Topic blender vs maya: Discover the strengths and unique features of Blender and Maya, as we dive into a comprehensive comparison to help you choose the ideal 3D creation tool for your artistic endeavors.
Table of Content
- Cost and Accessibility
- Customization and Scripting
- User Interface and Learning Curve
- Modeling and Texturing
- Rigging and Animation
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- Customization and Scripting
- User Interface and Learning Curve
- Modeling and Texturing
- What are the key differences between Blender and Maya in terms of features and usability?
- Rigging and Animation
- YOUTUBE: Blender vs Maya Comparison in 2024
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- User Interface and Learning Curve
- Modeling and Texturing
- Rigging and Animation
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- Modeling and Texturing
- Rigging and Animation
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- Rigging and Animation
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- Rendering Engines
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Blender and Maya
- Cost Comparison: Free vs Subscription-Based
- User Interface and Ease of Learning
- Modeling and Animation Features
- Texturing and Rendering Capabilities
- Community Support and Resources
- Software Customization and Extensibility
- Industry Usage: Indie vs Professional Studios
- Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Cost and Accessibility
Blender stands out as a free, open-source software, offering a cost-effective solution for individuals and small studios. In contrast, Maya is a licensed product, requiring a subscription but is often the choice for large studios due to its extensive features and industry-standard status.

READ MORE:
Customization and Scripting
Maya allows deep customization via its Maya Embedded Language (MEL), while Blender uses Python3 for scripting, making both highly extensible with a slight edge to Maya for more complex pipeline integration.

User Interface and Learning Curve
Maya is known for its more standardized, clear interface, potentially easing the learning curve for new users. However, Blender\"s ability to handle multiple windows may offer a more flexible workflow for some users.
%20(2).jpg)
Modeling and Texturing
- Blender provides simplified surface and texturing tools, making it accessible for beginners.
- Maya is recognized for its robust modeling capabilities, often considered the industry standard.
Rigging and Animation
- Maya excels in rigging, offering a range of plugins and an intricate system for greater control.
- Blender is favored for animation, with features that compete closely with Maya\"s capabilities.

_HOOK_
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
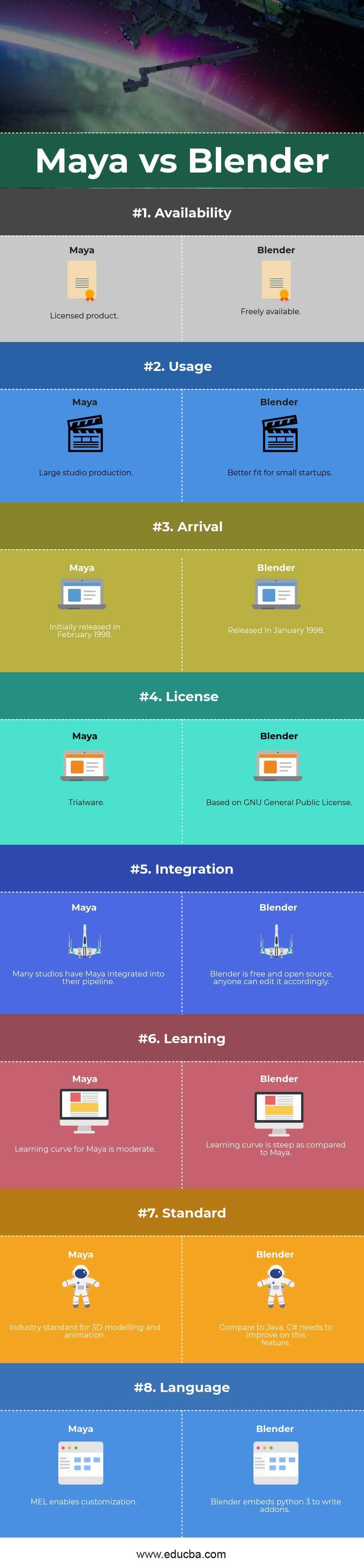
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.

Customization and Scripting
Maya allows deep customization via its Maya Embedded Language (MEL), while Blender uses Python3 for scripting, making both highly extensible with a slight edge to Maya for more complex pipeline integration.

User Interface and Learning Curve
Maya is known for its more standardized, clear interface, potentially easing the learning curve for new users. However, Blender\"s ability to handle multiple windows may offer a more flexible workflow for some users.

Modeling and Texturing
- Blender provides simplified surface and texturing tools, making it accessible for beginners.
- Maya is recognized for its robust modeling capabilities, often considered the industry standard.

_HOOK_
What are the key differences between Blender and Maya in terms of features and usability?
When comparing Blender and Maya in terms of features and usability, there are several key differences to consider:
- Cost: Blender is free and open-source, making it accessible to a wide range of users, while Maya is a paid software that can be quite expensive.
- Features: Blender offers a wide range of features including modeling, sculpting, animation, video editing, and more, all within a single software package. On the other hand, Maya is known for its industry-standard tools in animation, rendering, and simulation.
- Learning Curve: Maya has a steeper learning curve compared to Blender, as it is more complex and feature-rich. Blender, on the other hand, is known for its relatively intuitive user interface and beginner-friendly tools.
- Customization: Blender allows for a high level of customization and user-created add-ons, whereas Maya has a more structured and standardized workflow.
- Rendering: Maya is considered to have more efficient rendering tools, while Blender\'s rendering capabilities have improved significantly over the years.
Rigging and Animation
- Maya excels in rigging, offering a range of plugins and an intricate system for greater control.
- Blender is favored for animation, with features that compete closely with Maya\"s capabilities.
Blender vs Maya Comparison in 2024
Comparison - Discover the power of comparison in our latest video, showcasing how it can help you make informed decisions and choose the best option for your needs. Watch now for valuable insights! Use - Learn new and innovative ways to use everyday items in our exciting video! Find out how to maximize their potential and enhance your daily routines. Watch to unlock endless possibilities!
Blender vs Maya: Which One to Use
If you\'re a 3D artist or designer, you might be wondering which software is better suited for your needs: Blender or Maya?
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
User Interface and Learning Curve
Maya is known for its more standardized, clear interface, potentially easing the learning curve for new users. However, Blender\"s ability to handle multiple windows may offer a more flexible workflow for some users.
_HOOK_
Modeling and Texturing
- Blender provides simplified surface and texturing tools, making it accessible for beginners.
- Maya is recognized for its robust modeling capabilities, often considered the industry standard.
Rigging and Animation
- Maya excels in rigging, offering a range of plugins and an intricate system for greater control.
- Blender is favored for animation, with features that compete closely with Maya\"s capabilities.
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
Modeling and Texturing
- Blender provides simplified surface and texturing tools, making it accessible for beginners.
- Maya is recognized for its robust modeling capabilities, often considered the industry standard.
_HOOK_
Rigging and Animation
- Maya excels in rigging, offering a range of plugins and an intricate system for greater control.
- Blender is favored for animation, with features that compete closely with Maya\"s capabilities.
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
Rigging and Animation
- Maya excels in rigging, offering a range of plugins and an intricate system for greater control.
- Blender is favored for animation, with features that compete closely with Maya\"s capabilities.
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
_HOOK_
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
Rendering Engines
Blender comes equipped with Cycles and Eevee for ray tracing and real-time rendering, respectively. Maya uses Autodesk Arnold, a powerful option for high-quality renders.
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
Conclusion
Both Blender and Maya offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering. The choice between them depends on individual needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers a no-cost entry point with robust features for artists and small teams, while Maya remains a staple for high-end production environments demanding advanced features and industry-standard workflows.
Introduction to Blender and Maya
Blender and Maya are two of the most widely used 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software in the digital arts industry, each with its unique strengths and user base. Blender is renowned for being a completely free, open-source platform that supports a wide array of 3D creation tasks including modeling, animation, and rendering. Its accessibility and no-cost entry make it a popular choice among beginners, independent artists, and small studios. On the other hand, Maya is a professional, licensed product developed by Autodesk, and it is celebrated for its powerful features in modeling, animation, and rendering. Maya is often the go-to software for large studios and professionals working on high-end productions due to its advanced toolset and industry-standard workflows.
Both software offer robust features and capabilities, from intricate modeling and realistic rendering to complex animation and simulation tools. They cater to various needs across different sectors such as video games, film, television, and visual effects. The choice between Blender and Maya largely depends on the user\"s specific project requirements, budget constraints, and personal preference in workflow and interface.
- Blender is celebrated for its comprehensive feature set available entirely for free, including support for addons and a customizable interface.
- Maya is recognized for its sophisticated rigging, animation, and simulation tools that cater to high-end production needs.
Understanding the key differences and strengths of each software will help users make an informed decision based on their specific needs, whether they are students just starting out in 3D modeling or professionals working on complex projects.
_HOOK_
Cost Comparison: Free vs Subscription-Based
One of the most significant differences between Blender and Maya is their cost structure, which can greatly influence a user\"s choice depending on their budget and professional needs. Blender is celebrated for its completely free and open-source model, making it an accessible option for individuals, students, and small studios. This no-cost policy extends to all of Blender\"s features, updates, and plugins, providing a full suite of 3D creation tools without any financial barriers.
Maya, on the other hand, operates on a subscription-based model. As a professional-grade software developed by Autodesk, Maya is targeted towards industry professionals and large studios requiring advanced features and support. The subscription fee for Maya reflects its position as an industry-standard tool, with pricing options that vary based on the licensing terms, such as individual, business, or educational use. Although the cost of Maya can be a significant investment, it is justified by its extensive toolset, reliability, and integration into professional pipelines.
- Blender offers a zero-cost entry into 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, supported by a vibrant community and regular updates.
- Maya requires a subscription fee, with costs varying based on license type, but provides advanced features and industry-standard capabilities.
Understanding the cost implications of each software is crucial for users to align their choice with their budget, project requirements, and long-term professional goals. While Blender appeals to those seeking a cost-effective solution with a wide range of features, Maya is suited for professionals and studios willing to invest in top-tier software for complex projects.
User Interface and Ease of Learning
The user interface (UI) and learning curve of Blender and Maya significantly influence user preference and productivity. Blender boasts a customizable and modern interface that allows for a personalized workflow, which can be adapted to suit the unique needs of individual projects. Its recent updates have focused on making the UI more intuitive, thereby reducing the initial learning curve for new users. Blender\"s ability to handle multiple windows simultaneously enhances its flexibility, catering to a variety of user preferences.
Maya, with its longstanding reputation in the industry, provides a more standardized interface. Its UI is known for being both powerful and customizable, offering a wide range of tools and options to professionals. Maya\"s layout is designed to accommodate the complex needs of high-end production workflows, making it a staple in professional environments. However, this complexity can translate into a steeper learning curve for beginners, requiring more time to become proficient.
- Blender\"s interface is praised for its flexibility and adaptability, appealing to users who appreciate a more tailored approach to 3D modeling and animation.
- Maya\"s professional-grade UI is optimized for efficiency in complex projects, with a focus on streamlining the workflow for experienced users.
Choosing between Blender and Maya often comes down to the user\"s specific needs, experience level, and the type of projects they intend to work on. While Blender offers an accessible entry point for newcomers and independent creators, Maya remains the go-to choice for industry professionals seeking advanced functionality and control over their 3D projects.
Modeling and Animation Features
Blender and Maya both offer comprehensive toolsets for 3D modeling and animation, catering to a wide range of project types from simple to complex. Blender\"s interface and toolset are designed to be both user-friendly and powerful, offering a range of features for modeling, sculpting, and animation that make it a great choice for artists at all levels of expertise. Its modeling tools are particularly noted for their versatility and ease of use, making it a popular choice for quick prototyping as well as detailed 3D art and animation projects.
Maya, on the other hand, is recognized for its advanced modeling and animation capabilities, often considered the industry standard for high-end production work. Maya\"s modeling tools are designed for precision and complexity, offering a wide array of options for creating detailed and intricate models. Its animation tools are equally robust, providing a comprehensive suite of features for creating complex animations, including sophisticated rigging and character animation capabilities.
- Blender\"s modeling tools are highly versatile, offering features like sculpting, retopology, and modifiers that make it suitable for both beginners and advanced users.
- Maya excels in rigging and animation, with a wide range of tools and plugins that support intricate animation workflows, making it a preferred choice for film, television, and game development.
While both software are capable of producing high-quality work, the choice between Blender and Maya often comes down to the specific needs of the project and the preference of the artist or studio. Blender\"s free, open-source model makes it accessible to a wide audience, while Maya\"s advanced features and industry-standard status make it a go-to for professional production environments.
Texturing and Rendering Capabilities
When comparing Blender and Maya, both offer robust tools for texturing and rendering, key elements in the 3D creation process. Blender, a free and open-source software, provides a comprehensive suite of tools for modeling, texturing, animation, and rendering 3D objects and scenes. Its user-friendly interface and customizable workflow enhance efficiency, supported by Python scripting for extended capabilities. Blender\"s advanced simulation tools enable realistic animations for fluids, cloth, hair, and other physical effects, while its rendering capabilities are bolstered by the Cycles and Eevee engines, offering high-quality ray-tracing and real-time rendering options, respectively.
Maya, on the other hand, is a commercial software known for its sophistication in the 3D application space. It is preferred for its powerful CPU and GPU rendering capabilities, especially in tasks like UV mapping, texturing, and rendering 3D animations. Maya\"s rendering prowess is further exemplified by its integration with Arnold, a renderer that provides real-time scene changes, faster viewport renders, and accelerated render times by leveraging both GPU and CPU. This makes Maya ideal for detailed animations and large projects, with tools that expedite rendering processes.
Both platforms support third-party renderers like V-Ray, Octane Render, and Radeon ProRender, expanding their versatility. However, Blender\"s open-source nature allows for a wide range of free or inexpensive plugins to enhance texturing and rendering capabilities. Maya, with its industry-standard status, offers advanced rendering features and plugins that cater to high-end production needs.
Choosing between Blender and Maya for texturing and rendering tasks depends on the project\"s complexity, budget, and the artist\"s familiarity with the software. Blender offers a cost-effective, versatile solution with a steep learning curve, while Maya provides advanced features suitable for professional studio environments, albeit at a higher cost.
Community Support and Resources
Both Blender and Maya boast extensive communities and a wealth of resources that cater to users ranging from beginners to professionals. Blender, being an open-source platform, has fostered a passionate and engaged community. This community actively contributes to the software’s documentation, tutorials, and add-ons, making Blender a versatile tool for a wide range of 3D creation tasks. Users can find a wealth of online tutorials, forums, and free resources that make learning and mastering Blender accessible to all.
Maya, with its long-standing presence in the industry, offers a robust community and comprehensive professional support services. Users of Maya can easily find tutorials, forums, training videos, and professional advice, making it easier to solve problems and learn new techniques. Maya also offers regular webinars and has a strong network of users who share their knowledge and expertise, providing invaluable support for both new and experienced users.
When it comes to support and resources, both platforms offer:
- Online Tutorials and Forums: Extensive online tutorials and active forums where users can share knowledge, ask questions, and learn new skills.
- Documentation and Learning Resources: Comprehensive documentation and learning resources that help users understand the software\"s capabilities and how to utilize them effectively.
- Plugins and Add-ons: A wide range of plugins and add-ons that extend the functionality of both Blender and Maya, supported by their respective communities.
The choice between Blender and Maya often comes down to the specific needs, project requirements, and personal preferences of the user. Blender’s open-source nature and free access make it particularly appealing to hobbyists, independent creators, and small studios. In contrast, Maya is favored by professionals and studios requiring advanced features and industry-standard tools for large-scale productions.
Regardless of the choice, both Blender and Maya\"s communities play a crucial role in providing support, sharing knowledge, and fostering innovation within the 3D creation space.
_HOOK_
Software Customization and Extensibility
When it comes to software customization and extensibility, both Blender and Maya offer unique approaches that cater to different user needs and preferences. Blender, celebrated for its open-source nature, provides a highly customizable environment through its embedded Python3 scripting. This allows users to tailor the software to their specific workflow requirements, enhance functionality, and even develop new tools. The Python API\"s flexibility enables seamless integration into existing workflows and easier collaboration with other software, making Blender a versatile choice for a wide range of projects.
Maya, developed by Autodesk, offers customization through its Maya Embedded Language (MEL) and Python scripting. These capabilities allow for automation, advanced customization, and the creation of complex workflows tailored to professional studio environments. Maya\"s extensive plugin support further extends its capabilities, allowing users to add detailed features for modeling, animation, and rendering that cater to the needs of high-end production environments. The availability of numerous plugins and add-ons, including industry-standard options like ZBrush for sculpting and the Ziva plugin for muscle dynamics, underscores Maya\"s adaptability and power in professional settings.
Both platforms support a wide array of plugins and third-party tools, enhancing their usability and functionality. Blender, being community-driven, benefits from a wealth of free or low-cost plugins that contribute to its broad appeal among independents and small studios. Maya\"s plugin ecosystem, while often more professionally oriented, provides essential tools for feature film production and other high-end applications.
In conclusion, the choice between Blender and Maya for software customization and extensibility depends on the user\"s specific needs, budget, and project requirements. Blender offers an accessible, flexible solution with its open-source model and Python scripting, making it ideal for a broad range of creative projects. Maya, on the other hand, caters to professional environments requiring deep customization and integration with other industry-standard tools, supported by its robust MEL and Python scripting capabilities.
Industry Usage: Indie vs Professional Studios
The debate between Blender and Maya extends deeply into their respective industry usages, delineating a divide between indie developers and professional studios. Blender, with its open-source, free-to-use nature, has carved a niche among indie developers, hobbyists, and small studios. Its comprehensive toolset for modeling, texturing, animation, and rendering, coupled with advanced simulation capabilities, makes Blender an attractive option for those seeking a cost-effective, yet powerful 3D creation software. The Blender Foundation’s commitment to continuous improvement has seen the platform evolve significantly, gaining traction within the entertainment industry and being utilized by major studios like Pixar, DreamWorks Animation, and Sony Pictures Imageworks for various projects.
Maya, on the other hand, stands as the preferred choice for professional environments, especially within the realms of video game development, film animation, and VFX. Developed by Autodesk, Maya’s robust toolset, industry-standard workflows, and integration with other Autodesk products make it a staple in large-scale productions. Its advanced features for dynamics and effects, rigging, 3D rendering and shading, motion graphics, and pipeline integration align with the needs of top-tier game development and film production, making it a worthwhile investment for professional studios.
While Blender is acclaimed for its user-friendly interface and accessibility to beginners, Maya is recognized for its superior modeling tools and capabilities, adhering to industry standards and facilitating the creation of complex models and animations. Despite Blender\"s growing popularity and capabilities, Maya continues to be indispensable in professional settings, owing to its comprehensive features and compatibility with industry-standard software. Ultimately, the choice between Blender and Maya hinges on the specific needs, project requirements, and budget constraints of the user or studio, with both software offering unique strengths for different segments of the 3D creation and animation industry.
Both platforms, despite their distinct target audiences and usage contexts, underscore the dynamic landscape of 3D modeling and animation software. Whether it’s Blender\"s appeal among indie creators and small studios or Maya\"s indispensability in professional and large-scale productions, each has shaped industry practices and preferences in significant ways.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
Choosing between Blender and Maya ultimately depends on your specific needs, budget, and experience level. Both offer powerful features for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, but they cater to different user bases and project scales.
- Cost Efficiency: Blender stands out for its cost-effectiveness, being a free and open-source software, making it ideal for students, hobbyists, and small studios. Maya, on the other hand, requires a subscription, making it a significant investment but offering industry-standard tools for large studios and professional environments.
- User Interface and Learning Curve: Maya is known for its more traditional and customizable interface, which might be easier for users with experience in 3D modeling software. Blender has a more minimalist and integrated UI, potentially easier for new users but requires some adaptation to reach a power-user level.
- Community and Support: Blender boasts a strong, community-driven support system with numerous tutorials and forums, making it easier for newcomers to find help. Maya offers comprehensive official documentation and professional support, essential for large-scale projects and studios.
- Feature Set and Capabilities: Both applications provide robust toolsets for 3D modeling, rigging, and rendering. Maya has an edge in advanced features and is widely used in the industry for high-profile game and film projects. Blender\"s capabilities are also extensive, with strengths in modeling, animation, and its unique real-time rendering engine, Eevee.
- Project Scale and Professional Needs: Maya is more suited for large studio productions requiring advanced tools and integration with other industry-standard software. Blender is highly capable for a wide range of applications, including small to medium projects, freelancing, and education.
In summary, if budget constraints are significant and you\"re working on smaller to medium-scale projects, or if you\"re just starting out and wish to learn 3D modeling, Blender could be the perfect fit. For those working in or aspiring to enter a professional studio environment, or needing advanced features for large-scale productions, Maya might be the investment worth making.
Embark on a creative journey with our in-depth comparison of Blender and Maya, and discover which 3D modeling tool aligns with your artistic vision and project needs. Let your imagination soar and shape your future in 3D artistry.