Topic speed up blender render: Discover how to significantly speed up Blender renders with expert tips and optimizations, transforming your 3D modeling and animation projects into more efficient, productive workflows.
Table of Content
- Optimize Your Hardware Setup
- Rendering Settings Adjustments
- Scene Optimization Techniques
- Advanced Techniques
- How can I speed up Blender render times effectively?
- YOUTUBE: Increase Blender 3D Cycles Rendering Speed by up to 1000%
- Conclusion
- Rendering Settings Adjustments
- Scene Optimization Techniques
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion
- Scene Optimization Techniques
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
- Introduction to Speeding Up Blender Renders
- Understanding Blender\"s Rendering Engine
- Hardware Considerations for Improved Render Times
- Optimizing Blender Settings for Faster Rendering
- Scene Optimization Techniques
- Advanced Blender Features to Enhance Render Speed
- Practical Tips and Tricks from Blender Experts
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Blender Rendering
- Case Studies: Successful Speed Improvements in Blender
- Conclusion: Streamlining Your Blender Workflow
Optimize Your Hardware Setup
Upgrading your hardware, especially graphics cards, can significantly boost rendering speeds. For Blender, utilizing a powerful GPU over a CPU can drastically reduce rendering times.
READ MORE:
Rendering Settings Adjustments
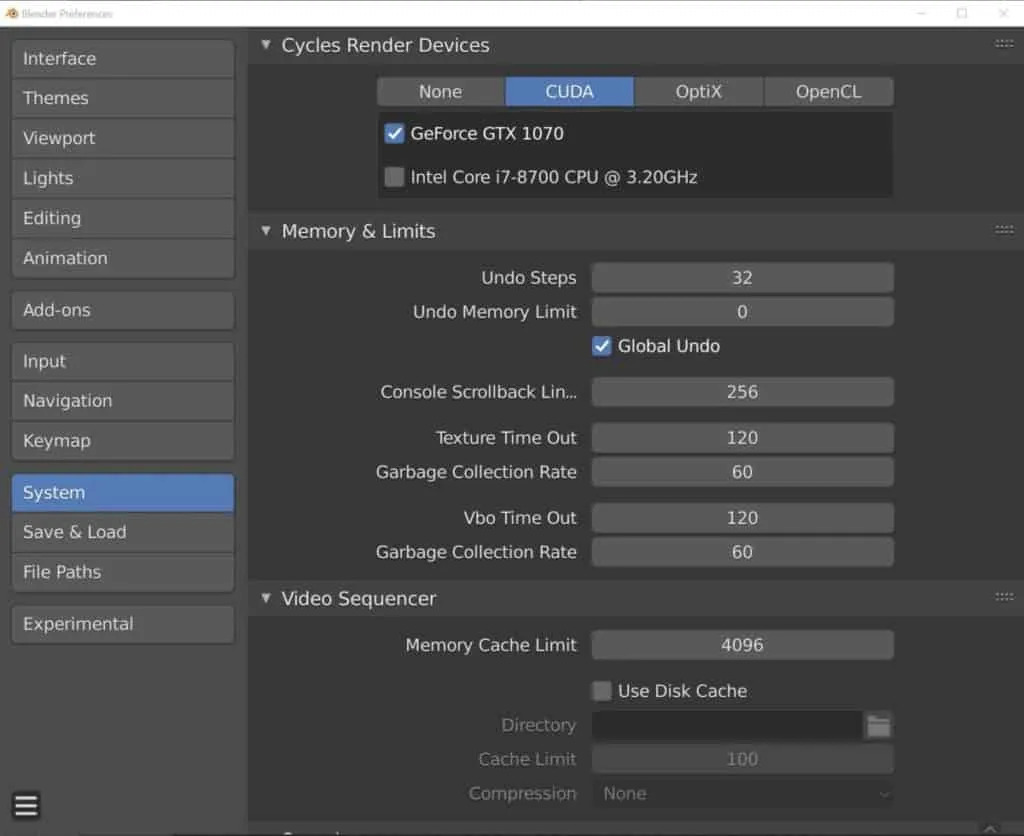
Enable GPU Rendering
Switching from CPU to GPU rendering in Blender\"s user preferences can lead to faster render times, leveraging the power of your graphics card.
Reduce Sample Count
Lowering the number of samples in your render settings can decrease render times while maintaining an acceptable level of quality.
Adjust Tile Sizes
Optimizing tile sizes for your rendering device (CPU or GPU) can improve performance. Larger tiles are generally better for GPU rendering, while smaller tiles can benefit CPU rendering.
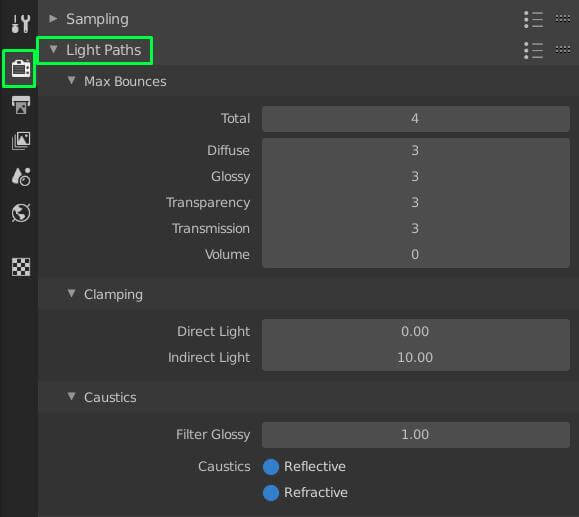
Utilize Light Paths Wisely
Adjusting light path settings, such as reducing bounces and using light clamping, can speed up renders without significant quality loss.

Scene Optimization Techniques
Simplify Your Scene
- Remove unnecessary objects and details that do not contribute to the final image.
- Use simpler materials and textures where high detail is not critical.
Optimize Geometry
Reducing the complexity of your models and using modifiers intelligently can reduce render times.
Efficient Use of Lighting
Minimizing the number of light sources and using environmental lighting can streamline the rendering process.
Advanced Techniques
Baking Textures and Lighting
Baking textures and lighting into your scenes can significantly reduce render times for complex scenes.
Use Denoising
Applying denoising can allow you to use lower sample counts without sacrificing image quality, speeding up renders.

How can I speed up Blender render times effectively?
To speed up Blender render times effectively, you can follow these steps:
- Enable GPU rendering in Blender\'s user preferences settings.
- Optimize your Light Path settings to reduce the number of bounces and increase render speed.
- Activate Blender\'s Persistence feature to cache data and speed up subsequent renders.
- Reduce the resolution of your render to decrease processing time.
- Consider lowering the frame rate if possible to reduce the workload on the renderer.
- Utilize AI tools like Topaz to interpolate or upres your images for faster rendering.
_HOOK_
Increase Blender 3D Cycles Rendering Speed by up to 1000%
Optimization: \"Unlock the secrets to improving efficiency and performance with our groundbreaking optimization techniques! Learn how to streamline processes and maximize results in our engaging and informative video presentation.\" Rendering: \"Dive into the fascinating world of rendering with our visually stunning video showcase! Discover the intricacies of creating lifelike images and animations that will leave you in awe.\"
Increase Blender 3D Cycles Rendering Speed by up to 1000%
Optimization: \"Unlock the secrets to improving efficiency and performance with our groundbreaking optimization techniques! Learn how to streamline processes and maximize results in our engaging and informative video presentation.\" Rendering: \"Dive into the fascinating world of rendering with our visually stunning video showcase! Discover the intricacies of creating lifelike images and animations that will leave you in awe.\"
Conclusion
By implementing these strategies, from hardware upgrades to rendering and scene optimization techniques, you can significantly speed up your Blender render times. This will allow you to work more efficiently and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.

Rendering Settings Adjustments
Enable GPU Rendering
Switching from CPU to GPU rendering in Blender\"s user preferences can lead to faster render times, leveraging the power of your graphics card.
Reduce Sample Count
Lowering the number of samples in your render settings can decrease render times while maintaining an acceptable level of quality.
Adjust Tile Sizes
Optimizing tile sizes for your rendering device (CPU or GPU) can improve performance. Larger tiles are generally better for GPU rendering, while smaller tiles can benefit CPU rendering.
Utilize Light Paths Wisely
Adjusting light path settings, such as reducing bounces and using light clamping, can speed up renders without significant quality loss.

Scene Optimization Techniques
Simplify Your Scene
- Remove unnecessary objects and details that do not contribute to the final image.
- Use simpler materials and textures where high detail is not critical.
Optimize Geometry
Reducing the complexity of your models and using modifiers intelligently can reduce render times.
Efficient Use of Lighting
Minimizing the number of light sources and using environmental lighting can streamline the rendering process.

Advanced Techniques
Baking Textures and Lighting
Baking textures and lighting into your scenes can significantly reduce render times for complex scenes.
Use Denoising
Applying denoising can allow you to use lower sample counts without sacrificing image quality, speeding up renders.

Conclusion
By implementing these strategies, from hardware upgrades to rendering and scene optimization techniques, you can significantly speed up your Blender render times. This will allow you to work more efficiently and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.
_HOOK_
Scene Optimization Techniques
Simplify Your Scene
- Remove unnecessary objects and details that do not contribute to the final image.
- Use simpler materials and textures where high detail is not critical.
Optimize Geometry
Reducing the complexity of your models and using modifiers intelligently can reduce render times.
Efficient Use of Lighting
Minimizing the number of light sources and using environmental lighting can streamline the rendering process.

Advanced Techniques
Baking Textures and Lighting
Baking textures and lighting into your scenes can significantly reduce render times for complex scenes.
Use Denoising
Applying denoising can allow you to use lower sample counts without sacrificing image quality, speeding up renders.
Conclusion
By implementing these strategies, from hardware upgrades to rendering and scene optimization techniques, you can significantly speed up your Blender render times. This will allow you to work more efficiently and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.
Advanced Techniques
Baking Textures and Lighting
Baking textures and lighting into your scenes can significantly reduce render times for complex scenes.
Use Denoising
Applying denoising can allow you to use lower sample counts without sacrificing image quality, speeding up renders.
Conclusion
By implementing these strategies, from hardware upgrades to rendering and scene optimization techniques, you can significantly speed up your Blender render times. This will allow you to work more efficiently and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.
_HOOK_
Conclusion
By implementing these strategies, from hardware upgrades to rendering and scene optimization techniques, you can significantly speed up your Blender render times. This will allow you to work more efficiently and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.
Introduction to Speeding Up Blender Renders
Blender, a powerhouse in the 3D modeling and animation world, offers endless possibilities for creators. However, long render times can slow down the creative process, leading many to seek ways to accelerate these times without compromising on quality. This section delves into the core strategies and adjustments that can significantly reduce your render times, ensuring a smoother, more efficient workflow.
Understanding the dynamics between Blender\"s render engine, your hardware configuration, and your project settings is crucial for optimizing render speeds. By fine-tuning your approach to these areas, you can achieve faster renders, whether you\"re working on complex animations or high-detail static scenes.
- Hardware Optimization: Upgrading or optimizing your hardware, especially your GPU, can have a profound impact on rendering speeds.
- Render Settings Adjustment: Simple tweaks in Blender\"s render settings, such as adjusting sample rates or tile sizes, can drastically reduce render times.
- Scene Complexity Reduction: Streamlining your scene to remove unnecessary elements or optimizing meshes can lead to quicker renders.
- Utilizing Blender Features: Features like render layers, baking, and denoising can improve render efficiency.
Each of these strategies offers a pathway to more efficient rendering, allowing artists to focus more on creativity and less on waiting. The following sections will explore these strategies in detail, providing step-by-step guidance on how to implement them effectively.
Understanding Blender\"s Rendering Engine
Blender is equipped with powerful rendering engines, each designed to cater to different project needs and workflows. Understanding these engines—Cycles and Eevee—is fundamental to optimizing your rendering process and achieving the best balance between speed and visual fidelity.
- Cycles: A ray-trace based production engine known for its ability to produce highly realistic renders through physically accurate simulations of light. It\"s ideal for projects where visual realism is paramount.
- Eevee: A real-time render engine designed for speed and interactivity, making it suitable for animation previews and projects where time is of the essence. While it may not achieve the same level of detail as Cycles, it offers a substantial reduction in rendering time.
Choosing the right engine depends on your project\"s specific needs:
- For high-quality, photorealistic images and animations, Cycles offers the depth and realism needed at the cost of longer render times.
- For rapid prototyping, animation previews, or when working under tight deadlines, Eevee provides a fast, albeit less detailed, rendering option.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each rendering engine allows you to tailor your workflow for efficiency and quality, leading to faster renders without sacrificing the artistic vision of your projects.
Hardware Considerations for Improved Render Times
Optimizing your hardware is a crucial step in reducing Blender render times. The right setup can significantly enhance your rendering speed, allowing for a smoother and more efficient production process. Here\"s how to tailor your hardware for optimal performance:
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Blender\"s rendering engines, especially Cycles, can leverage the power of GPUs for accelerated rendering. High-end GPUs can drastically reduce render times compared to CPU rendering.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): While GPUs are often faster, a powerful CPU is also essential for efficient rendering, especially when using Blender\"s CPU render mode. Multi-core processors can handle more tasks simultaneously, improving overall speed.
- Memory (RAM): Adequate RAM is necessary for handling large scenes or high-resolution textures. It ensures smooth performance and prevents bottlenecks during rendering.
- Storage: Solid-state drives (SSDs) can speed up load times for your Blender projects and assets, contributing to a faster workflow.
Combining a powerful GPU with a strong CPU, sufficient RAM, and fast storage can create an ideal environment for Blender rendering. This setup not only reduces render times but also enhances your overall 3D modeling and animation experience.
Optimizing Blender Settings for Faster Rendering
Optimizing settings within Blender can significantly impact your rendering speeds. Here are some crucial adjustments and practices to consider for faster rendering:
- Enable GPU Rendering: Switching from CPU to GPU rendering in Blender\"s user preferences can drastically reduce render times, utilizing the power of your graphics card.
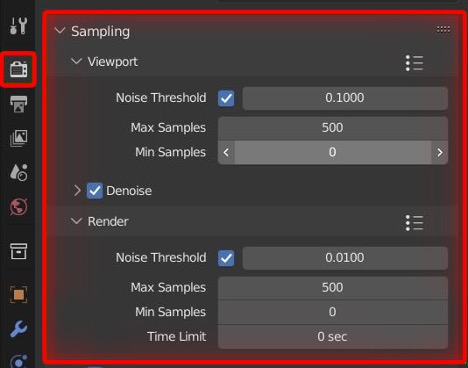
- Adjust Sample Rates: Lowering the number of samples in render settings can decrease render times. Finding the right balance between quality and speed is key.
- Optimize Light Sources: Minimizing the number of light sources and using environment lighting can speed up the rendering process without compromising the scene\"s aesthetics.
- Use Render Layers: Blender allows for different parts of your scene to be rendered separately using render layers, which can be more efficient for complex scenes.
- Tile Size Optimization: Adjusting tile sizes according to your hardware (larger tiles for GPU, smaller for CPU) can improve rendering efficiency.
- Denoising: Utilizing Blender\"s denoising feature allows for lower sample counts while maintaining image quality, thus reducing render times.
- Resolution and Output Settings: Experimenting with render resolution and output formats can also offer speed benefits, with some formats saving quicker than others.
These adjustments, tailored to your specific project needs and hardware capabilities, can lead to significant improvements in render times, enabling a more fluid creative process in Blender.
_HOOK_
Scene Optimization Techniques
Optimizing your Blender scene is pivotal for reducing render times without sacrificing quality. Here are some effective techniques to streamline your scene and enhance rendering efficiency:
- Reduce Geometry Complexity: Simplify models and use modifiers judiciously. Higher polygon counts increase render times, so consider using less complex geometry where high detail is not necessary.
- Limit Light Sources: Each additional light source increases render time. Use the minimum number of lights necessary for your scene, and consider ambient occlusion or world lighting for ambient effects.
- Optimize Materials and Textures: High-resolution textures and complex shaders can slow down rendering. Where possible, use lower resolution textures and simplify material setups.
- Use Proxies for Complex Objects: For heavy geometry like trees or characters, use proxy models during scene setup and switch to the high-detail models only for final rendering.
- Manage Render Layers: Divide your scene into render layers. This allows you to render complex scenes in manageable portions and can significantly reduce overall render time.
- Bake Textures and Lighting: Baking textures and lighting into your scenes can drastically reduce render times, especially for static elements in animations or large scenes.
- Viewport Culling: Utilize Blender’s viewport culling features to automatically exclude objects not seen by the camera from the render process, reducing unnecessary calculations.
By applying these scene optimization techniques, you can achieve faster render times, enabling you to iterate more rapidly and focus on the creative aspects of your projects.
Advanced Blender Features to Enhance Render Speed
Blender offers several advanced features that can significantly enhance render speed, providing both new and experienced users with powerful tools to streamline their rendering workflows. Implementing these features can lead to substantial improvements in render efficiency and time savings:
- Render Layers and Passes: Utilize render layers and passes to separate your scene into manageable parts. This allows for selective rendering of elements, reducing overall render times by focusing computational resources only where needed.
- Baking: Baking complex computations like textures, lighting, or shadows into simpler, pre-calculated images can drastically reduce render times, especially useful for static scenes or repetitive elements.
- Simplified Shading Models: For scenes where ultra-realism isn\"t necessary, using simpler shading models can speed up rendering without a significant loss in visual quality.
- Adaptive Sampling: Adaptive sampling automatically adjusts the number of samples in different areas of your scene based on the level of detail required, reducing render times while maintaining quality where it matters most.
- Light Portals: In scenes with complex lighting, especially indoor scenes with natural light coming from small windows, light portals can help focus the rendering engine’s efforts, speeding up calculations for indirect light.
- Optimization Add-ons: Various add-ons are available for Blender that optimize rendering settings and scene configurations to maximize efficiency and speed.
- Denoising: Blender’s denoising tools can greatly reduce the need for high sample counts by cleaning up noise in post-processing, offering a good balance between speed and quality.
By leveraging these advanced features, Blender users can achieve faster render times, allowing for more iterations and faster project completions. These tools and techniques are particularly beneficial in workflows where time is a critical factor, without compromising the final output quality.
Practical Tips and Tricks from Blender Experts
Gaining insights from seasoned Blender professionals can transform your rendering workflow, making it faster and more efficient. Here are expert-recommended tips and tricks to speed up your Blender renders:
- Switch to GPU Rendering: Utilizing your GPU for rendering can significantly decrease render times compared to using your CPU alone.
- Use Baked Textures: Baking allows you to pre-compute certain aspects of your scene, such as lighting or shadows, reducing the computational load during rendering.
- Optimize Light Sources: Minimize the number of light sources in your scene. Fewer lights mean less computation, which can lead to faster renders.
- Selective Rendering: Focus on rendering only the parts of your scene that are necessary. This can be particularly useful during the development phase, saving time by not rendering the entire scene.
- Instance Instead of Duplicate: Instancing objects allows you to create multiple copies of an object without the additional computational overhead of duplicated geometry.
- Adopt Efficient Material and Texture Practices: Simplify materials and textures where possible. Higher resolution and complexity can increase render times.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update Blender to the latest version. Each update often includes optimizations that can speed up rendering processes.
- Combine CPU & GPU Rendering: If supported, using both CPU and GPU for rendering can leverage all available computing power, reducing render times.
- Adjust the Light Sampling Threshold: Increasing the light sampling threshold in your render settings can speed up rendering at the cost of some quality, suitable for previews or less critical renders.
Implementing these tips from Blender experts can drastically reduce your render times, allowing you to focus more on creativity and less on waiting for renders to complete.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Blender Rendering
Efficiency in Blender rendering is not just about doing things right; it\"s also about avoiding common mistakes that can unnecessarily increase render times or compromise the quality of your output. Here are several pitfalls to be aware of:
- Overloading Scenes with High-Polygon Models: Adding too many high-polygon models to your scene can drastically slow down render times. Use lower-polygon models where high detail is not necessary.
- Ignoring the Importance of Simplifying Materials: Complex materials can significantly increase render times. Simplify materials whenever possible without compromising the visual quality of your scene.
- Not Utilizing Blender\"s Optimization Features: Features like simplifying the scene, using bounding boxes, or viewport shading can improve performance during the development phase but are often overlooked.
- Overuse of Subsurface Scattering (SSS): While SSS can add realism to materials, it can also slow down renders. Use it judiciously and only when necessary.
- Excessive Light Sources: Each additional light source increases computational load. Use the minimum number of lights needed for your scene and consider baking lighting where possible.
- Neglecting to Bake Animations and Simulations: Baking animations and simulations can save considerable render time, especially for complex scenes or physics simulations.
- Failure to Optimize Render Settings: Using default render settings without optimization for your specific project can lead to longer render times. Adjust settings such as sample rates, tile sizes, and resolution according to your needs.
- Forgetting to Clean Up the Scene: Unused materials, textures, and objects that are not visible in the final render can still affect render times. Regularly clean your scene to remove unnecessary elements.
Avoiding these pitfalls will not only speed up your rendering process but also improve your workflow efficiency, allowing you to focus more on creativity and less on waiting for renders to finish.
Case Studies: Successful Speed Improvements in Blender
Exploring real-world examples provides valuable insights into how various techniques and optimizations can significantly enhance Blender\"s rendering speeds. These case studies highlight the effectiveness of strategic improvements:
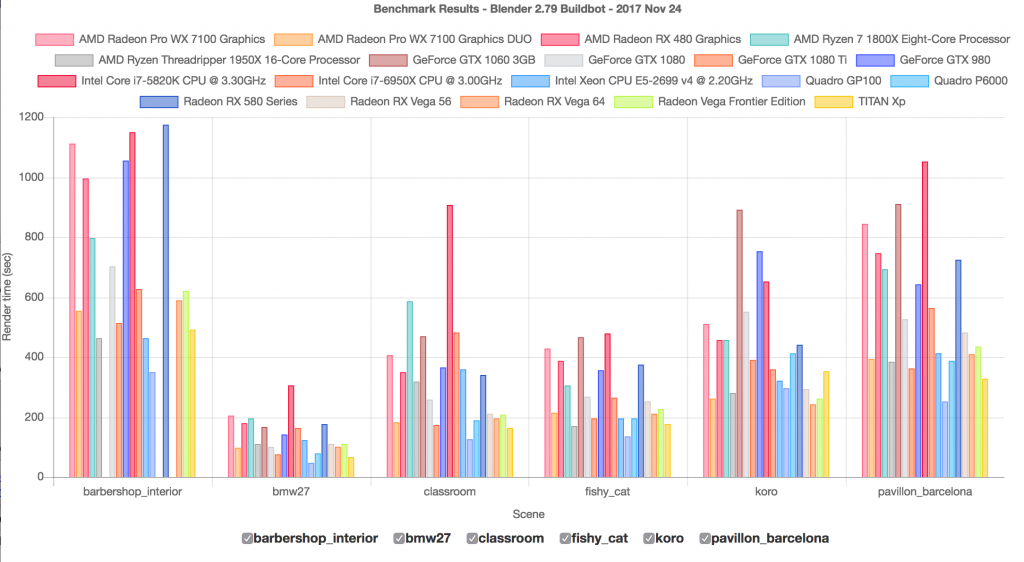
- Upgrading to High-Performance GPUs: Implementing NVIDIA\"s RTX 40 series GPUs resulted in rendering performance improvements of over 100%, demonstrating the impact of advanced hardware on rendering times.
- Utilizing Blender Updates: Transitioning to Blender 3.6 introduced performance optimizations like GPU rendering enhancements and viewport shader compiling speed-ups, showcasing the importance of staying updated.
- Adopting Hybrid Rendering Approaches: Combining CPU and GPU rendering capabilities can optimize resource use and speed up rendering processes, as seen with Blender 2.80\"s hybrid rendering feature.
- Implementing Software Optimizations: Adjustments in render settings, such as enabling GPU rendering and optimizing light sources, have shown to drastically reduce render times in various projects.
- Baking Textures and Lighting: Case studies have illustrated that baking textures and lighting can considerably decrease render times, especially for static scenes or repetitive elements.
These case studies underscore the multifaceted approach required to achieve significant render speed improvements in Blender. By leveraging hardware upgrades, software optimizations, and efficient rendering techniques, artists and developers can significantly reduce render times, allowing for a more dynamic and productive creative process.
_HOOK_
READ MORE:
Conclusion: Streamlining Your Blender Workflow
Accelerating Blender renders involves a combination of hardware optimization, software settings adjustments, and efficient scene management. By embracing these strategies, users can significantly reduce render times, enhancing productivity and allowing for more creative exploration within the Blender environment. Key takeaways include:
- Investing in high-performance GPUs and ensuring your system is optimally configured for Blender.
- Making strategic adjustments to Blender\"s render settings to balance quality and speed.
- Optimizing scene complexity, leveraging Blender\"s features like render layers and baking, and staying updated with the latest versions and techniques.
- Avoiding common pitfalls by maintaining a clean and efficient workflow.
In conclusion, while every project has unique requirements, the principles of speeding up Blender renders are universally applicable. Implementing these strategies can lead to a more efficient workflow, allowing artists and designers to focus on the creative aspects of their projects rather than being hindered by long render times.
Embrace these proven strategies to speed up your Blender renders, unlocking faster workflows and more creative freedom. Transform your 3D modeling and animation projects into efficient, enjoyable processes with these expert tips.