Topic blender 3d printer software: Explore the transformative power of Blender 3D printer software, a cutting-edge tool that revolutionizes the way creators design and print 3D models, fostering endless possibilities for innovation and creativity in the 3D printing world.
Table of Content
- What are the best 3D printer software options compatible with Blender?
- Features and Capabilities
- Learning Resources
- Community and Support
- Conclusion
- Learning Resources
- Community and Support
- Conclusion
- Community and Support
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Blender Model to 3D Print Quick Guide
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Blender for 3D Printing
- Benefits of Using Blender with 3D Printers
- Getting Started: Installing Blender for 3D Printing
- Blender Add-ons for Enhancing 3D Printing Workflows
- Designing Your First 3D Model in Blender
- Optimizing Blender Models for 3D Printing
- Exporting Models from Blender to 3D Printer Software
- Advanced Techniques and Tips for 3D Printing with Blender
- Community and Resources for Blender 3D Printing Enthusiasts
- Future Trends: Blender and 3D Printing Technology
What are the best 3D printer software options compatible with Blender?
- Cura: Cura is a popular slicing software that is compatible with Blender. It offers a user-friendly interface and powerful features for preparing models for 3D printing.
- Simplify3D: Simplify3D is a premium 3D printing software that is known for its advanced customization options and support for a wide range of 3D printers. It can be used alongside Blender for efficient 3D printing workflows.
- Meshmixer: Meshmixer is a free software from Autodesk that can be used to edit and repair 3D models. It can work well with models created in Blender and prepare them for 3D printing.
- PrusaSlicer: PrusaSlicer is another slicing software that is highly compatible with Blender. It offers various printing profiles and settings to optimize the print quality of models created in Blender.
READ MORE:
Features and Capabilities
- 3D Modeling: Utilize powerful tools to create detailed models.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: Access specialized tools for preparing models for printing.
- Mesh Analysis: Ensure models are optimized for 3D printing with real-time analysis.
- Sculpting and Texturing: Enhance models with advanced sculpting tools and textures.

Learning Resources
Blender offers a plethora of tutorials and courses, from beginner guides to advanced techniques, ensuring users can fully leverage its capabilities for 3D printing.
Tutorial Highlights
- Basic Shapes to Complex Sculptures: Learn to design printable models.
- Optimizing Models: Techniques for scaling, applying modifiers, and exporting.
- Comprehensive 3D Printing Course: From modeling to slicing and printing.
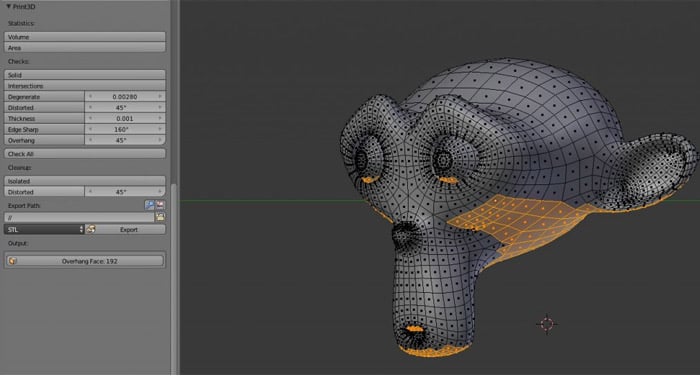
Community and Support
Blender\"s vibrant community and open-source nature foster a collaborative environment where users can share tips, tricks, and get support for their 3D printing projects.
Conclusion
Whether you\"re looking to create, edit, or optimize your 3D models for printing, Blender offers a robust platform filled with resources to guide you through the process. Its support for 3D printing modeling and file formats makes it an invaluable tool in the arsenal of any 3D printing enthusiast.
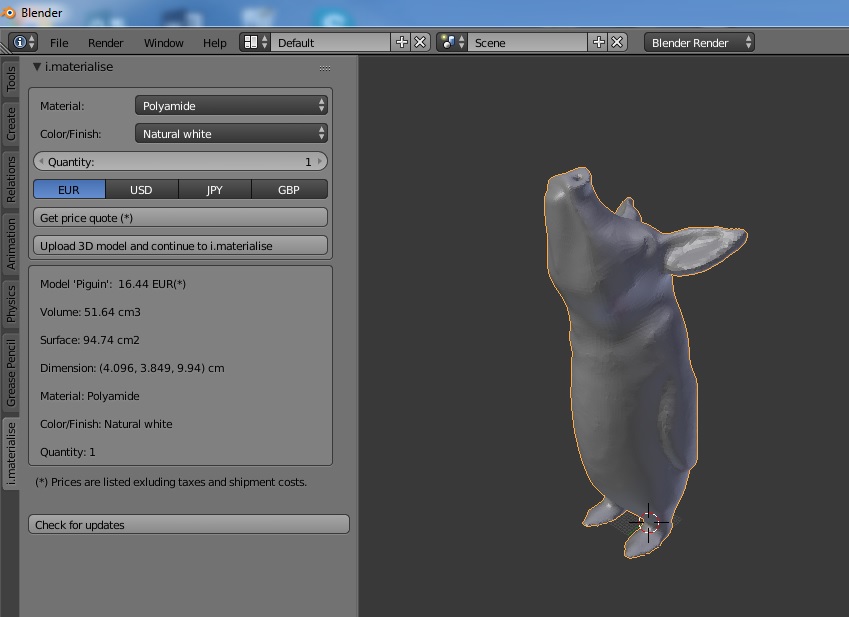
_HOOK_
Learning Resources
Blender offers a plethora of tutorials and courses, from beginner guides to advanced techniques, ensuring users can fully leverage its capabilities for 3D printing.
Tutorial Highlights
- Basic Shapes to Complex Sculptures: Learn to design printable models.
- Optimizing Models: Techniques for scaling, applying modifiers, and exporting.
- Comprehensive 3D Printing Course: From modeling to slicing and printing.
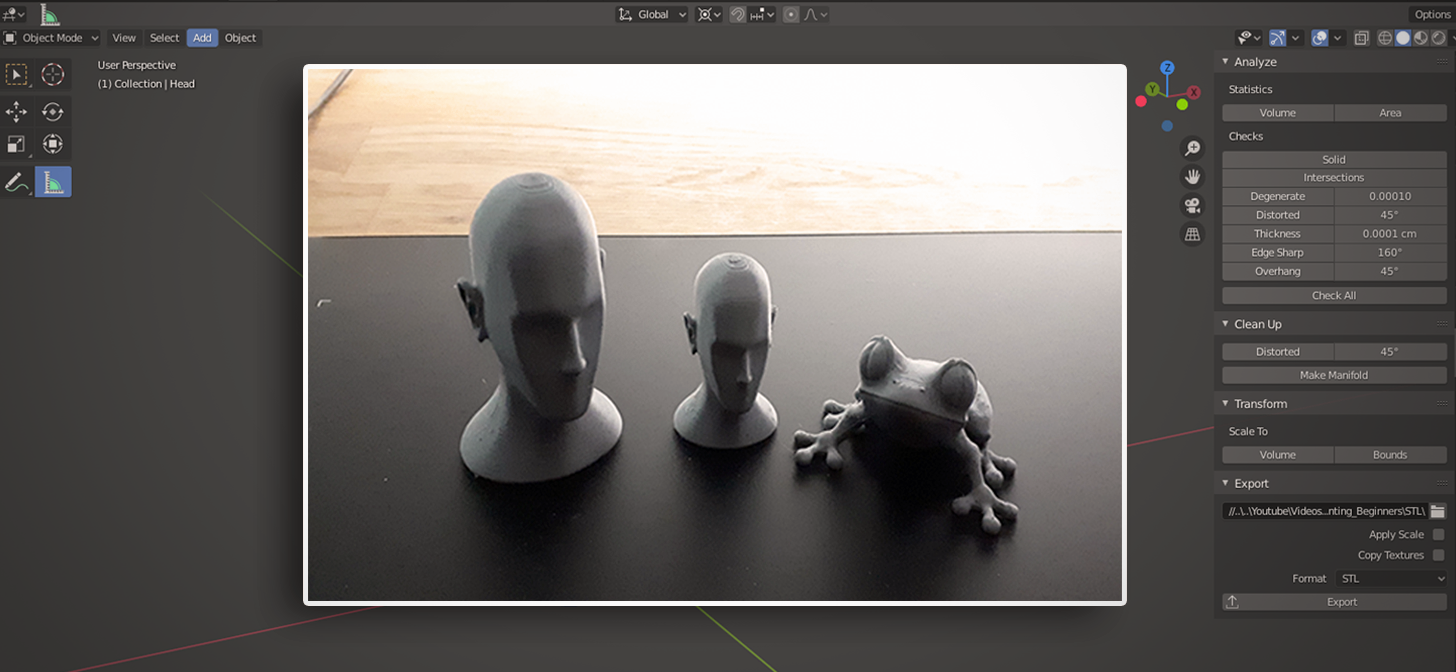
Community and Support
Blender\"s vibrant community and open-source nature foster a collaborative environment where users can share tips, tricks, and get support for their 3D printing projects.
_qYYgrmi.jpg)
Conclusion
Whether you\"re looking to create, edit, or optimize your 3D models for printing, Blender offers a robust platform filled with resources to guide you through the process. Its support for 3D printing modeling and file formats makes it an invaluable tool in the arsenal of any 3D printing enthusiast.
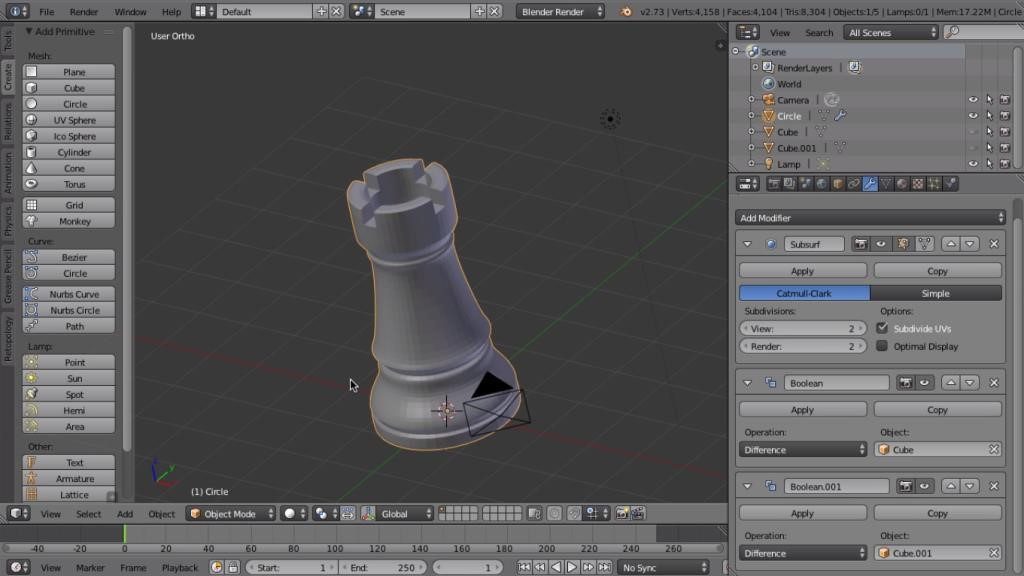
Community and Support
Blender\"s vibrant community and open-source nature foster a collaborative environment where users can share tips, tricks, and get support for their 3D printing projects.
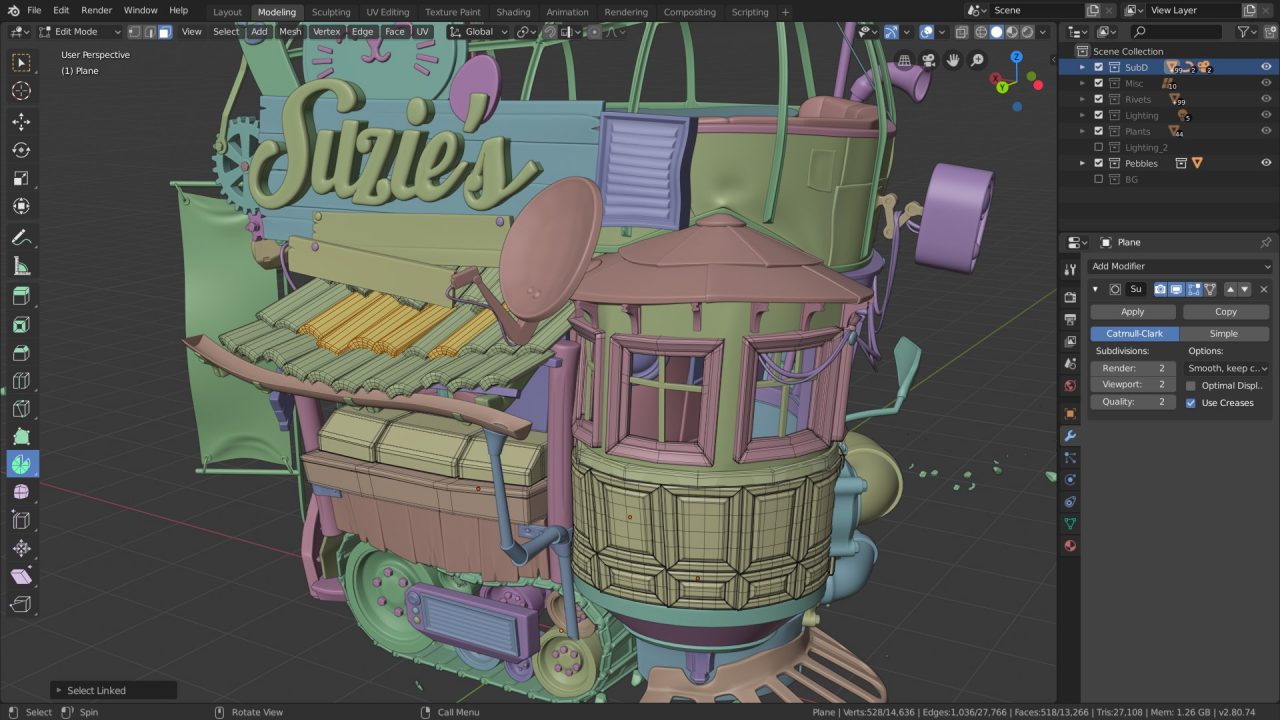
Conclusion
Whether you\"re looking to create, edit, or optimize your 3D models for printing, Blender offers a robust platform filled with resources to guide you through the process. Its support for 3D printing modeling and file formats makes it an invaluable tool in the arsenal of any 3D printing enthusiast.
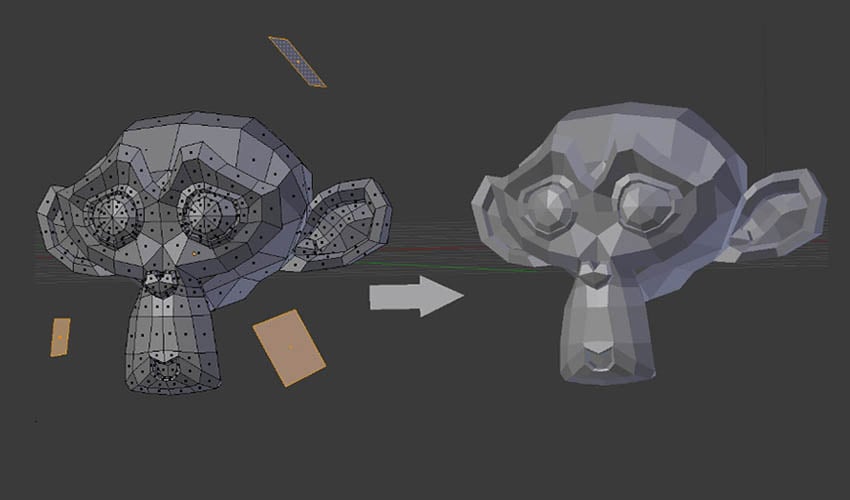
_HOOK_
Blender Model to 3D Print Quick Guide
Optimization: Discover the power of optimization in this video as we unlock the secrets to maximizing efficiency and performance. Learn valuable strategies to enhance your workflow and reach your goals faster. Comprehensive: Dive into a comprehensive exploration of the topic at hand with this engaging video. Gain a deep understanding of all aspects related to the subject, ensuring you leave with a wealth of knowledge and insights.
Full Blender Tutorial for 3D Modeling and 3D Printing
This is a full Blender 2.83 tutorial for beginners and advanced users. The focus is on how to create 3d models which can be ...
Conclusion
Whether you\"re looking to create, edit, or optimize your 3D models for printing, Blender offers a robust platform filled with resources to guide you through the process. Its support for 3D printing modeling and file formats makes it an invaluable tool in the arsenal of any 3D printing enthusiast.
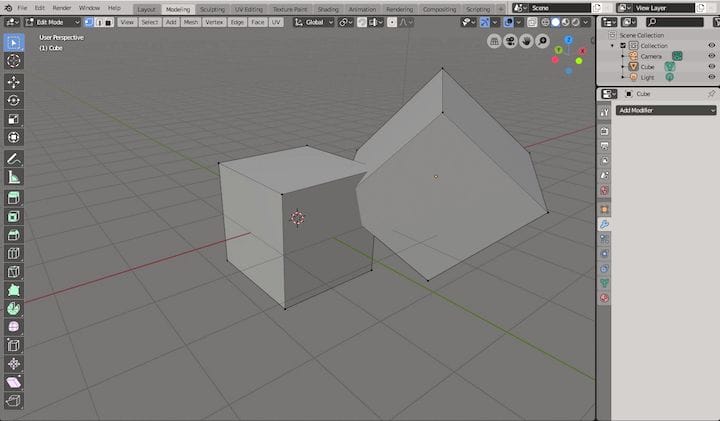
Introduction to Blender for 3D Printing
Blender, a comprehensive, open-source 3D creation suite, offers a plethora of functionalities for 3D printing enthusiasts. From modeling and sculpting to rendering, Blender equips users with the tools needed to bring their imaginative concepts to life. With its robust set of features, Blender supports the entire 3D printing process, enabling the creation of detailed, print-ready models.
- Blender\"s interface is designed to be intuitive for newcomers while offering depth for experienced users.
- The software includes a specialized 3D Printing Toolbox, enhancing the workflow for 3D print designs.
- Blender allows for the creation of complex models using polygonal modeling techniques, perfect for 3D printing.
- It supports a variety of file formats crucial for 3D printing, including STL, OBJ, and more.
- Users can optimize their models for 3D printing within Blender, applying modifications such as scaling, mesh analysis, and fixing non-manifold edges.
For those new to 3D printing or Blender, the journey begins with understanding Blender\"s interface and basic modeling techniques. The software offers comprehensive guides and tutorials, making it easier to start designing 3D printable models. Whether you\"re looking to create simple shapes or intricate sculptures, Blender provides the tools necessary for every step of the 3D printing process.
Benefits of Using Blender with 3D Printers
Blender offers a unique combination of flexibility, power, and cost-effectiveness, making it an invaluable tool for 3D printing projects. Its comprehensive feature set caters to both beginners and professionals, enhancing the 3D printing process from conceptualization to final print.
- Cost Efficiency: As an open-source platform, Blender is freely available, reducing the overhead costs associated with 3D modeling software.
- Comprehensive Toolset: Blender\"s extensive array of modeling tools allows for the creation of complex and detailed models suitable for 3D printing.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: The integrated 3D Printing Toolbox offers features for checking and correcting models to ensure they are print-ready.
- Support for Various File Formats: Blender supports exporting models in formats compatible with most 3D printers, including STL and OBJ.
- Versatility: Suitable for creating both organic shapes and mechanical parts, Blender meets a wide range of design needs.
- Active Community: A vibrant community of users and developers provides support, shares knowledge, and offers a plethora of tutorials and resources.
Whether you\"re a hobbyist looking to bring your ideas to life or a professional seeking efficient modeling tools, Blender\"s integration with 3D printing technology offers an accessible and powerful platform for creative exploration and production.
Getting Started: Installing Blender for 3D Printing
To begin using Blender for 3D printing, the first step is installing the software. Blender is a free, open-source 3D creation suite available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. Follow these steps to install Blender and set it up for 3D printing projects:
- Visit the official Blender website (www.blender.org) and navigate to the download section.
- Select the version compatible with your operating system and download the installer.
- Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
- Once installed, open Blender and go to the Edit menu to access Preferences.
- In the Add-ons tab, search for the 3D Print Toolbox and enable it by checking the box next to it. This toolbox provides essential tools for preparing models for 3D printing.
- With the 3D Print Toolbox enabled, you can now use Blender to create models for 3D printing.
For new users, Blender offers an array of tutorials and resources to get started with 3D modeling. The 3D Print Toolbox add-on is a crucial component for ensuring your models are ready for printing, offering features for analyzing and fixing common issues.
Blender Add-ons for Enhancing 3D Printing Workflows
Blender\"s capabilities for 3D printing can be significantly enhanced with the use of specific add-ons. These tools streamline the design process, improve model quality, and ensure compatibility with 3D printing requirements. Here are some key add-ons that can elevate your 3D printing projects:
- 3D Print Toolbox: This essential add-on offers a suite of tools for preparing models for 3D printing, including checks for errors and optimizations for printing.
- MeasureIt: Allows for precise measurement of objects within your scene, crucial for creating models that fit real-world dimensions and tolerances.
- Archipack: While primarily for architectural design, it offers tools that can be useful for creating geometrically complex components for 3D prints.
- Tissue: This add-on is great for creating tessellations and complex patterns, adding an artistic touch to functional prints.
- BoolTool: Simplifies the process of using boolean operations, a common technique in preparing models for 3D printing.
By integrating these add-ons into your Blender workflow, you can take advantage of advanced tools specifically designed to tackle the challenges of 3D printing. They help in refining your models, ensuring that your designs are not only creative but also print-ready.
_HOOK_
Designing Your First 3D Model in Blender
Creating your first 3D model in Blender for 3D printing is an exciting journey into the world of digital fabrication. Here\"s a simple guide to get you started:
- Understanding the Interface: Begin by familiarizing yourself with Blender\"s interface. Explore the layout, tools, and viewports to get comfortable navigating the software.
- Starting Your Project: Press \"Shift + A\" to add a new mesh object. Starting with simple shapes like cubes or spheres can help you learn the basics of modeling.
- Modifying Your Object: Use Blender\"s edit mode to modify your object. You can extrude, scale, and rotate faces, edges, and vertices to shape your model.
- Checking for Printability: Activate the 3D Print Toolbox add-on (if not already done) to analyze your model for common 3D printing issues such as non-manifold edges or overhangs.
- Exporting Your Model: Once satisfied with your design, export it as an STL file, the most common format for 3D printing.
Remember, designing for 3D printing in Blender requires attention to detail, such as ensuring your model is watertight and has the necessary thickness for printing. Patience and practice will lead to successful prints and a rewarding modeling experience.
Optimizing Blender Models for 3D Printing
Optimizing your Blender models for 3D printing is crucial for achieving high-quality prints. Here are steps and tips to ensure your models are ready for the printer:
- Check Model Scale: Ensure your model\"s scale matches the physical dimensions you desire. Use Blender\"s units setting to match real-world measurements.
- Apply Modifiers: Before exporting, apply any modifiers to ensure the geometry is correctly interpreted by the slicing software.
- Ensure Model Solidity: Models must be watertight, with no holes or non-manifold edges. Use the 3D Print Toolbox to identify and fix any issues.
- Optimize Geometry: Reduce the polygon count without losing detail to ensure a smoother print process. Tools like Decimate can help in reducing complexity.
- Consider Printing Orientation: Adjust the model\"s orientation to minimize overhangs and support material, improving the overall print quality.
- Export Correctly: Export your model in a format compatible with your 3D printer, typically STL or OBJ, and check the export settings to ensure all aspects of your model are preserved.
Following these guidelines will help in creating models that are not only easier to print but also maintain the quality and detail envisioned during the design process.
Exporting Models from Blender to 3D Printer Software
Transferring your 3D models from Blender to your 3D printer\"s software involves a few crucial steps to ensure your design prints correctly. Follow this guide to successfully export your models:
- Finalize Your Model: Make sure your model is complete, with all modifications applied and the mesh clean of any errors.
- Choose the Right Format: Most 3D printers accept the STL format, which Blender supports. OBJ is another common format for color prints.
- Export Your Model: Go to File > Export and select STL or OBJ. In the export options, ensure you choose the correct scale and orientation for your print.
- Preparation in Slicing Software: Open your exported file in your 3D printer\"s slicing software. Here, you can adjust print settings such as support structures, layer height, and infill.
- Print Preview: Utilize the slicing software\"s preview feature to check for any potential issues before printing.
- Export G-Code: Once satisfied with the setup, export the G-code, which is the file that your 3D printer will use to print the model.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your Blender models are properly prepared and optimized for 3D printing, leading to successful and high-quality prints.
Advanced Techniques and Tips for 3D Printing with Blender
Mastering Blender for 3D printing involves not just basic modeling but also applying advanced techniques to enhance printability and model quality. Here are some advanced tips and strategies to refine your 3D printing projects:
- Utilize Modifiers for Complex Shapes: Employ Blender\"s modifiers, like Boolean, to create intricate designs and complex geometrical shapes with ease.
- Simulation for Realistic Effects: Use Blender\"s physics simulations to add realistic effects, such as cloth or fluid dynamics, to your models for unique 3D printed objects.
- Material and Texture Baking: For models that require detailed textures, use Blender\"s baking process to create color and texture maps that can be printed with full-color 3D printers.
- Topology Optimization: Optimize your model\"s topology for 3D printing by reducing unnecessary vertices without compromising on the detail, to ensure a smoother printing process.
- Custom Support Structures: Instead of relying on automatic support generation in slicing software, create custom supports in Blender for areas that are prone to failure during printing.
- Multi-part Printing: Design your model in separate parts for printing, which can be assembled later. This approach allows for larger and more complex models to be printed on printers with smaller build volumes.
- Slicing within Blender: Use add-ons that allow for slicing directly within Blender, giving you more control over the print settings before exporting to G-code.
These advanced techniques will help push the boundaries of what\"s possible with 3D printing, allowing for more creative and complex projects. Continuous learning and experimenting with Blender\"s vast toolkit can significantly enhance the quality and feasibility of your 3D printed models.
Community and Resources for Blender 3D Printing Enthusiasts
The Blender community and the wealth of resources available are invaluable for anyone delving into 3D printing with Blender. Whether you\"re seeking advice, tutorials, or inspiration, here\"s where you can find support:
- Blender Artists Forum: A vibrant community where users share projects, offer feedback, and provide support for 3D printing queries.
- BlenderNation: Offers daily news about Blender and its uses, including 3D printing, with tutorials, art showcases, and more.
- Blender 3D Printing Toolbox: An official Blender add-on that provides tools for preparing models for printing and analyzing potential issues.
- Thingiverse: While not Blender-specific, this vast repository of 3D models offers inspiration and examples of what\"s possible with 3D printing.
- Blender Stack Exchange: A Q&A site where you can ask specific questions about Blender and receive detailed answers from the community.
- YouTube Tutorials: There are countless video tutorials available for free, covering every aspect of using Blender for 3D printing.
- Blender Courses and Workshops: Online platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and even Blender\"s own website offer structured learning paths for 3D printing with Blender.
Engaging with the community and leveraging these resources can significantly enhance your skills and understanding of 3D printing with Blender, helping you to achieve better results and solve complex challenges.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Future Trends: Blender and 3D Printing Technology
As we look toward the future, Blender and 3D printing technology are set to evolve in ways that will further revolutionize design, manufacturing, and creativity. Here are some emerging trends and predictions:
- Increased Integration: Expect to see deeper integration between Blender and 3D printing software, streamlining the workflow from model creation to printing.
- Advanced Material Support: Advances in 3D printing materials will allow Blender users to simulate and prepare models for printing with a wider range of materials, including multi-material prints.
- Improved Simulation Capabilities: Blender is likely to enhance its simulation tools, enabling more accurate predictions of how models will behave during the printing process.
- AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning into Blender could automate and optimize many aspects of 3D printing preparation, from support generation to model correction.
- Community-Driven Development: As the community of Blender users grows, expect to see more community-driven add-ons and tools specifically tailored for 3D printing applications.
- Sustainability Focus: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, future developments in Blender and 3D printing technology will likely prioritize eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient printing processes.
- Expansion into New Industries: Blender and 3D printing will continue to find new applications in industries such as bioprinting, construction, and fashion, pushing the boundaries of what can be designed and produced.
These trends underscore the dynamic nature of 3D printing and the pivotal role of Blender in shaping the future of digital fabrication. As technology advances, the possibilities for creators, designers, and engineers will expand, offering new opportunities for innovation and creativity.
Embracing Blender for 3D printing opens a world of creativity and innovation. Its evolving capabilities promise to transform ideas into reality, making it an indispensable tool for designers, hobbyists, and professionals alike.