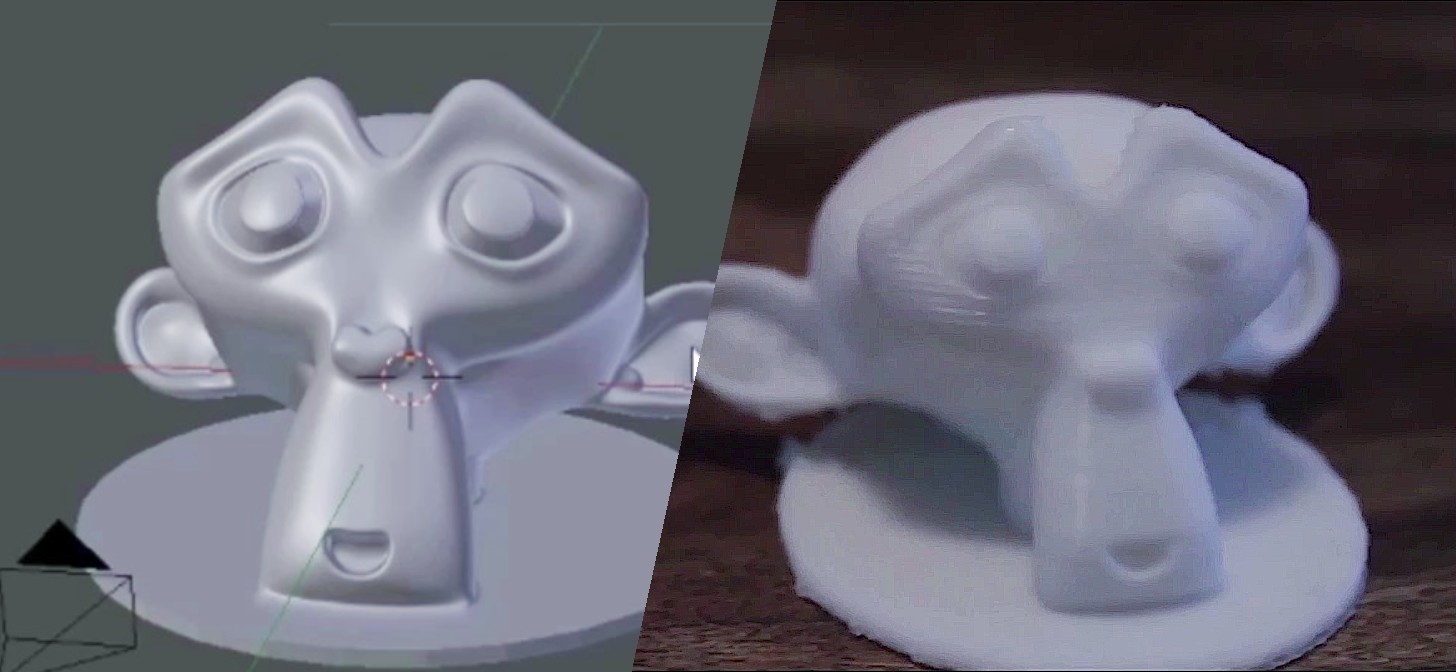
Topic blender software for 3d printing: Discover how Blender software transforms 3D printing, empowering creators with tools to bring their most ambitious ideas to life. Dive into the world of endless possibilities with Blender for 3D printing.
Table of Content
- What is the latest version of Blender software for 3D printing and its features?
- Key Features for 3D Printing
- Benefits of Using Blender for 3D Printing
- Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Conclusion
- Benefits of Using Blender for 3D Printing
- Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Conclusion
- Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Blender Software
- YOUTUBE: Learn Blender for 3D Printing - Complete Quick and Easy Guide for Beginners
- Why Blender is Ideal for 3D Printing
- Key Features of Blender for 3D Printing
- Getting Started with Blender: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Optimizing Your Models for 3D Printing with Blender
- Advanced Techniques and Tips for 3D Printing
- Common Challenges and Solutions in 3D Printing with Blender
- Case Studies: Successful 3D Printing Projects Using Blender
- Comparing Blender to Other 3D Modeling Software
- Future of 3D Printing and Blender\"s Role
- Resources and Communities for Blender Users
What is the latest version of Blender software for 3D printing and its features?
The latest version of Blender software for 3D printing is version 2.83. This version comes with various features that are beneficial for 3D printing enthusiasts. Some of the notable features include:
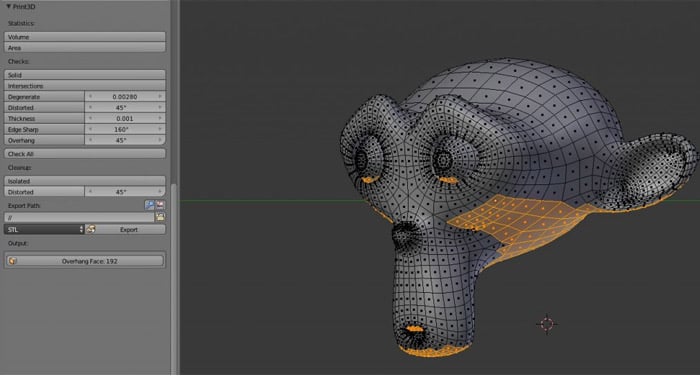
- Improved 3D Printing Toolbox: Blender has an enhanced 3D printing toolbox that makes it easier to prepare models for 3D printing. This includes functions for checking wall thickness, overhangs, and other factors that are crucial for successful 3D prints.
- Customizable Supports: Blender allows users to create and customize supports for their 3D prints, helping to ensure stability and quality during printing.
- Mesh Analysis Tools: The software provides advanced mesh analysis tools that help users identify and fix issues in their 3D models before sending them to the printer.
- Improved STL Export: Blender has improved its STL export capabilities, making it easier to export models in a format that is compatible with most 3D printers.
Overall, Blender version 2.83 offers a range of features that cater to the needs of 3D printing users, making it a powerful tool for creating and preparing models for 3D printing.
READ MORE:
Key Features for 3D Printing
- 3D Printing Toolbox: Provides real-time analysis of models to ensure they are print-ready.
- Mesh Analysis: Helps in identifying and fixing potential issues before printing.
- Advanced Sculpting Tools: Allow for the creation of complex and detailed designs.
- Full N-Gon Support: Facilitates the modeling process with enhanced flexibility.
- Export Options: Supports exporting models in STL format, compatible with most 3D printers.
Benefits of Using Blender for 3D Printing
Blender\"s polygonal modeling approach is ideal for creating 3D shapes through the assembly of polygons, making it a strong tool for 3D printing enthusiasts. It combines ease of use with powerful features, making it suitable for both beginners and professionals.

Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface: Familiarize yourself with the layout and tools available in Blender.
- Modeling Basics: Learn how to create basic shapes and models to start your 3D printing projects.
- Optimizing Models: Discover how to scale, apply modifiers, and prepare your models for 3D printing.
- Exporting Models: Learn the process of exporting your models in the correct format for 3D printing.
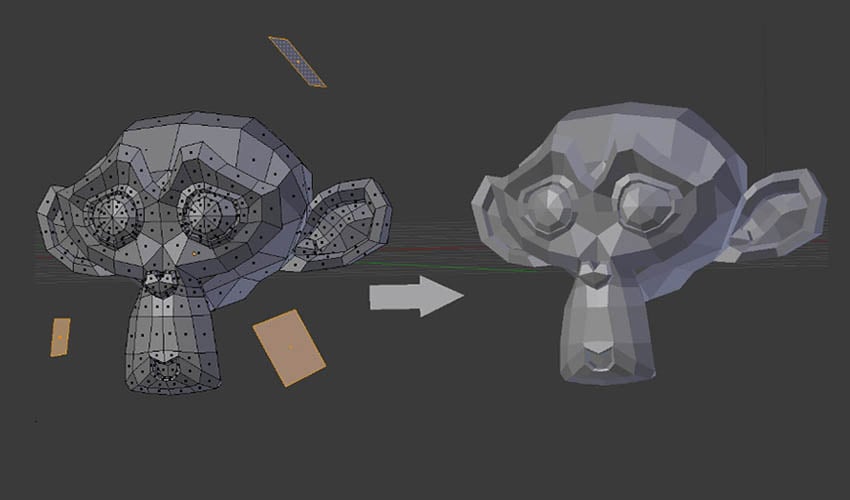
Conclusion
Blender offers a comprehensive platform for 3D modeling with a wide range of tools and features tailored for 3D printing. Its ability to create detailed, complex models, along with the 3D Printing Toolbox and Mesh Analysis features, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing.
_HOOK_
Benefits of Using Blender for 3D Printing
Blender\"s polygonal modeling approach is ideal for creating 3D shapes through the assembly of polygons, making it a strong tool for 3D printing enthusiasts. It combines ease of use with powerful features, making it suitable for both beginners and professionals.
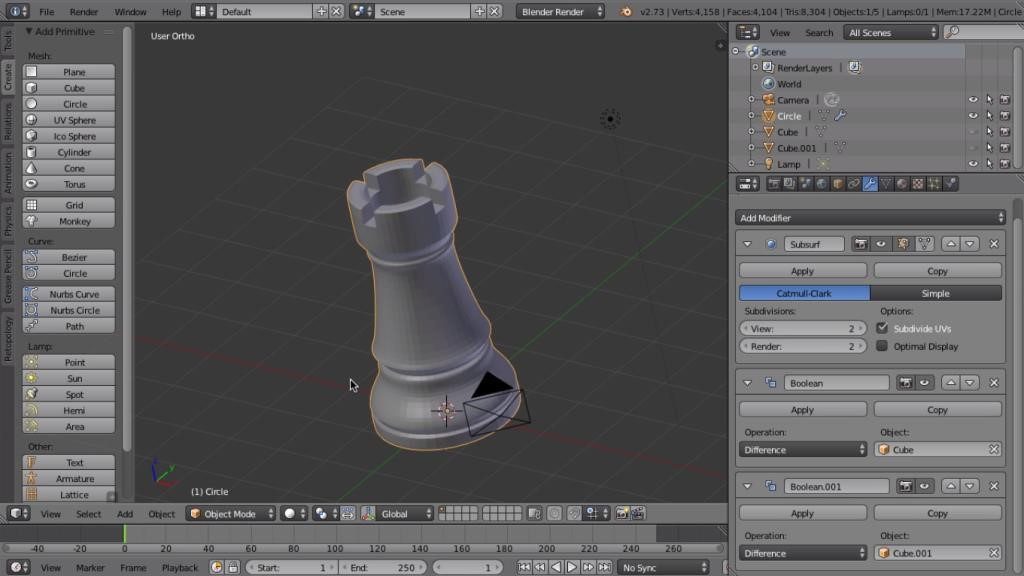
Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface: Familiarize yourself with the layout and tools available in Blender.
- Modeling Basics: Learn how to create basic shapes and models to start your 3D printing projects.
- Optimizing Models: Discover how to scale, apply modifiers, and prepare your models for 3D printing.
- Exporting Models: Learn the process of exporting your models in the correct format for 3D printing.
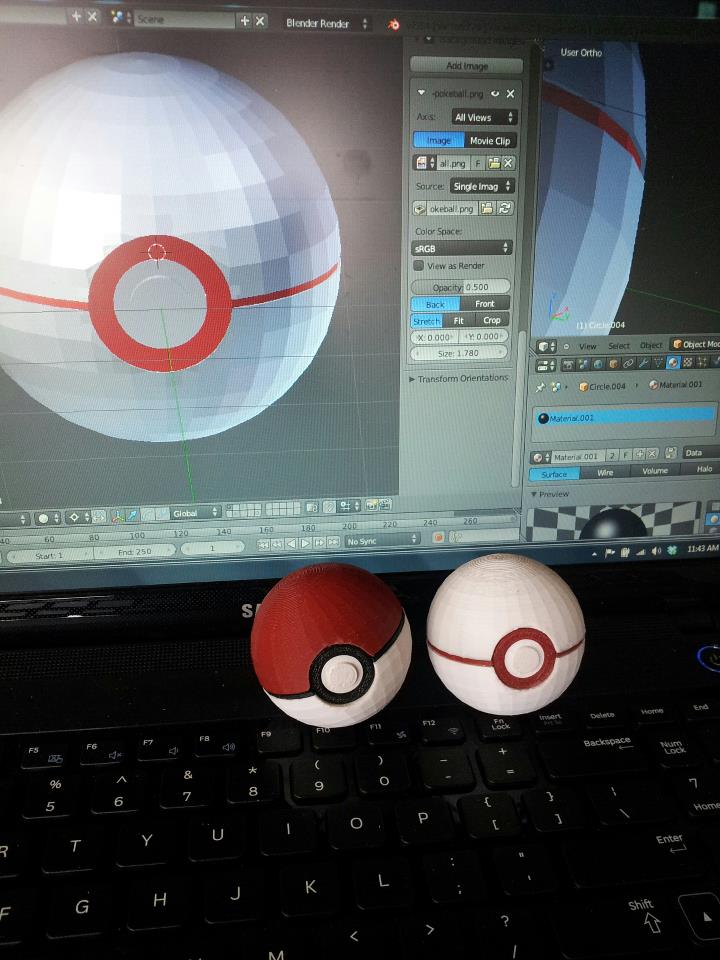
Conclusion
Blender offers a comprehensive platform for 3D modeling with a wide range of tools and features tailored for 3D printing. Its ability to create detailed, complex models, along with the 3D Printing Toolbox and Mesh Analysis features, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing.
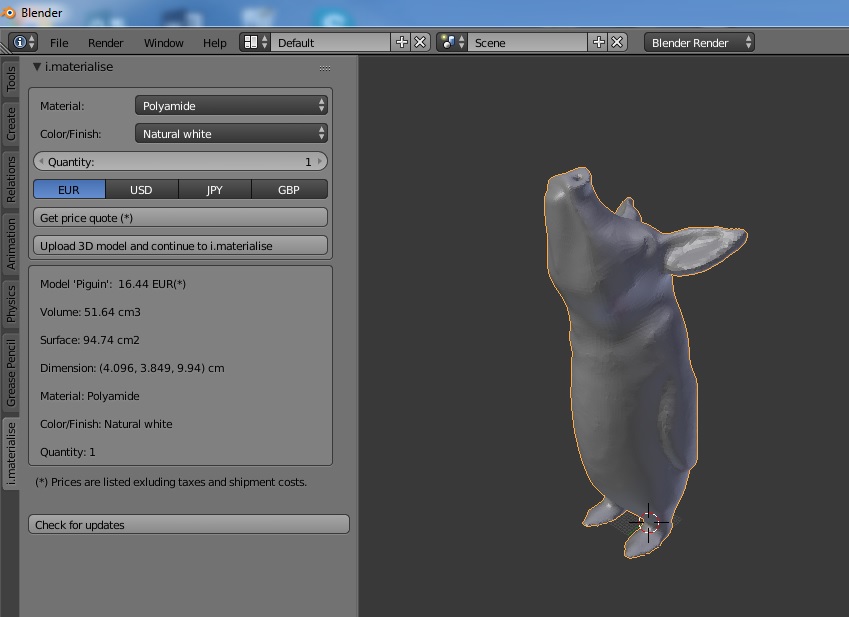
Getting Started with Blender for 3D Printing
- Understanding Blender\"s Interface: Familiarize yourself with the layout and tools available in Blender.
- Modeling Basics: Learn how to create basic shapes and models to start your 3D printing projects.
- Optimizing Models: Discover how to scale, apply modifiers, and prepare your models for 3D printing.
- Exporting Models: Learn the process of exporting your models in the correct format for 3D printing.
Conclusion
Blender offers a comprehensive platform for 3D modeling with a wide range of tools and features tailored for 3D printing. Its ability to create detailed, complex models, along with the 3D Printing Toolbox and Mesh Analysis features, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing.
_qYYgrmi.jpg)
_HOOK_
Conclusion
Blender offers a comprehensive platform for 3D modeling with a wide range of tools and features tailored for 3D printing. Its ability to create detailed, complex models, along with the 3D Printing Toolbox and Mesh Analysis features, makes it an invaluable resource for anyone interested in 3D printing.
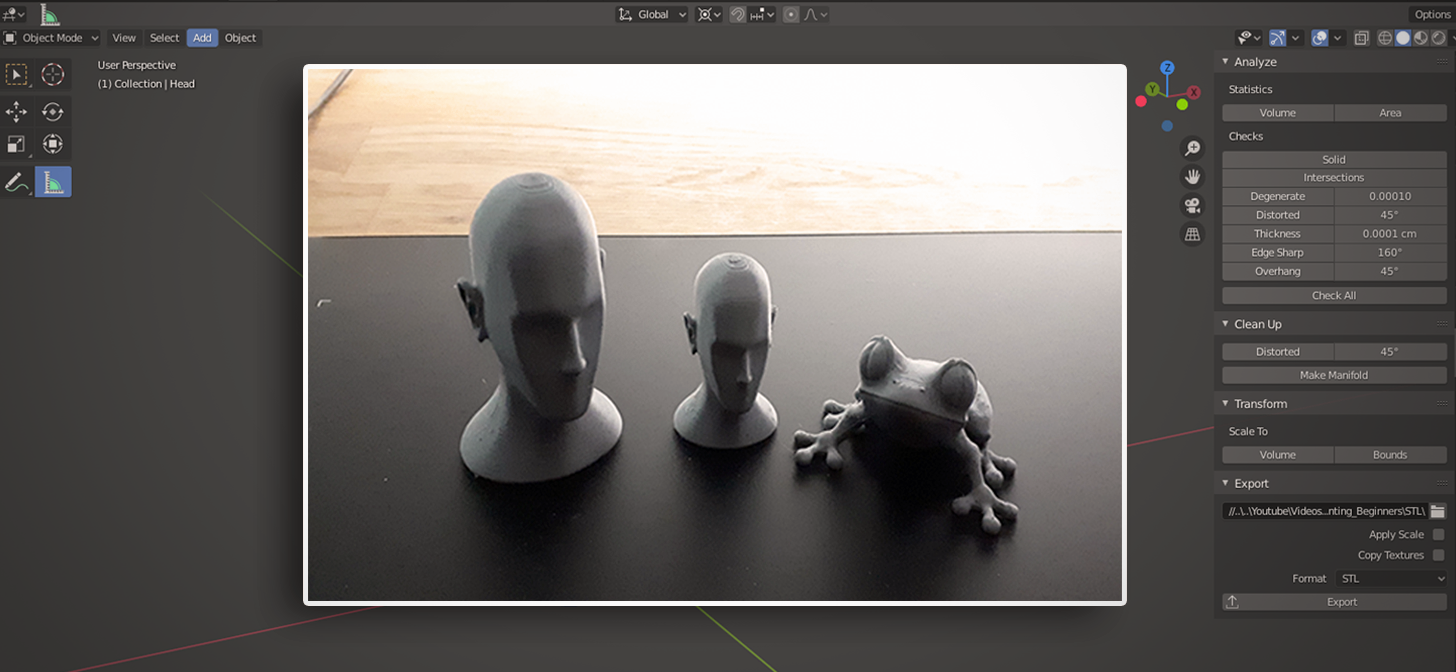
Introduction to Blender Software
Blender is a powerful, free, and open-source 3D modeling software widely acclaimed for its versatility in 3D creation. It caters to a broad spectrum of digital production needs, including 3D modeling, animation, rendering, post-production, and, notably, 3D printing. Originating in the early 2000s, Blender has evolved significantly over the years, offering an extensive range of tools and features that support the entire 3D design workflow.
- Comprehensive Modeling Tools: Blender\"s array of modeling capabilities, such as full N-Gon support, advanced sculpting tools, and UV mapping, make it ideal for creating detailed 3D models for printing.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: Integrated directly into the software, this feature provides essential tools for preparing models for 3D printing, including real-time analysis and error detection.
- Polygonal Modeling: Utilizing polygons for model creation, Blender allows for the precise assembly of 3D shapes, making it perfect for designing complex and detailed print-ready models.
- Export Options: Blender supports exporting models in formats compatible with most 3D printers, ensuring a seamless transition from digital design to physical object.
Whether you\"re a beginner interested in diving into the world of 3D printing or a professional looking to refine your design process, Blender offers a robust platform to bring your ideas to life. Its continuous development and supportive community make it an excellent choice for anyone looking to explore the potential of 3D printing.
Learn Blender for 3D Printing - Complete Quick and Easy Guide for Beginners
Tutorial: \"Unlock your creative potential with our engaging tutorial video! Learn step-by-step techniques, tips, and tricks to master the art in no time. Get ready to embark on an exciting learning journey!\" Basics: \"New to the subject? Our video covers all the basics you need to know, breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand bite-sized information. Start your learning adventure today with us!\"
How to Use Blender for 3D Printing - The Basics Tutorial
UPDATED VERSION OF THIS VIDEO: https://youtu.be/9EF2VryBAq4 A detailed guide of the basics of bringing a file into and out ...
Why Blender is Ideal for 3D Printing
Blender\"s reputation as a comprehensive tool for 3D printing stems from its robust feature set tailored for creating detailed and print-ready models. Its capabilities extend beyond mere modeling, offering a suite of tools that cater to the nuanced needs of 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
- Comprehensive Toolset: From sculpting to texturing, Blender provides all the necessary tools to create detailed 3D models suitable for printing.
- 3D Printing Toolbox: This specialized toolset enables users to prepare their models for printing by analyzing and correcting issues directly within Blender.
- Compatibility with Printing Formats: Blender supports STL and OBJ formats, among others, ensuring models are easily exportable to 3D printing software.
- Precision Modeling: Blender\"s precision modeling capabilities allow for the creation of intricate designs with accuracy, essential for successful 3D printing.
- Active Community and Resources: A vast community of Blender users contributes tutorials, advice, and shared projects, facilitating learning and problem-solving.
These features, combined with Blender\"s open-source nature, make it not only a powerful tool for 3D design but also a preferred choice for those looking to delve into 3D printing. Whether for hobbyist projects or professional endeavors, Blender equips users with the necessary tools to bring their visions to life in the physical world.
Key Features of Blender for 3D Printing
Blender is not only versatile in 3D modeling and animation but also specifically tailored for 3D printing. Its comprehensive set of features makes it an indispensable tool for creating detailed, print-ready models. Here are some key features that highlight Blender\"s compatibility with 3D printing:
- 3D Printing Toolbox: An integrated tool that evaluates your models for common 3D printing issues, helping to ensure that your designs are ready to print.
- Mesh Analysis: This feature allows for the detection and correction of potential problems in your model, such as non-manifold edges or intersecting faces.
- Advanced Sculpting Tools: Blender\"s sculpting capabilities enable the creation of complex and detailed models, offering high precision for intricate designs.
- Support for Multiple File Formats: Blender supports exporting models in STL, OBJ, and other formats, making it easy to work with a wide range of 3D printers.
- Modifier-Based Modeling: Use Blender\"s modifiers to apply complex transformations and effects non-destructively, allowing for flexible adjustments until the final export.
These features, combined with Blender\"s user-friendly interface and extensive community resources, make it an excellent choice for both novices and professionals in the 3D printing field.
Getting Started with Blender: A Step-by-Step Guide
Embarking on your 3D printing journey with Blender begins with understanding its interface and tools. This guide will help you navigate through the initial stages of learning and using Blender for your 3D printing projects.
- Download and Install Blender: Ensure you have the latest version by downloading it from the official Blender website.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Interface: Blender\"s interface might be overwhelming at first, but take time to learn where the essential tools are located.
- Start with Basic Tutorials: There are numerous beginner tutorials available online that cover the basics of modeling in Blender.
- Experiment with Simple Models: Begin your practice by creating simple objects. This will help you get comfortable with the modeling process.
- Learn to Use the 3D Printing Toolbox: This Blender add-on provides tools specifically for preparing models for 3D printing.
- Understand Mesh Analysis: Use Blender\"s mesh analysis tools to identify and fix potential issues with your model before printing.
- Practice Exporting Models: Learn how to export your models in the STL format, which is commonly used for 3D printing.
- Join the Blender Community: Engage with Blender\"s community forums and social media groups to seek advice, share your work, and learn from others.
By following these steps, you\"ll gradually build your skills in using Blender for 3D printing, allowing you to bring your creative visions to life.
_HOOK_
Optimizing Your Models for 3D Printing with Blender
Optimizing your Blender models for 3D printing is a crucial step to ensure high quality and efficient print times. Here are comprehensive strategies and tips to prepare your models:
- Model Size and Scaling: Consider the physical size of your model. Utilize Blender\"s scaling tools to adjust your model to appropriate dimensions without losing essential details.
- Wall Thickness: Ensure your model has sufficient wall thickness. Use Blender\"s \"Solidify\" modifier to measure and adjust wall thickness to meet your printer\"s capabilities, preventing print failures.
- Geometry Optimization: Simplify complex geometries. Blender\"s \"Decimate\" modifier can reduce polygon count, speeding up printing while maintaining the model\"s integrity.
- Orientation for Printing: Properly orient your model to optimize print quality and strength. Use \"Align to Transform Orientation\" for the best positioning on the print bed.
- Support Structures: Evaluate the need for support structures based on your material\"s properties. Blender offers tools to add supports where necessary, enhancing print success.
- Sculpting for Detail: For models requiring fine details or organic shapes, Blender\"s sculpting mode, especially with dynamic topology (Dyntopo), allows for intuitive detailing and creativity.
- Booleans for Hard Surfaces: Utilize Boolean operations for models with mechanical parts. Techniques such as using the Boolean modifier or add-ons like BoolTool can help achieve precise hard surface models.
By implementing these strategies, from initial scaling to advanced sculpting and Boolean operations, you can significantly enhance both the quality and speed of your 3D prints using Blender.
Advanced Techniques and Tips for 3D Printing
Unlock the full potential of your 3D printing projects with Blender by exploring advanced techniques and tips that cater to both creativity and precision. Here\"s how you can elevate your 3D printing with Blender:
- Utilizing Metaballs for Organic Shapes: Metaballs offer a parametric approach to creating organic shapes by merging multiple objects into a single, fluid mass. This technique is particularly useful for sculpting base shapes quickly before converting them into meshes for detailed refinement.
- Fluid Simulator for Mesh Joining: Blender\"s fluid simulator can be used innovatively to join multiple meshes. This approach simulates a fluid dynamic process to merge objects, creating a uniform vertex distribution across the combined shape without altering the original meshes. It\"s a powerful method for creating complex, organic forms.
- Mesh Conditioning for 3D Printing: Preparing your model for printing involves ensuring a manifold, watertight mesh, triangulating your geometry for compatibility with most 3D printers, and confirming the model is correctly sized for the print bed. These steps are crucial for a successful print job.
- Ruler/Protractor Tool: Use Blender\"s built-in Ruler and Protractor tool to measure and adjust parts of your mesh, ensuring they meet the physical requirements for 3D printing. This tool is essential for identifying and correcting overly thin or potentially problematic areas of your model.
- 3D Printing Toolbox Add-on: This add-on provides an array of tools for checking and fixing your mesh to ensure it\"s ready for 3D printing. It helps identify and select problem areas for correction, streamlining the preparation process.
- STL Export: Once your model is prepared, export it as an STL file, the most widely supported format for 3D printing. This step is simplified with the 3D Printing Toolbox add-on, but can also be accessed via Blender\"s File menu.
By leveraging these advanced techniques in Blender, from creative modeling with Metaballs and the Fluid Simulator to meticulous preparation with the 3D Printing Toolbox, you can achieve detailed, high-quality prints that bring your digital creations to life.
Common Challenges and Solutions in 3D Printing with Blender
Blender is a versatile and powerful tool for 3D printing, but users may encounter several common challenges. Here\"s how to tackle these issues effectively:
- Ignoring Material and Printing Technology Guidelines: Each material and printing technology has its own set of guidelines. For successful printing, adhere to these specifications, such as wall thickness, support needs, and object orientation, to ensure compatibility and quality of the print.
- Managing Wall Thickness: Incorrect wall thickness is a frequent problem. Too thin walls may not print at all, or if they do, they could be fragile and break easily. Conversely, overly thick walls can cause internal stress, leading to cracking. Familiarize yourself with the material-specific guidelines to maintain the correct wall thickness.
- Optimizing File Resolution: The resolution of your 3D model affects the quality of your print. A low-resolution model can result in a \"pixelated\" print, while an excessively high-resolution model may be too large to process. Adjust the tolerance settings during export to balance detail and file size, aiming for a model that captures detail without exceeding the printer\"s capabilities.
- Preparing Non-Manifold Models: Ensure your model is manifold, meaning it is a completely enclosed volume without any gaps. Non-manifold models cannot exist in the real world and thus cannot be printed accurately. Use tools like Blender\"s 3D Print Toolbox to analyze and repair your model.
- Learning Curve and Calibration: Blender has a steep learning curve, and mastering its use for 3D printing takes time and practice. Begin with simple projects to familiarize yourself with the software. Additionally, properly calibrate your 3D printer to match the specifications of your Blender models for optimal results.
By addressing these common challenges, you can enhance your 3D printing experience with Blender and bring your creative visions to life with greater ease and accuracy.
Case Studies: Successful 3D Printing Projects Using Blender
Blender, a free and open-source 3D creation suite, has been instrumental in various successful 3D printing projects. One notable example is the work by WASP, the World’s Advanced Saving Project, which focuses on sustainability and basic needs fulfillment. WASP has leveraged Blender\"s capabilities to address global challenges such as housing, medical needs, and food sustainability. Their projects include 3D printed houses, medical casts, cranial implants, prosthetic legs, and specifically designed orthoses. Their initiatives highlight Blender\"s versatility in creating complex designs that are both functional and sustainable.
Blender\"s application extends beyond traditional design into the realm of organic modeling, making it ideal for creating detailed and intricate models such as characters, animals, and more. Its comprehensive toolset supports a wide range of 3D printing needs, from conceptual designs to detailed model preparation and analysis.
For example, Blender\"s 3D Print Toolbox and real-time Mesh analysis tools have significantly simplified the process of preparing models for 3D printing. These tools allow for detailed analysis and optimization of models, ensuring they are print-ready. This includes checking for watertightness, managing non-manifold geometry, and ensuring the model is suitable for the intended printing process.
Furthermore, Blender\"s extensive community and open-source nature have fostered a collaborative environment where individuals and organizations can share insights, tools, and modifications to improve 3D printing outcomes. The WASP Med Blender Add-on is a testament to this, offering a specialized tool for medical professionals to develop orthopedic prints directly from 3D scans.
In the broader scope, Blender has been pivotal in advancing 3D printing technology across various sectors, including medical, architectural, and entertainment industries. Its ability to create both hard surface and organic models, coupled with the freedom to modify and optimize designs, positions Blender as a key player in the future of 3D printing.
Comparing Blender to Other 3D Modeling Software
Blender, an open-source 3D modeling application, is renowned for its comprehensive suite of tools for modeling, animation, rendering, and more. When compared to other 3D modeling software like Maya, ZBrush, and SketchUp, Blender holds its own with distinct advantages and considerations.
Blender vs. Maya
Maya, developed by Autodesk, is a leader in 3D modeling and animation, offering a wide range of tools for realistic character creation and environment modeling. It is particularly popular in the video game industry. Blender and Maya offer similar tools, but their user interfaces, cost, and target audiences differ significantly. Maya is known for its clearer, more standard interface and is favored in professional studios due to its advanced toolset and industry-standard status. However, Blender\"s free, open-source nature and strong community support make it a powerful option for freelancers, small studios, and hobbyists.
Blender vs. ZBrush
ZBrush specializes in digital sculpting and is famous for creating detailed characters like King Kong and Godzilla. It supports very high poly counts, making it suitable for large digital sculptures. Blender, while also capable of sculpting and modeling, is better suited for smaller productions and offers a more diverse range of applications beyond just sculpting. ZBrush might require a financial investment for premium features, but Blender is freely available and supports a wide array of creative projects.
Blender vs. SketchUp
SketchUp is primarily a CAD program focused on architectural and design projects, offering tools geared towards creating accurate representations of objects. Blender, while capable of precise modeling, excels in animation, game design, and artistic projects, providing a more versatile toolset for creative endeavors. SketchUp\"s simplicity and focus on design make it preferable for CAD-related tasks, but Blender\"s comprehensive feature set and flexibility make it superior for a broad range of 3D modeling and animation projects.
System Requirements and Community Support
Both ZBrush and Blender require solid computing power, with recommendations for a powerful CPU and sufficient RAM to handle detailed projects. Blender\"s compatibility with a variety of operating systems and its minimal hard drive space requirements make it accessible to a broader audience. Both applications have vibrant communities offering extensive tutorials and support, aiding both beginners and advanced users in mastering the software.
In conclusion, Blender stands out as a versatile, powerful, and free alternative to other 3D modeling software. Its capability to handle a wide range of 3D modeling and animation tasks, combined with the strong support of its user community, makes it a valuable tool for anyone interested in 3D creation, from hobbyists to professionals.
_HOOK_
Future of 3D Printing and Blender\"s Role
The future of 3D printing (AM) and Blender\"s role in it is marked by innovation, diversification, and an expanding scope of applications. Experts predict a shift towards more routine, series production uses for additive manufacturing, leading to increased adoption and integration across various industries. The development of new materials and more advanced polymers is expected to enhance the performance capabilities of 3D printed objects, moving towards higher-value applications similar to those seen in metal additive manufacturing.
Software improvements, including smarter, potentially AI-integrated systems, will streamline the AM workflow, making it more efficient and adaptable. The industry anticipates a narrowing skills gap as education in additive manufacturing becomes more widespread, preparing a new generation of workers proficient in AM technologies from the start of their careers.
Blender, with its rapid growth and development driven by a focus on innovation and community support, is set to play a crucial role in this evolving landscape. Its versatility for game design, 3D printing, architectural visualization, and more demonstrates its potential to support a wide range of additive manufacturing applications. As Blender continues to evolve, driven by its not-for-profit ethos and focus on serving the creative community, it is poised to meet the needs of artists, designers, and small studios navigating the expanding possibilities of 3D printing.
The broader adoption of 3D printing for mass manufacturing, digital warehousing, and on-demand production of spare parts will see additive manufacturing becoming a dominant technique in the industry. This transformation will be supported by Blender\"s capabilities in creating detailed models and prototypes, reinforcing its importance in the future of digital and physical production.
As the 3D printing industry looks towards a future of specialized, high-quality, and sustainable manufacturing processes, Blender\"s role as a versatile, open-source tool for 3D modeling and animation will undoubtedly be integral to the innovation and growth of additive manufacturing technologies.
READ MORE:
Resources and Communities for Blender Users
Blender\"s vibrant and expansive community offers a wide array of resources and platforms for users to connect, learn, and share their work. Whether you\"re a beginner seeking tutorials or an experienced artist looking for advanced tips, the Blender community has something for everyone.
- Blender Artists: An active independent user site for Blender enthusiasts to discuss projects, share work, and find solutions to challenges. Visit Blender Artists
- BlenderNation: Provides comprehensive updates on Blender developments, tutorials, artwork, and community news. Explore BlenderNation
- Blender.Today: A platform for user-submitted stories, engaging discussions, and weekly live streams. Check out Blender.Today
- Right Click Select: A place to share and vote on ideas for Blender. Discover Right Click Select
- Reddit /r/blender: A very active subreddit devoted to Blender, featuring news, critiques, and a monthly contest. Join the Reddit Blender Community
- Blend Swap: A community of passionate Blender artists who share their work under Creative Commons licenses. Explore Blend Swap
- CG Cookie: Offers Blender tutorials, asking questions, and peer feedback. Learn with CG Cookie
- Local Blender User Groups: Including PhillyBUG for users in Philadelphia, offering beginner-friendly sessions and more. Visit PhillyBUG
Additionally, Blender provides extensive documentation and tutorials for both beginners and advanced users, available on the Blender Documentation site and through the Blender Studio website. For more direct support, users can join chat rooms such as #blender-coders on blender.chat for development support or #support for community chat support.
For those interested in contributing to Blender\"s development or needing enterprise support, Blender offers avenues for involvement and professional services. Bugs can be reported to help improve Blender for everyone, and there\"s also an option for enterprise-grade support through Canonical for Blender LTS releases.
Whether you\"re looking to learn, share, or contribute, the Blender community is welcoming and rich with resources. Discover more at blender.org and join the vibrant community today!
Discover the limitless possibilities of Blender for 3D printing, a tool that brings your creative visions to life with precision and ease. Join a vibrant community eager to share, learn, and innovate together in the exciting world of 3D modeling.