative and artistic applications, Fusion 360 is distinguished by its comprehensive suite of engineering, design, and manufacturing tools. The choice between them hinges on whether the project\"s focus is on artistic creativity or technical precision.
User Interface and Experience
The user interfaces of Blender and Fusion 360 offer distinct experiences tailored to their respective audiences. Blender, known for its versatility in 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, presents a complex interface that can be customized extensively. Its comprehensive suite of tools supports a wide range of creative tasks, from animation to game development. However, this versatility comes with a steep learning curve, requiring time and effort to master.
On the other hand, Fusion 360, designed with engineering and product design in mind, features a more streamlined and intuitive interface. Its focus on CAD, CAM, and CAE applications makes it particularly user-friendly for those in product development. Fusion 360 integrates design, manufacturing, and electronics in a single platform, facilitating rapid prototyping and collaboration. The software\"s cloud-based nature allows for easy access to projects and collaboration with team members, although it does raise concerns regarding regulatory compliance and security for some businesses.
Both platforms offer extensive support and training resources. Blender boasts a vibrant community and a wealth of online tutorials, while Fusion 360 provides comprehensive documentation and learning materials, albeit with a focus on digital resources over in-person training. Each software caters to different needs and skill levels, emphasizing the importance of choosing the tool that best aligns with your project requirements and workflow preferences.
In summary, Blender is ideal for users seeking a broad range of 3D design and animation capabilities, while Fusion 360 is suited for those focused on product design and engineering projects. The choice between Blender and Fusion 360 ultimately depends on the specific needs of the user, the type of projects being undertaken, and the desired workflow efficiency.
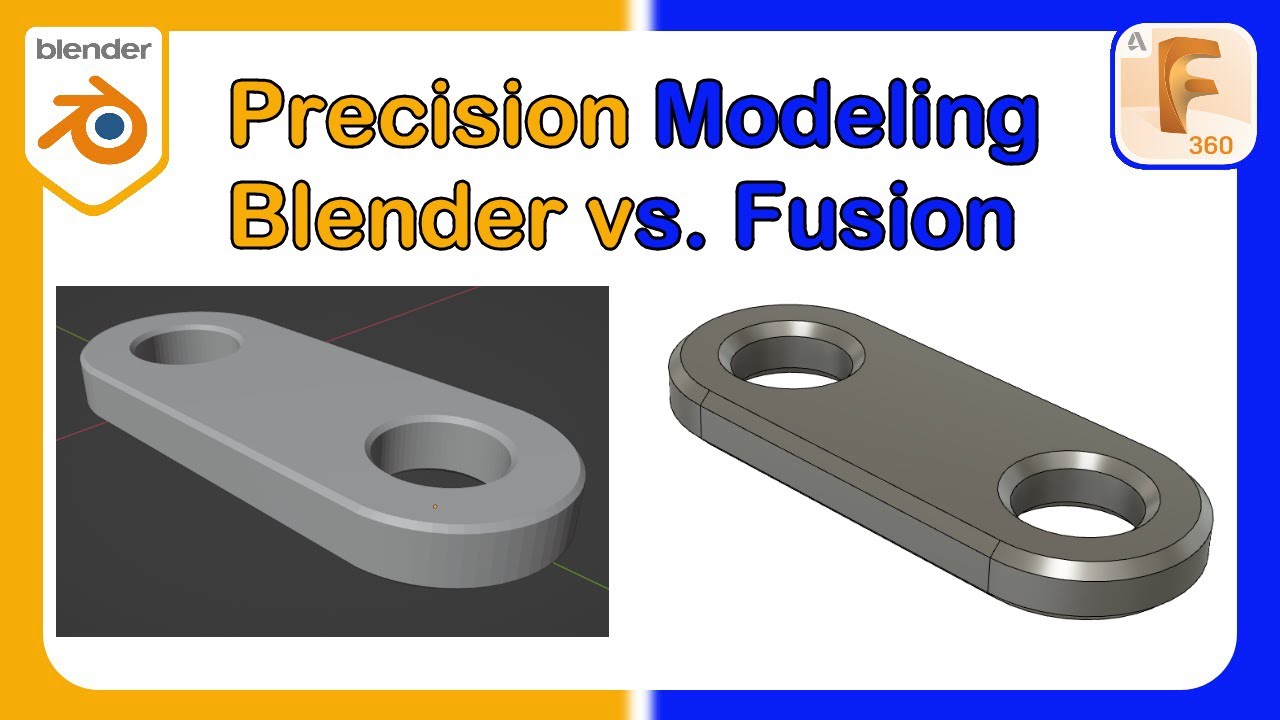
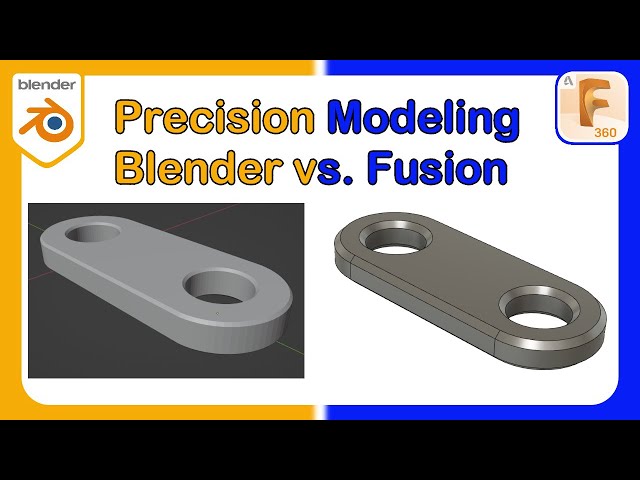
3D Modeling and Design Capabilities
Blender and Fusion 360 offer robust 3D modeling and design capabilities tailored to different user needs and project types. Blender shines with its comprehensive suite for animation, modeling, rigging, rendering, motion tracking, and creating composites. Its versatility extends to supporting a wide array of 3D formats, powerful rendering with the Cycles engine, and extensive customization through Python scripting. Blender excels in creating detailed and complex models, benefiting from features like N-Gon support, edge slide, sculpting with various brushes, and UV unwrapping tools for direct painting on models.
Fusion 360, designed for engineering, product design, and manufacturing, integrates CAD, CAM, and CAE tools in one platform. It streamlines product development with features like configurable design rules, a component library for using ready-made parts, and the ability to design electronics cooling systems. Fusion 360\"s unified development process aids in data management, real-time collaboration, and rapid prototyping. It supports generative design to optimize performance, reduce weight, and minimize parts usage. Additionally, Fusion 360\"s simulation environment and rendering tools allow for the thorough testing and presentation of designs.
- Blender is ideal for creative projects requiring detailed modeling, animation, and rendering.
- Fusion 360 caters to professional engineering and design projects with its integrated CAD/CAM/CAE environment.
Choosing between Blender and Fusion 360 depends on the project requirements, with Blender being a top choice for artistic and animation projects and Fusion 360 preferred for engineering and design workflows.
_HOOK_
Support for Add-ons and Extensions
Blender and Fusion 360 both offer robust support for add-ons and extensions, enhancing their capabilities and allowing users to customize their experience to better suit their project needs.
Blender is celebrated for its open-source nature, empowering users with a vast library of free and commercial add-ons. These add-ons extend Blender\"s functionality across a wide range of applications, from advanced modeling and animation to rendering and simulation. Blender integrates Python for scripting, which not only makes it flexible for creating custom add-ons but also for automating tasks, extending the interface, and rigging characters. This extensive support for add-ons makes Blender highly customizable, catering to a wide spectrum of 3D design and animation projects.
Fusion 360, on the other hand, offers extensions as a way to unlock advanced design and manufacturing capabilities within the software. These extensions are available directly within the Fusion 360 platform, allowing users to enhance their workflow with additional features as needed. Extensions cover a range of functionalities, including advanced machining strategies, generative design, additive manufacturing, and data management. Fusion 360\"s approach to extensions is modular, meaning users can select and pay for only the capabilities they need, on a monthly or annual subscription basis. This system is designed to keep the core software lightweight and efficient, focusing on enhancing productivity and collaboration without overwhelming the user interface with unnecessary features.
In summary, both Blender and Fusion 360 offer powerful ways to expand and tailor their functionalities through add-ons and extensions. Blender\"s open-source add-ons appeal to a broad community of users, from hobbyists to professionals, looking for no-cost or low-cost ways to enhance their software. Fusion 360\"s extensions cater to professionals needing advanced features in manufacturing and design, providing a scalable solution based on the specific needs of a project or organization.

Fusion 360 vs Blender: Best 3D Modeling Software for Beginners
Discover the amazing world of 3D modeling software and unlock your creative potential! Create stunning visualizations, designs, and animations with ease using this powerful tool. Watch the video now and step into a whole new dimension of digital artistry!
Fusion 360 vs Blender: Which is Superior for Hardsurface Modeling?
Experience the unparalleled quality and performance of our superior product. Designed with precision and engineered for excellence, our cutting-edge technology brings you a truly remarkable user experience. Watch the video to witness the extraordinary capabilities of our superior product.
Application in Professional and Hobbyist Projects
Blender and Fusion 360 serve distinct niches in the 3D modeling and design world, catering to both professional and hobbyist projects with their unique strengths.
Blender is renowned for its comprehensive suite of tools for artistic modeling, texturing, animation, and video editing. It is widely used by professionals in the film, animation, and game development industries for creating detailed 3D graphics, animations, and visual effects. Blender\"s capabilities extend to hobbyists and freelancers who leverage its open-source accessibility for a variety of creative projects. The software\"s sculpting tools are particularly favored for their organic feel, making it ideal for artists and digital animators focused on natural shapes and detailed textures.
Fusion 360, developed by Autodesk, focuses on the industrial side of design and manufacturing. It offers a complete CAD, CAM, and CAE suite that is invaluable for product design, simulation, and manufacturing projects. Fusion 360 is designed to facilitate collaboration among remote teams, providing effective data management, version control, and cloud computing. This software is essential for professionals in engineering, development, and production, enabling them to create detailed designs, simulate real-world conditions, and manufacture prototypes efficiently. It also supports 3D printing, making it a versatile tool for product developers.
Both platforms offer support for educational and small business settings, with Fusion 360 being particularly beneficial for small businesses in product development due to its specialized tools. While Fusion 360 operates on a subscription model, Blender remains free, providing a valuable resource for students and educators. Despite their differing focuses, both Blender and Fusion 360 have been used in notable projects, with Blender being used to create entire animated films like Netflix\"s Next Gen and Fusion 360 being utilized in the development of innovative products like lightweight drone frames.
In summary, Blender and Fusion 360 cater to a wide range of applications from creative artistic projects to precise engineering designs. Their selection depends on the specific needs of the project, whether it is for professional use in the film and gaming industries or for detailed product design and manufacturing in the engineering field.

Compatibility and System Requirements
Both Blender and Fusion 360 cater to a wide range of users, from hobbyists to professionals, and are designed to work on most modern computer systems. However, their system requirements do vary slightly, reflecting their different use cases and operational needs.
Blender System Requirements
- Operating System: Windows 8.1, 10, and 11; macOS 10.15 Intel, 11.0 Apple Silicon; Linux distributions using glibc 2.28 or newer.
- Minimum Hardware: 64-bit quad-core CPU with SSE4.2 support, 8 GB RAM, Full HD display, mouse or pen+tablet, 2 GB VRAM Graphics Card supporting OpenGL 4.3.
- Recommended Hardware: 64-bit eight core CPU, 32 GB RAM, 2560×1440 display, three-button mouse or pen+tablet, 8 GB VRAM Graphics Card.
- Blender is highly portable, requiring no installation and can run directly from a USB stick.
Fusion 360 System Requirements
- Operating System: macOS (Ventura, Monterey, Big Sur) or Windows 11/Windows 10 (Version 1809 or newer).
- CPU: 64-bit processor with 4 cores or more; 1.7 GHz or greater for Intel-based Mac devices or Apple Silicon ones (through Rosetta 2 emulation).
- RAM: Minimum 16 GB recommended for smooth operation in creative workflows, with 32 GB preferred for more complex projects.
- Graphics: Integrated graphics for basic designs; dedicated GPU recommended for more complex tasks to improve performance in viewport, textures, and effects.
- Fusion 360\"s performance benefits from CPUs with high single-core performance. Intel Core i7 or AMD Ryzen processors are recommended for optimal performance.
Blender supports a range of graphics cards from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel, ensuring broad compatibility across devices. Fusion 360, while less demanding on the GPU, benefits from a dedicated graphics card for more detailed designs. Both software are compatible with the latest operating systems and hardware, but checking for the most recent system requirements on their official websites is recommended to ensure compatibility.

Learning Curve and Community Support
Blender and Fusion 360 both offer robust tools for 3D modeling, but they differ significantly in terms of learning curve and community support, reflecting their distinct user bases and applications.
Blender Learning Curve and Community Support
Blender is known for its steep learning curve, attributed to its extensive range of features and less intuitive user interface. However, it compensates with a vast, active community and a wealth of learning resources. The open-source nature of Blender fosters a supportive environment where users share knowledge, tutorials, and add-ons freely. This community support makes Blender especially appealing to newcomers eager to learn through community engagement and extensive online tutorials.
Fusion 360 Learning Curve and Community Support
Fusion 360, while also complex, is often seen as having a more accessible learning curve for beginners, particularly those with a background in engineering or product design. Its user interface is designed to be more intuitive, with streamlined workflows that cater to its core audience in product development and manufacturing. Autodesk provides comprehensive support through tutorials, documentation, and a responsive community. The community around Fusion 360 is very active, offering help and sharing knowledge on forums and through various online platforms, making it easier for new users to find assistance and learn the software.
Both Blender and Fusion 360 have extensive online communities and resources aimed at helping users master the software. Whether through forums, video tutorials, or official documentation, users of both platforms can find the support they need to overcome the initial learning hurdles. Choosing between Blender and Fusion 360 often comes down to the specific needs and background of the user, with Blender being favored for its broad application in creative projects and Fusion 360 for its specialized tools in engineering and product design.

Cost, Licensing, and Availability
Blender and Fusion 360 cater to different audiences with varying pricing models, licensing terms, and availability, reflecting their distinct applications in the 3D design and engineering spaces.
Blender
- Cost: Blender is completely free to use. It is an open-source software licensed under the GPL, making it accessible to everyone without any cost.
- Licensing: The open-source nature of Blender allows users to modify, distribute, and use the software for any purpose, commercial or non-commercial, without any licensing fees.
- Availability: Blender can be downloaded and used on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring wide accessibility for users across different operating systems.
Fusion 360
- Cost: Fusion 360 uses a subscription-based pricing model. It offers a free version for students, educators, and hobbyists, but professionals need to subscribe to a paid plan for full access to its features.
- Licensing: The licensing for Fusion 360 is structured around different user needs, offering options for personal, educational, or commercial use, each with specific terms and conditions.
- Availability: Being a cloud-based platform, Fusion 360 requires internet access for most of its functionalities. It supports a variety of operating systems, including Windows and macOS, making it broadly accessible with an emphasis on connectivity and collaboration.
While Blender appeals to users looking for a no-cost, versatile tool for 3D modeling, animation, and more, Fusion 360 targets professionals and hobbyists in the engineering and product design fields with a more focused set of tools and collaborative features, all under a subscription-based model.
.jpg)
_HOOK_
Pros and Cons: A Comparative Summary
Blender and Fusion 360 each have their strengths and weaknesses, tailored to different types of users and purposes. Below is a comparative summary of their pros and cons, highlighting their primary advantages and limitations.
Blender
- Pros:
- Free and open-source, accessible to everyone without cost.
- Powerful rendering engine with cycles, allowing complex and accurate rendering.
- Highly versatile for a wide range of applications from 3D modeling, animation, video editing, and more.
- Large community support with extensive learning resources available.
- Python scripting for automation, customization, and extension.
- Cons:
- Steep learning curve, making it potentially difficult for beginners.
- Limited particle system which might hinder some specific operations.
- Lacks a cloud-based system for sharing work unless the software is installed on another device.
Fusion 360
- Pros:
- Cloud-based, facilitating collaboration and remote work with ease.
- User-friendly interface suitable for beginners and students.
- Free for non-commercial use, with access to full features for students, educators, and hobbyists.
- Integrates CAD, CAM, and CAE tools for comprehensive design and manufacturing processes.
- Cons:
- Subscription-based for commercial use, which might be a barrier for some users.
- Requires internet access for most functionalities due to its cloud-based nature.
- Can be resource-intensive, taking up significant memory space on the device.
- Some users might find it less intuitive if unfamiliar with CAD or 3D modeling software.
Ultimately, the choice between Blender and Fusion 360 should be based on your specific needs, expertise level, and project requirements. Blender excels in creative and artistic projects, offering a wide range of tools for animation and visual effects. In contrast, Fusion 360 is tailored for engineering and design, with powerful tools for CAD, CAM, and CAE, making it ideal for product development and manufacturing processes.
READ MORE:
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
When deciding between Blender and Fusion 360, the best choice depends on your specific needs, skill level, and project requirements. Here\"s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
- Project Type:
- If your work primarily involves 3D modeling, animation, or rendering for creative projects such as video games, films, or art, Blender is highly recommended due to its comprehensive set of tools for artistic endeavors.
- For engineering-focused projects that require precise measurements, CAD, CAM, or 3D printing, Fusion 360 offers specialized tools for product design and manufacturing, making it the better choice.
- User Experience:
- Blender is known for its steep learning curve but offers extensive resources and a large community for support. It\"s well-suited for users willing to invest time in learning complex 3D modeling and animation techniques.
- Fusion 360 provides a more streamlined experience for CAD design, with user-friendly tools that are easier for beginners to grasp, especially for those with an engineering background.
- Compatibility and System Requirements:
- Consider your hardware capabilities. Blender works well on most systems, including lower-end hardware, while Fusion 360 requires a more robust setup for optimal performance.
- Cost Considerations:
- Blender is completely free and open source, making it an attractive option for individuals and small studios looking to minimize software costs.
- Fusion 360 offers a free version for hobbyists and startups but requires a paid subscription for professional use, which includes advanced features and support.
- Community and Support:
- Both software have strong communities. Blender\"s community is vast, offering a wide range of tutorials, forums, and resources. Fusion 360 also has a dedicated user base with professional support and resources, particularly beneficial for those in engineering fields.
- Future Project Expansion:
- Consider your long-term goals. If you aim to expand into areas like game development or film production, Blender\"s extensive features may serve you well. Conversely, if your path leans towards product design or manufacturing, Fusion 360\"s specialized tools will likely be more beneficial.
In summary, Blender is ideal for artists and designers seeking a powerful, cost-effective tool for 3D creation, whereas Fusion 360 is suited for professionals and hobbyists in the engineering and product design sectors looking for precise, technical modeling capabilities. Evaluate your specific needs, project types, and personal learning curve to choose the tool that best aligns with your goals.
Choosing between Blender and Fusion 360 ultimately hinges on your project\"s nature and your creative or engineering ambitions. Explore each tool\"s unique strengths to unlock your full potential in 3D design and innovation.