Topic blender lighting tips: Unlock the full potential of your 3D projects with essential Blender lighting tips. Master the art of creating lifelike scenes that captivate and impress, using techniques that bring your digital worlds to vivid life.
Table of Content
- What are some effective tips for improving lighting in Blender?
- Realistic Lighting Techniques
- Advanced Lighting Tips
- Shading Techniques
- Advanced Lighting Tips
- Shading Techniques
- Shading Techniques
- Introduction to Lighting in Blender
- YOUTUBE: The Power of Lighting in Blender
- Top Lighting Techniques for Realism
- Understanding HDRI in Blender
- Global Illumination Explained
- Shadow Manipulation for Mood Enhancement
- The Role of Color in Lighting
- Advanced Lighting Tips: Textures, Gradients, and Animation
- Common Lighting Mistakes to Avoid
- Integrating Shading and Reflections for Depth
- Practical Examples and Case Studies
- Conclusion: Bringing It All Together
What are some effective tips for improving lighting in Blender?
Improving lighting in Blender is essential for creating realistic and visually appealing renders. Here are some effective tips to enhance your lighting in Blender:
- Experiment with Shadow Size: Adjust the size of your lamps to control the intensity of shadows. Larger sizes can create softer shadows for a calm atmosphere.
- Focus on Accuracy: Ensure that the brightness and scale of your lighting elements are accurate to achieve realistic results.
- Consider Color Temperature: Utilize color temperature to set the mood and enhance the realism of your scene.
- Utilize Environment Lighting: Incorporate environment lighting to simulate natural light sources and create a more immersive scene.
- Understand Lamp Strength: Increasing the size of a lamp can make the lighting darker, as it simulates a larger area of light emission.
By following these tips and experimenting with different settings in Blender, you can significantly improve the quality of lighting in your renders.
READ MORE:
Realistic Lighting Techniques
- Understanding the impact of light intensity and color on the scene\"s mood and realism.
- Using HDRI images for dynamic environment lighting, providing detailed light information.
- Emphasizing global illumination to simulate realistic light bouncing, enhancing scene authenticity.

Advanced Lighting Tips
- Experiment with the size and softness of shadows to convey different atmospheres.
- Balance lighting to avoid overexposure and maintain depth through shadows.
- Incorporate varied light colors to add emotional depth and realism to renders.
- Highlight the main subject with strategic lighting to guide viewer focus.
- Add textures to lights for added visual interest and to suggest off-screen elements.
- For animated scenes, consider dynamic lighting changes to enhance storytelling.

Shading Techniques
Utilize gradients and colored lighting to introduce depth, contrast, and visual interest to your scenes. Recognize the importance of glossy reflections and fresnel effects for achieving realistic material appearances.
Key Takeaways
Effective lighting and shading in Blender require a combination of technical skills and creative experimentation. By applying these tips, artists can create more engaging and lifelike renders.
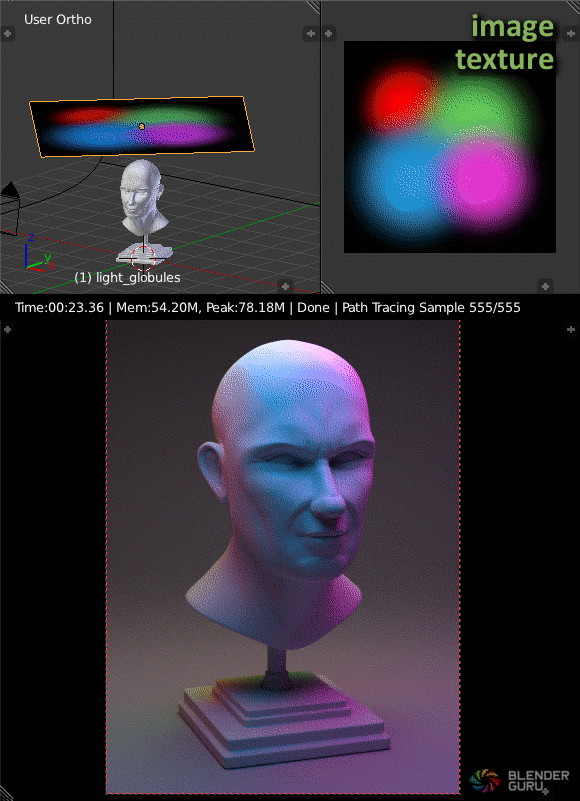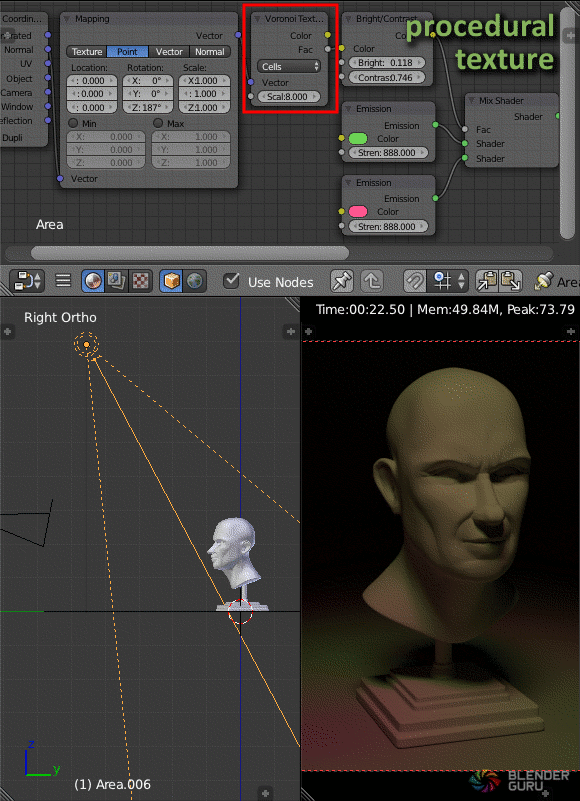
Advanced Lighting Tips
- Experiment with the size and softness of shadows to convey different atmospheres.
- Balance lighting to avoid overexposure and maintain depth through shadows.
- Incorporate varied light colors to add emotional depth and realism to renders.
- Highlight the main subject with strategic lighting to guide viewer focus.
- Add textures to lights for added visual interest and to suggest off-screen elements.
- For animated scenes, consider dynamic lighting changes to enhance storytelling.
_HOOK_
Shading Techniques
Utilize gradients and colored lighting to introduce depth, contrast, and visual interest to your scenes. Recognize the importance of glossy reflections and fresnel effects for achieving realistic material appearances.
Key Takeaways
Effective lighting and shading in Blender require a combination of technical skills and creative experimentation. By applying these tips, artists can create more engaging and lifelike renders.

Shading Techniques
Utilize gradients and colored lighting to introduce depth, contrast, and visual interest to your scenes. Recognize the importance of glossy reflections and fresnel effects for achieving realistic material appearances.
Key Takeaways
Effective lighting and shading in Blender require a combination of technical skills and creative experimentation. By applying these tips, artists can create more engaging and lifelike renders.

Introduction to Lighting in Blender
Lighting is a cornerstone of visual storytelling in Blender, transforming the mundane into the extraordinary. It not only illuminates your 3D scene but also sets the mood, enhances textures, and guides the viewer’s eye. Understanding the fundamentals of lighting in Blender is essential for any artist aiming to bring their creations to life. This introduction explores the key concepts, types of lights available in Blender, and foundational techniques to get started.
- Types of Lights: Blender offers several types of lights, including Point, Sun, Spot, and Area lights, each with its unique properties and uses. Experimenting with these lights can help you achieve the desired effect in your scene.
- Lighting Techniques: From three-point lighting setups to ambient occlusion, mastering various lighting techniques is crucial for creating depth and realism in your renders.
- Shadows and Reflections: Proper manipulation of shadows and reflections can add a layer of realism to your scenes, making objects feel grounded and enhancing spatial perception.
- Color and Mood: The color and intensity of light can dramatically affect the mood and emotion of a scene. Understanding color theory and its application in lighting will enable you to convey the right atmosphere.
- Environmental Lighting: Using HDRI images for environmental lighting can add realism to your scene by providing complex, real-world lighting conditions.
By the end of this section, you’ll have a solid foundation in lighting principles and be ready to explore more advanced techniques to light up your Blender projects effectively.
The Power of Lighting in Blender
Illuminate: \"Get ready to be mesmerized as you watch our video on how to perfectly illuminate your living space. Discover tips and tricks to make your home glow with warmth and style!\" Tutorial: \"Looking to master a new skill? Our tutorial video has got you covered! Learn step-by-step instructions and expert techniques to help you easily achieve your goals. Let\'s start learning together!\"
Three Point Lighting Tutorial Blender Product Rendering Series
A quick lighting setup for Studio Product renders. =================== ▻GUMROAD - https://blenderisms.gumroad.com/ ...
Top Lighting Techniques for Realism
Creating realistic lighting in Blender is an art that requires understanding both the tools at your disposal and the physics of light in the real world. This section covers the top techniques to achieve photorealism in your renders, emphasizing the importance of light\"s role in conveying the texture, depth, and atmosphere of a scene.
- Three-Point Lighting: A classic technique that uses three lights (key, fill, and back) to fully model your subjects. This setup provides depth, reduces flatness, and enhances textures.
- HDRI Lighting: Utilizing High Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI) for environmental lighting brings in rich, realistic light variations and reflections, mimicking real-world conditions.
- Global Illumination: Simulates light bouncing off surfaces, filling shadows, and ensuring that light interacts with the environment in a lifelike manner. Blender\"s Cycles renderer is particularly adept at handling global illumination.
- Color Temperature: Paying attention to the color temperature of light sources adds realism by mimicking how light behaves in different settings—cooler light for overcast days and warmer light for sunsets, for example.
- Soft Shadows: In the real world, shadows are rarely completely sharp. Adjusting shadow softness based on distance and light source size can greatly enhance realism.
- Use of Gobos: Gobos are objects placed in front of light sources to create patterns or textures in the light. This technique can simulate light filtering through windows, foliage, and other semi-transparent materials.
- Light Layering: Combining various light types and intensities can add complexity to a scene, simulating the nuanced way light interacts in real environments.
Mastering these techniques will elevate your Blender projects, making them more dynamic and immersive. Remember, the best lighting setups often involve experimentation and adaptation to the unique requirements of each scene.

Understanding HDRI in Blender
High Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI) plays a pivotal role in achieving photorealistic lighting in Blender. It captures a wider range of light and shadow details than standard digital imaging techniques, offering a powerful tool for artists. This section delves into the basics of HDRI, its benefits, and how to effectively use it in Blender to enhance your 3D scenes.
- What is HDRI: HDRI is a set of techniques that allow for the capture and use of light information from the real world in a way that standard digital images cannot. It stores more data about the light intensity and colors in a scene.
- Benefits of Using HDRI: Utilizing HDRI in your scenes can drastically improve lighting realism by introducing complex light interactions such as soft shadows, rich reflections, and accurate color hues that mimic real-world environments.
- How to Use HDRI in Blender:
- Importing HDRI: Start by downloading an HDRI image, then in Blender, go to the World settings and use the \"Environment Texture\" node to import your HDRI.
- Adjusting the HDRI Settings: Once loaded, you can adjust the rotation, scale, and intensity of the HDRI to match your scene\"s lighting needs.
- Previewing and Rendering: Use Blender’s viewport shading mode to preview the HDRI effects in real-time. Adjustments can be made until the desired lighting is achieved.
- Tips for Effective HDRI Lighting: Choose HDRI maps that complement your scene’s setting and mood. Pay attention to the direction and quality of light the HDRI provides, and adjust its intensity to blend seamlessly with any additional light sources you may have in your scene.
- Common Uses of HDRI: HDRI is extensively used for background environments, realistic sky lighting, and as a light source for reflective materials, enhancing the overall realism of 3D renders.
Mastering HDRI in Blender can significantly elevate the realism and immersion of your 3D projects. With practice, it becomes a vital tool in your lighting toolkit, providing a depth and authenticity difficult to achieve through other means.
_HOOK_
Global Illumination Explained
Global Illumination (GI) is a key technique in 3D rendering that simulates the complex way light bounces off surfaces and illuminates other surfaces, creating a more realistic depiction of a scene. This section explores what GI is, its importance in Blender, and how to utilize it effectively for achieving lifelike results in your renders.
- What is Global Illumination: GI refers to a set of algorithms used in rendering that simulate the indirect lighting received by surfaces. This includes light that has bounced from other surfaces, rather than direct light from a primary source such as the sun or a light bulb.
- Importance of Global Illumination: Using GI in your scenes adds depth, realism, and a sense of atmosphere that is difficult to achieve with direct lighting alone. It helps in creating softer shadows, subtle color blending from reflective surfaces, and overall, a more cohesive visual experience.
- Implementing GI in Blender:
- Enable Global Illumination: In Blender, GI can be enabled through the use of the Cycles or Eevee rendering engines, each offering different approaches to simulate GI.
- Adjust Settings: Fine-tune the intensity, bounces, and other relevant settings to control how light interacts within your scene. This includes adjusting the number of light bounces, which can greatly affect the realism and render times.
- Experiment with Light Sources: Different light sources can have a significant impact on how GI affects your scene. Experiment with positioning and intensity to achieve the desired effect.
- Tips for Optimizing Global Illumination: While GI can greatly enhance the realism of your renders, it can also increase render times. Use optimization techniques such as baking the lighting for static scenes or reducing the number of bounces in complex scenes to maintain a balance between quality and efficiency.
Understanding and effectively utilizing Global Illumination within Blender can transform your 3D projects, bringing them closer to photorealism. With careful setup and optimization, GI can be a powerful tool in your rendering toolkit.

Shadow Manipulation for Mood Enhancement
Shadows play a crucial role in setting the mood and enhancing the emotional impact of a scene in Blender. Through careful manipulation of shadows, artists can evoke specific feelings, create depth, and guide the viewer\"s attention. This section delves into techniques for manipulating shadows to enrich the mood of your renders.
- Soft vs. Hard Shadows: The hardness or softness of a shadow can significantly affect the atmosphere of a scene. Soft shadows often evoke a calm, natural, and diffuse light environment, while hard shadows can create drama, tension, and a sense of harshness or realism.
- Shadow Color: Shadows are not always black or grey. Adding color to shadows can subtly influence the mood of the scene, with cooler shadows suggesting a colder, more somber atmosphere and warmer shadows adding a sense of warmth and vibrancy.
- Directional Shadows: The direction from which a shadow falls can dramatically affect the composition and mood. For instance, long shadows can create a feeling of the late afternoon or early morning, often associated with nostalgia or tranquility.
- Shadow Intensity: The intensity of shadows can be adjusted to highlight specific areas of your scene or to direct focus. Reducing shadow intensity can make a scene feel more ethereal or dreamlike, whereas increasing it can add depth and contrast.
- Dynamic Shadows: Dynamic shadows, which change over time or in relation to movement, can add a layer of complexity and realism to animated scenes, influencing the mood through the interplay of light and darkness.
By mastering shadow manipulation, Blender artists can significantly enhance the narrative and emotional depth of their projects. Experimentation and observation of real-world lighting scenarios are key to effectively applying these techniques.
The Role of Color in Lighting
Color is a powerful tool in lighting design, significantly affecting the mood, perception, and effectiveness of a scene. In Blender, understanding and utilizing color in lighting can elevate your renders from good to visually stunning. This section explores how color influences lighting and ways to harness its potential effectively.
- Emotional Impact: Different colors evoke different emotions. Warm colors such as red, orange, and yellow can create feelings of warmth and comfort, while cool colors like blue, green, and purple can convey calmness and serenity.
- Color Temperature: The concept of color temperature is crucial in lighting. Warmer lights (with lower Kelvin values) are used to simulate evening or sunrise, while cooler lights (higher Kelvin values) mimic daylight. Blender allows for precise control over the color temperature of lights, enabling artists to shape the scene’s atmosphere.
- Color Contrast: Using contrasting colors in lighting can add depth and dimension to a scene. For instance, a warm light against a cool background can make a subject stand out, enhancing the visual interest of the composition.
- Realism and Depth: Subtle variations in light color can mimic real-world lighting conditions more accurately, adding realism and depth to renders. Natural light is rarely purely white; incorporating slight color variations can replicate the nuances of real-world light.
- Use of Colored Shadows: In the real world, shadows are not entirely devoid of color. Utilizing colored shadows in Blender can add an extra layer of realism and visual appeal to your scenes, particularly when combined with corresponding light sources.
Effectively using color in lighting within Blender requires experimentation and observation. By considering the emotional impact, color temperature, contrast, and realism, artists can dramatically enhance the visual storytelling and emotional depth of their renders.
Advanced Lighting Tips: Textures, Gradients, and Animation
As you delve deeper into Blender\"s lighting capabilities, incorporating advanced techniques like textures, gradients, and animation can bring unparalleled depth and realism to your scenes. This section explores these advanced strategies to enhance your 3D projects.
- Lighting Textures: Adding textures to your lights can introduce patterns, simulating realistic effects such as light filtering through leaves or the interplay of light and shadow through windows. This technique involves using an image or procedural texture to affect the distribution and color of light.
- Utilizing Gradients: Gradients in lighting can create a dynamic atmosphere, subtly shifting from one color to another. This can mimic the natural progression of the sky at sunrise or sunset, or be used to highlight specific areas of your scene, guiding the viewer’s eye.
- Animating Lights: Animation can breathe life into your scenes, whether it’s the flickering of a candle, the shifting shadows of a day passing, or the gradual change of light color temperature from dawn till dusk. Keyframing properties like intensity, color, and position can add dynamic storytelling elements to your renders.
- Practical Implementation:
- To add a texture to a light source, select the light in Blender, go to the Shader Editor, and connect a texture node to the light’s color or strength input.
- For gradients, use the Gradient Texture node in combination with a Color Ramp node in the Shader Editor to control the transition of colors.
- For animation, right-click on any light property (such as intensity or color) and select ‘Insert Keyframe’ at different points in your timeline to create changes over time.
These advanced lighting techniques in Blender are powerful tools for creating more engaging, dynamic, and realistic scenes. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering these methods and fully unleashing your creative potential.
Common Lighting Mistakes to Avoid
Effective lighting is essential for bringing realism and depth to your Blender projects. However, certain common mistakes can detract from the quality of your renders. Identifying and avoiding these pitfalls can significantly improve your lighting setup. Here are some of the most frequent lighting errors and how to avoid them.
- Overusing Ambient Light: Relying too much on ambient light can result in flat, uninteresting scenes without depth. Instead, use a balanced mix of light sources to create contrast and highlight details.
- Ignoring Light Source Size: The size of the light source affects the softness of the shadows it produces. Small light sources create hard shadows, while larger sources produce softer shadows. Matching the light source size to the mood you want to convey is crucial.
- Misusing Shadows: Neglecting the role of shadows can make scenes look unrealistic. Use shadows to add depth and shape to your scenes, but avoid making them too dark or too light.
- Incorrect Color Temperature: Every light source has a color temperature, and using the wrong temperature can affect the mood of the scene. Warm lights create a cozy atmosphere, while cool lights evoke a colder feel.
- Lack of Contrast: A common mistake is not using contrast effectively. Contrast between light and dark areas adds interest and guides the viewer’s eye around the scene.
- Forgetting about the Environment: Lighting doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Consider how environmental factors like time of day and weather conditions affect lighting and include these elements in your setup.
Avoiding these common lighting mistakes will help you create more dynamic, engaging, and realistic renders in Blender. Remember, good lighting is about balance, attention to detail, and understanding how light works in the real world.
_HOOK_
Integrating Shading and Reflections for Depth
Shading and reflections are crucial components in creating visually compelling and realistic 3D scenes in Blender. They add depth, dimensionality, and a sense of realism to objects, making them appear more integrated within their environment. This section covers strategies for effectively using shading and reflections to enhance the depth of your renders.
- Understanding Material Properties: Begin by familiarizing yourself with Blender’s material properties. Different materials reflect and absorb light in unique ways, affecting how they should be shaded and how they will reflect their surroundings.
- Using Reflective Surfaces: Incorporate reflective surfaces in your scene to add depth and realism. Reflections can suggest the scale, distance, and spatial relationship between objects, especially in scenes with water, glass, or metallic objects.
- Adjusting Specularity: Specularity controls the shininess and reflectiveness of a surface. Adjusting specularity can help you achieve the desired level of reflection, from matte surfaces with diffuse reflections to highly polished, mirror-like finishes.
- Implementing Fresnel Effects: The Fresnel effect describes how the amount of reflection changes depending on the viewing angle. Use Blender’s Fresnel node to simulate this effect, adding more depth and realism to your materials.
- Creating Depth with Shadows: Shadows are not just a lack of light; they are an integral part of shading that adds depth to a scene. Use soft shadows to create a sense of distance and hard shadows for more dramatic, high-contrast scenes.
- Experimenting with Environmental Lighting: Environmental lighting, such as HDRI maps, can significantly impact reflections and shading. Experiment with different lighting setups to see how they influence the appearance of materials and the depth of the scene.
By integrating advanced shading techniques and reflections into your Blender projects, you can achieve a level of depth and realism that brings your scenes to life. Practice and experimentation are key to mastering these concepts and applying them effectively in your work.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Learning from practical examples and case studies can significantly enhance your understanding of effective lighting techniques in Blender. This section highlights a few scenarios where specific lighting strategies were applied to achieve remarkable results, offering insights and inspiration for your own projects.
- Architectural Visualization: In a case study focusing on architectural visualization, a combination of HDRI for environmental lighting and carefully placed area lights was used to simulate natural daylight and artificial interior lighting, highlighting textures and materials of the architectural model.
- Character Modeling: For a character modeling project, three-point lighting was employed to enhance the character’s features, with a key light for highlighting, a fill light to soften shadows, and a rim light to outline the character against the background, adding depth and dimension.
- Product Visualization: In product visualization, reflective materials were showcased using a studio lighting setup with soft boxes to produce soft shadows and specular highlights, emphasizing the product\"s shape and material properties.
- Animation: A case study on animation highlighted the use of dynamic lighting to convey the passage of time, using keyframed changes in light color and intensity to simulate sunrise to sunset, adding realism and mood to the scene.
- Landscape Scenes: For a landscape scene, global illumination combined with fog and volumetric lighting was used to create atmospheric depth and a sense of vastness, effectively conveying the time of day and weather conditions.
These examples illustrate the diversity of lighting applications in Blender, demonstrating how different techniques can be tailored to suit the unique requirements of various types of projects. Experimentation and adaptation of these techniques will be key to mastering lighting in your own works.
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Bringing It All Together
Mastering lighting in Blender is a journey that combines artistry with technical skill. Throughout this guide, we\"ve explored a variety of techniques and principles, all aimed at enhancing the realism and emotional impact of your scenes. From the importance of shadow manipulation and the use of HDRI to the subtleties of color temperature and global illumination, every element plays a critical role in the final presentation.
Key takeaways include the value of experimenting with shadow sizes to convey mood, the necessity of restraint to prevent overlighting, and the power of color to add depth and emotion to your renders. The use of textures and gradients in your lighting setup can introduce complexity and realism, while animation can bring dynamic storytelling elements to your work.
- Remember that less is often more when it comes to lighting; subtle changes can have profound effects on the atmosphere and focus of your scenes.
- Embrace the full spectrum of light by incorporating a variety of sources, including environmental textures and global illumination, to mimic the complexity of real-world lighting.
- Experiment with color and gradients to enhance visual appeal and guide the viewer’s eye through your composition.
- Understand the technical tools at your disposal, such as HDRI and global illumination, but also recognize the art of lighting as a means to tell a story or evoke an emotion.
- Finally, continuously learn and adapt. The field of 3D rendering is ever-evolving, and staying informed about new techniques and technologies will keep your skills sharp and your renders stunning.
In conclusion, the art of lighting in Blender is a balance between science and intuition, requiring both understanding of the tools and a creative vision. By applying the principles and techniques discussed, you can illuminate your scenes in ways that bring out the best in your models, textures, and animations. So, keep experimenting, keep learning, and let your creativity shine through your work.
Unlock the full potential of your Blender projects with our comprehensive lighting tips, designed to breathe life into your renders. Master the art of illumination to create stunning, realistic visuals that captivate and inspire. Begin your journey to visual excellence today!