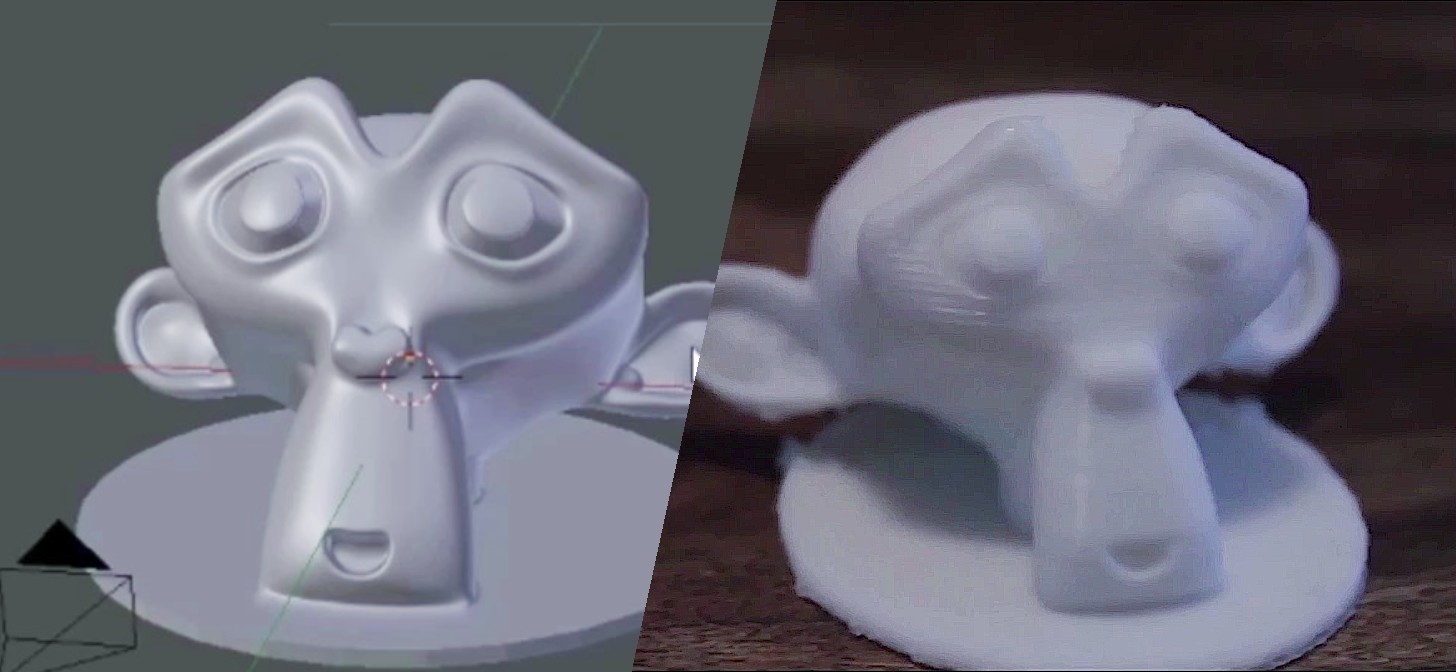
Topic blender for 3d printing: Discover how Blender, the powerful free 3D modeling software, transforms the realm of 3D printing, enabling artists and engineers to bring their most intricate designs to life with precision and ease.
Table of Content
- How can Blender be used for 3D printing?
- Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Optimizing Models for 3D Printing
- Learning Resources
- Optimizing Models for 3D Printing
- Learning Resources
- Learning Resources
- YOUTUBE: Learn Blender for 3D Printing - Complete Quick and Easy Guide
- Introduction to Blender and Its Importance in 3D Printing
- Key Features of Blender for 3D Printing
- Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Optimizing Your Models for 3D Printing
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Techniques in Blender for Professional Quality Prints
- Comparing Blender with Other 3D Modeling Software for 3D Printing
- Community and Resources for Learning More About Blender
- Future of 3D Printing and Blender\"s Role
- Conclusion: Why Blender is Your Go-to Software for 3D Printing
How can Blender be used for 3D printing?
To use Blender for 3D printing, follow these steps:
- Create or import your 3D model in Blender.
- Ensure that your model is correctly scaled and oriented for 3D printing.
- Use Blender\'s tools to optimize the model for printing, such as checking for non-manifold geometry and ensuring watertight meshes.
- Add any supports or rafts that may be needed for printing complex models.
- Export your model in a file format supported by your 3D printer, such as STL or OBJ.
- Transfer the exported file to your 3D printer software and prepare it for printing, adjusting settings as necessary.
- Start the printing process and monitor it to ensure a successful print.
READ MORE:
Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
Blender offers an extensive range of tools for designing 3D printable models. From basic shapes to complex sculptures, users can learn to optimize their models for 3D printing by scaling, applying modifiers, and exporting in the appropriate formats. Blender\"s interface facilitates the creation, transformation, and editing of models, making it accessible to users of all skill levels.
Key Features for 3D Printing
- 3D Printing Toolbox: Allows for analysis of your mesh to identify and fix errors that could affect printing.
- Real-time Mesh Analysis: Offers immediate feedback on potential issues with your model.
- Exporting Models: Guides on exporting models in formats compatible with 3D printers.
Optimizing Models for 3D Printing
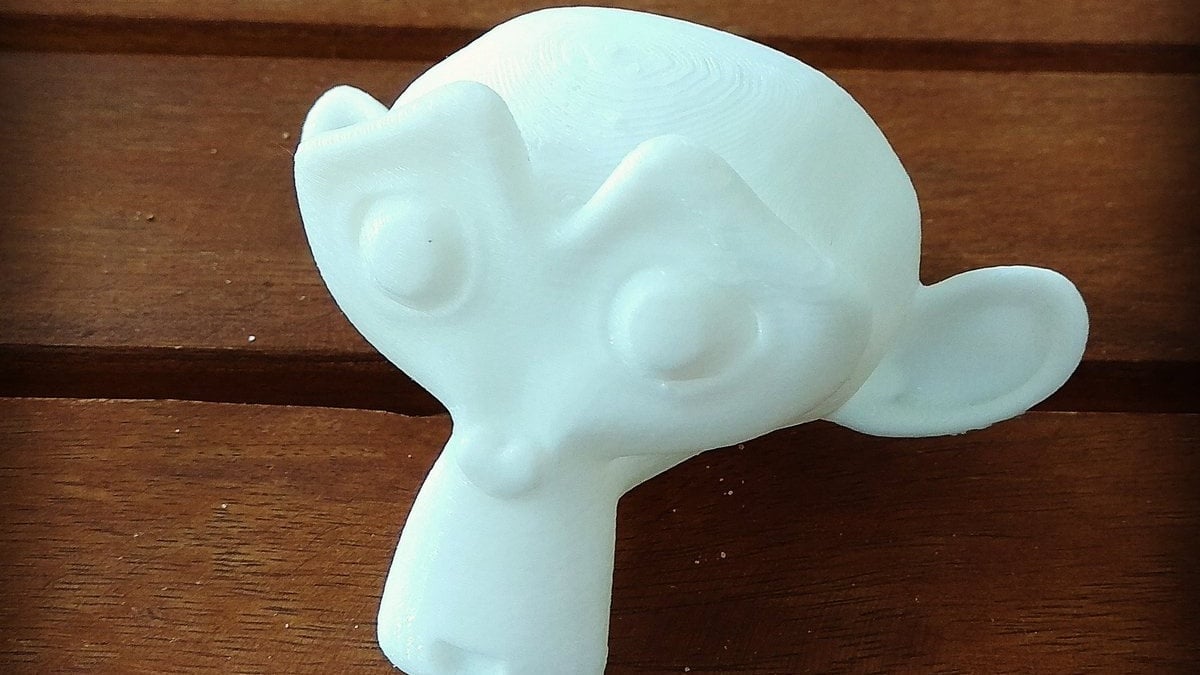
Ensuring your model is ready for 3D printing involves checking for non-manifold edges and making sure your mesh meets the requirements of your 3D printer. Blender\"s tools help in identifying these issues and offer solutions to correct them before exporting your model as an STL file, which is commonly used in 3D printing.
Design Tips and Best Practices
- Start with simple models to familiarize yourself with Blender\"s tools and features.
- Use the 3D Printing Toolbox to check for and fix any errors in your model.
- Experiment with different modifiers and settings to achieve the desired level of detail and complexity.
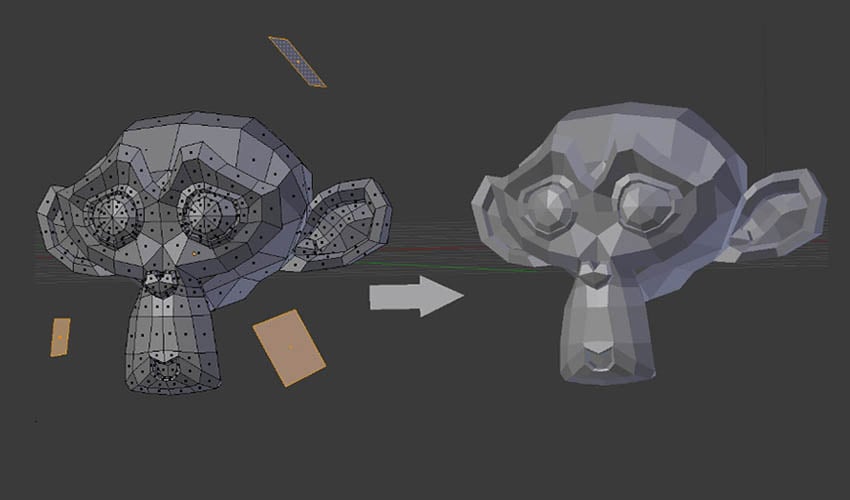
Learning Resources
For those new to Blender or 3D printing, a multitude of tutorials and guides are available online. These resources range from beginner to advanced levels, covering everything from the basics of 3D modeling to detailed instructions on preparing your models for 3D printing.
Conclusion
Blender\"s comprehensive toolset, combined with its 3D Printing Toolbox, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing. Whether you are creating simple objects or intricate designs, Blender provides all the necessary tools to bring your ideas to life.

Optimizing Models for 3D Printing
Ensuring your model is ready for 3D printing involves checking for non-manifold edges and making sure your mesh meets the requirements of your 3D printer. Blender\"s tools help in identifying these issues and offer solutions to correct them before exporting your model as an STL file, which is commonly used in 3D printing.
Design Tips and Best Practices
- Start with simple models to familiarize yourself with Blender\"s tools and features.
- Use the 3D Printing Toolbox to check for and fix any errors in your model.
- Experiment with different modifiers and settings to achieve the desired level of detail and complexity.
_HOOK_
Learning Resources
For those new to Blender or 3D printing, a multitude of tutorials and guides are available online. These resources range from beginner to advanced levels, covering everything from the basics of 3D modeling to detailed instructions on preparing your models for 3D printing.
Conclusion
Blender\"s comprehensive toolset, combined with its 3D Printing Toolbox, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing. Whether you are creating simple objects or intricate designs, Blender provides all the necessary tools to bring your ideas to life.
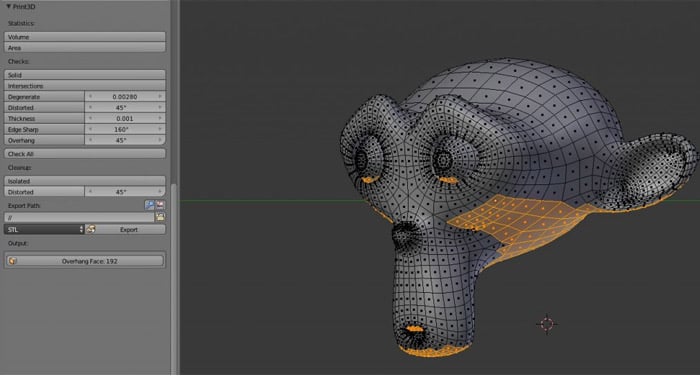
Learning Resources
For those new to Blender or 3D printing, a multitude of tutorials and guides are available online. These resources range from beginner to advanced levels, covering everything from the basics of 3D modeling to detailed instructions on preparing your models for 3D printing.
Conclusion
Blender\"s comprehensive toolset, combined with its 3D Printing Toolbox, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing. Whether you are creating simple objects or intricate designs, Blender provides all the necessary tools to bring your ideas to life.

Learn Blender for 3D Printing - Complete Quick and Easy Guide
Modeling: \"Watch our exciting video showcasing the world of modeling, where beauty meets creativity. See top models strut their stuff on the runway and discover the glamorous and captivating life of a model.\" Printing: \"Discover the fascinating process of printing in our informative video. From digital to traditional methods, learn how designs come to life on paper. Explore the world of printing with us!\"
Learn Blender for 3D Printing - Complete Quick and Easy Guide
Modeling: \"Watch our exciting video showcasing the world of modeling, where beauty meets creativity. See top models strut their stuff on the runway and discover the glamorous and captivating life of a model.\" Printing: \"Discover the fascinating process of printing in our informative video. From digital to traditional methods, learn how designs come to life on paper. Explore the world of printing with us!\"
Introduction to Blender and Its Importance in 3D Printing
Blender, an open-source 3D modeling software, has revolutionized the way designers, artists, and engineers approach 3D printing. Since its inception in 2002, Blender has grown in popularity, offering a robust suite of tools for creating detailed 3D models. With the release of Blender version 2.67, the software enhanced its capabilities for 3D printing through features like the 3D Printing Toolbox and real-time Mesh Analysis, making it easier than ever to prepare models for printing.
The importance of Blender in the 3D printing community cannot be overstated. It provides a powerful, yet free, toolset for creating everything from simple objects to intricate designs that are ready for 3D printing. Its comprehensive features allow users to sculpt, model, and edit their creations with precision, ensuring that their designs are not only imaginative but also printable.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: A feature that analyzes meshes for common 3D printing issues, offering solutions to fix them.
- Real-time Mesh Analysis: This tool provides instant feedback on the printability of your model, highlighting areas that may cause problems during the printing process.
- Export Options: Blender supports exporting models in formats compatible with most 3D printers, simplifying the transition from design to print.
Blender\"s role in the 3D printing workflow is invaluable. It serves not only as a design and modeling platform but also as a bridge between the digital and physical worlds. Whether for hobbyists, educators, or professionals, Blender equips users with the skills and tools necessary to bring their visions to life through 3D printing.

Key Features of Blender for 3D Printing
Blender is equipped with a range of features specifically designed to enhance the 3D printing process. These features not only streamline the design phase but also ensure that models are optimized for printing, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving print quality.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: This tool provides users with a comprehensive analysis of their models, identifying and offering solutions for issues that could impact the printing process. It checks for common errors such as non-manifold edges, overhangs, and wall thickness.
- Real-time Mesh Analysis: Blender offers real-time feedback on the printability of models, highlighting potential problems and allowing for immediate corrections. This feature is invaluable for ensuring that models are ready for printing without the need for extensive post-processing.
- Support for STL and OBJ Files: Blender supports the export of models in STL and OBJ formats, which are widely used in 3D printing. This compatibility simplifies the transition from model to print, making Blender a versatile tool for 3D printing projects.
- Advanced Modeling Tools: With a wide array of modeling tools, Blender allows for the creation of detailed and complex models. These tools include sculpting, retopology, and modifiers, which are essential for creating print-ready designs.
- Customizable Interface and Workflow: Blender\"s interface is highly customizable, enabling users to tailor the software to their specific needs. This flexibility allows for a more efficient workflow, particularly when working on complex 3D printing projects.
These key features make Blender an ideal choice for anyone involved in 3D printing, from hobbyists creating simple objects to professionals developing intricate designs. By leveraging Blender\"s capabilities, users can expect a smoother design-to-print process, resulting in higher quality prints.
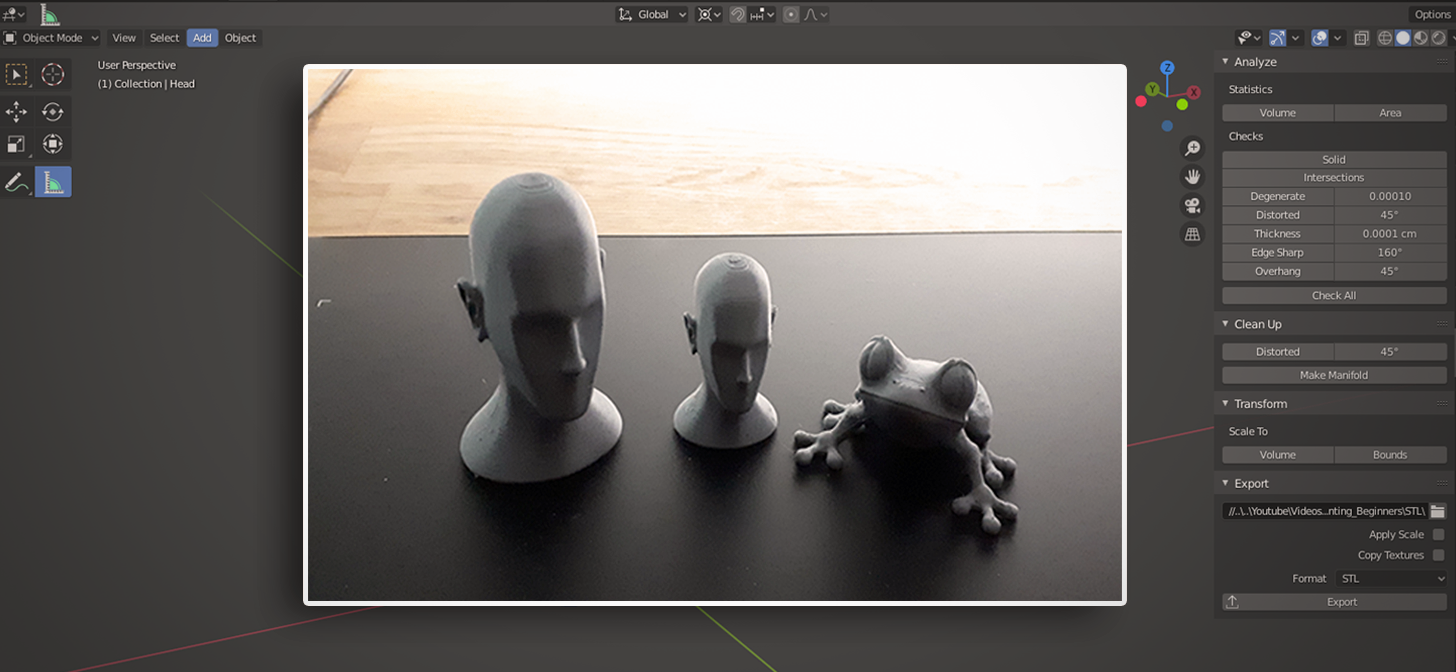
Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
Embarking on your 3D printing journey with Blender begins with understanding its interface and the core features that make it a powerful tool for 3D modeling. This section will guide you through the initial steps, from downloading Blender to creating your first 3D printable model.
- Download and Install Blender: Blender is free and open-source. Download it from the official website to ensure you have the latest version.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Interface: Blender\"s interface might seem daunting at first, but it\"s designed for efficiency. Spend some time exploring the layout, panels, and shortcuts.
- Start with Basic Shapes: Begin by experimenting with Blender\"s basic shapes to understand how to manipulate objects in 3D space.
- Learn the Tools: Blender offers a variety of tools for modeling, sculpting, and editing. Tutorials can be incredibly helpful in learning how to use these tools effectively for 3D printing.
- Use the 3D Printing Toolbox: This addon is essential for preparing your models for 3D printing. It helps identify and fix common issues like non-manifold edges or thin walls.
- Practice Modeling: Try to create simple objects that you can print. This will give you a sense of how models transition from the digital to the physical world.
- Export Your Model: Once satisfied with your model, export it in a 3D printing-friendly format such as STL or OBJ.
Remember, mastering Blender for 3D printing takes time and practice. Start with simple projects to build your confidence and gradually move on to more complex models as you become more comfortable with the software.
_HOOK_
Optimizing Your Models for 3D Printing
Optimizing models for 3D printing is a crucial step in the design process to ensure successful prints. Blender offers several tools and features to help prepare and refine your models for the best possible outcomes. This section outlines essential tips and strategies for optimizing your 3D models in Blender.
- Check for Non-Manifold Edges: Non-manifold edges can cause issues during printing. Use Blender\"s 3D Printing Toolbox to identify and repair these edges.
- Ensure Wall Thickness: Models must have sufficient wall thickness to be printed. Blender can help you visualize and adjust the thickness of your model\"s walls to meet printing requirements.
- Reduce Mesh Complexity: Simplify your model without losing detail to reduce printing time and material usage. Blender\"s modifiers, such as Decimate, can help reduce polygon count while maintaining the model\"s integrity.
- Optimize Overhangs: Overhangs require support structures during printing. Use Blender to adjust the angle of overhangs or add manual supports to minimize post-processing.
- Scale and Dimensions: Accurately set your model\"s scale and dimensions in Blender to match the desired physical size. Use the unit system that corresponds with your 3D printer\"s requirements.
- Export in the Correct Format: Export your optimized model in a format compatible with your 3D printer, typically STL or OBJ. Blender provides options to ensure the exported file is ready for slicing.
By following these steps, you can prepare your models in Blender for a seamless transition from digital design to physical object, enhancing the quality and reliability of your 3D prints.
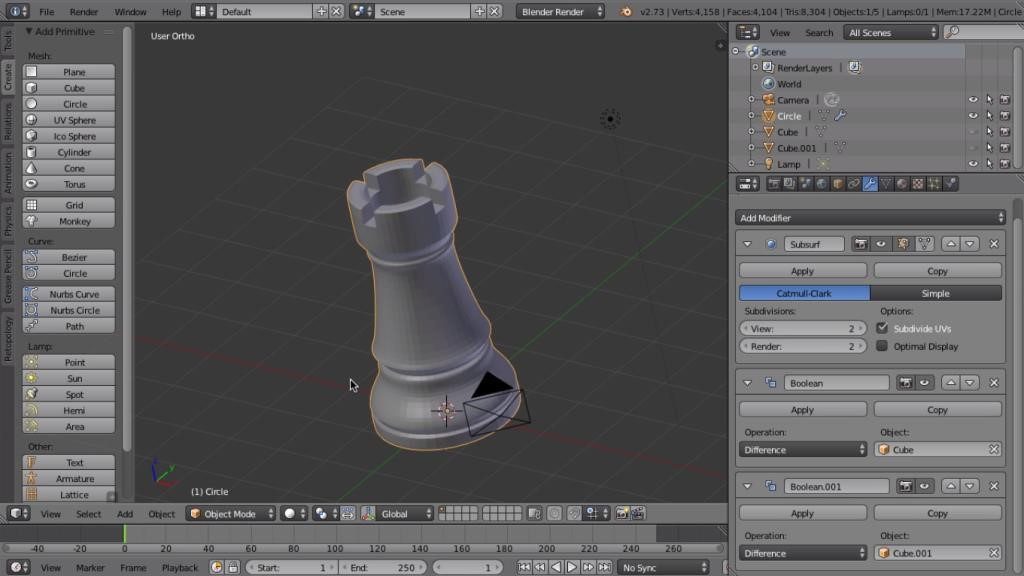
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Navigating through the intricacies of 3D printing with Blender can sometimes be challenging. Awareness of common pitfalls and understanding how to avoid them is crucial for a smooth design-to-print process. Here are some key pitfalls and strategies to avoid them:
- Ignoring Mesh Errors: Before exporting your model for printing, ensure that all mesh errors, such as non-manifold edges or intersecting faces, are fixed. Utilize Blender\"s 3D Printing Toolbox to identify and rectify these issues.
- Overlooking Scale and Units: A common mistake is not setting the correct scale and units in Blender to match the physical world dimensions. Always double-check the scale of your model and set the units (metric or imperial) according to your 3D printer\"s specifications.
- Inadequate Wall Thickness: Models with walls too thin to be printed can lead to failure. Use the Thickness tool in Blender to measure and adjust walls to meet the minimum thickness required by your printer.
- Complex Models Without Support: Printing complex models without adequate support structures can result in print failures. Plan and generate necessary supports within Blender or your slicing software to ensure model stability during printing.
- High-Poly Models: Extremely detailed models with high polygon counts can cause slicing software to crash or extend print times unnecessarily. Use Blender\"s decimation tools to reduce polygon count without significantly affecting the model\"s appearance.
- Exporting Incorrect File Types: Ensure you export your model in a file format compatible with your 3D printer, typically STL or OBJ. Incorrect file formats can lead to printing errors or compatibility issues.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls and applying the recommended solutions, you can enhance your Blender to 3D printing workflow, resulting in successful and high-quality prints.
Advanced Techniques in Blender for Professional Quality Prints
For those aiming to achieve professional quality prints with Blender, mastering advanced techniques is essential. These methods not only improve the aesthetics of your 3D prints but also enhance their structural integrity and functionality. Below are some advanced strategies to elevate your 3D printing projects.
- Boolean Operations for Complex Shapes: Utilize Boolean modifiers to combine or subtract mesh objects, allowing for intricate designs and seamless assemblies in your 3D prints.
- Non-Destructive Modeling with Modifiers: Employ Blender’s array of modifiers for non-destructive editing, enabling flexible design adjustments without permanently altering the base geometry. This approach is ideal for iterative design processes.
- Sculpting for Detailed Textures: Use Blender\"s sculpting tools to add fine details and textures to your models, enhancing their realism and tactile qualities.
- Topology Optimization for Print Efficiency: Optimize your model\"s topology to balance detail with print efficiency. Proper topology ensures smoother surfaces and minimizes printing errors.
- Custom Support Structures: Design custom support structures directly within Blender to support overhangs and complex geometries, reducing material use and post-processing time compared to auto-generated supports.
- Material Simulation for Realistic Previews: Simulate different materials and finishes within Blender to visualize the final look of your print, aiding in material selection and finish techniques.
- Multi-Part Models for Assembly: Design models in separate parts for complex assemblies or large prints. This technique facilitates easier printing, handling, and post-processing.
Implementing these advanced techniques in Blender can significantly improve the quality and functionality of your 3D prints, pushing the boundaries of what\"s possible in 3D printing.
Comparing Blender with Other 3D Modeling Software for 3D Printing
Blender stands out in the 3D printing community for its comprehensive features and open-source accessibility. However, when considering software for 3D printing projects, it\"s essential to understand how Blender compares with other popular 3D modeling tools. This comparison highlights the strengths and considerations of using Blender versus other software like Fusion 360, Maya, and Tinkercad for 3D printing.
- Cost and Accessibility: Blender is free and open-source, offering powerful modeling capabilities without the expense. In contrast, software like Maya is subscription-based, which may be a barrier for hobbyists or independent designers.
- User Interface and Usability: Blender has a steep learning curve but offers extensive customization and a vast array of tools. Software like Tinkercad is designed for beginners, offering a more user-friendly experience but with limited capabilities.
- Features for 3D Printing: Blender\"s 3D Printing Toolbox and real-time Mesh Analysis are specifically tailored for 3D printing, offering detailed analysis and preparation tools. Fusion 360, while also comprehensive, is more CAD-oriented but still highly effective for 3D printing projects.
- Community and Support: Blender boasts a large, active community, providing a wealth of tutorials, forums, and resources. While other software options have support, Blender\"s community is particularly notable for its openness and collaborative spirit.
- Flexibility and Scope: Blender is versatile, catering to a wide range of 3D modeling, animation, and rendering needs beyond 3D printing. Software like SolidWorks, while excellent for engineering applications, may not offer the same breadth of creative tools.
Each software has its unique strengths and suitability depending on the user\"s needs, project requirements, and skill level. Blender is particularly appealing for those seeking a no-cost solution with professional-grade features, whereas other programs may be preferred for their specialized functions or ease of use for beginners.
Community and Resources for Learning More About Blender
The Blender community is vibrant and supportive, offering an array of resources for both beginners and advanced users looking to dive into 3D printing. Below, we explore some of the best platforms and resources to accelerate your learning curve and enhance your 3D printing projects with Blender.
- Blender Studio: Offers comprehensive training for 3D printing, covering basics to advanced techniques. Ideal for those looking to deepen their understanding of Blender\"s capabilities.
- Blender Artists Community: An active forum where users share their projects, ask for help, and provide feedback to others. A great place to find inspiration and practical advice.
- BlenderNation: This blog covers the latest news, tutorials, and showcases from the Blender community. It\"s a useful resource for staying updated on new features and community projects.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer structured courses on Blender for 3D printing, catering to different skill levels from beginner to advanced.
- YouTube Tutorials: A wealth of free tutorials is available on YouTube, covering everything from basic modeling to complex printing preparations in Blender.
- Maker Tales Academy: Focuses on using Blender for practical 3D printing projects, helping makers bring their ideas to life.
- Thingiverse: While not Blender-specific, Thingiverse is an excellent source for 3D printable models. It can inspire your projects and help you understand how to structure models for printing.
Leveraging these resources can significantly enhance your Blender skills and improve your 3D printing outcomes. The community\"s willingness to share knowledge and resources makes learning Blender an enriching experience for anyone interested in 3D printing.
_HOOK_
Future of 3D Printing and Blender\"s Role
The future of 3D printing is poised for expansive growth, transforming industries from healthcare to architecture with innovative applications. As this technology evolves, Blender\"s role becomes increasingly significant, offering robust tools and features to meet the demands of future 3D printing projects. Below, we explore how Blender aligns with the anticipated trends and advancements in 3D printing.
- Increased Accessibility: As 3D printing becomes more accessible, Blender\"s free and open-source nature makes it an ideal tool for educators, hobbyists, and startups to explore and innovate within the 3D printing space.
- Advanced Material Usage: Future 3D printing technologies will utilize a broader range of materials. Blender\"s comprehensive material simulation features will be crucial for designers to prototype and visualize their creations with these new materials.
- Complex Geometries and Customization: The demand for complex, customized 3D prints is growing. Blender\"s sophisticated modeling and sculpting tools enable the creation of intricate designs that are ready for 3D printing, catering to this demand.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: As 3D printing intersects with other technologies like AI and VR, Blender\"s adaptability and community-driven development ensure it remains at the forefront of these integrations, offering users innovative ways to design and print.
- Sustainability in 3D Printing: With a growing focus on sustainability, Blender\"s efficiency in modeling and resource management will play a vital role in designing eco-friendly and material-efficient prints.
Blender\"s continuous development, driven by its community and the Blender Foundation, ensures it stays aligned with the future needs of 3D printing. Its adaptability, comprehensive toolset, and open-source philosophy make Blender an invaluable asset in pushing the boundaries of what\"s possible in the world of 3D printing.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Why Blender is Your Go-to Software for 3D Printing
In the realm of 3D printing, Blender distinguishes itself as an indispensable tool, blending powerful features with unparalleled accessibility. Its significance extends beyond its no-cost offering, presenting a suite of advanced tools tailored for 3D printing. Here are key reasons why Blender stands out as the premier choice for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
- Comprehensive Toolset: From modeling to texturing, Blender offers a complete range of tools for creating detailed and print-ready models, accommodating both simple and complex project needs.
- 3D Printing Specific Features: The inclusion of the 3D Printing Toolbox and real-time mesh analysis ensures models are optimized for printing, minimizing errors and enhancing print quality.
- Active Community Support: Blender is supported by a vast community of users and developers, providing resources, tutorials, and plugins to enhance your 3D printing projects.
- Continuous Improvement: Being open-source, Blender undergoes constant updates and improvements, integrating the latest technologies and user feedback to remain at the cutting edge of 3D modeling and printing.
- Versatility: Blender\"s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications beyond 3D printing, including animation, VFX, and game development, making it a valuable skill set for any digital artist or designer.
Blender\"s alignment with the future of 3D printing, combined with its robust feature set, community support, and adaptability, solidifies its position as the go-to software for 3D printing. Whether you are a novice exploring the possibilities of 3D printing or a professional refining your craft, Blender offers the tools and resources to bring your visions to life.
Embrace the power of Blender for your 3D printing projects, where creativity meets efficiency in a community-driven platform that turns your visions into tangible realities, making it the ultimate companion for digital sculpting.