Topic how to rig in blender: Discover the art of bringing your 3D characters to life with our comprehensive guide on how to rig in Blender, tailored for both beginners and seasoned artists looking to refine their skills.
Table of Content
- Getting Started with Rigging
- Rigging Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Free Models & Character Rigs
- Rigging Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- What is the process for rigging in Blender?
- YOUTUBE: Blender - Completely Rigging A Character in 5 Minutes
- Free Models & Character Rigs
- Free Models & Character Rigs
- Introduction to Blender Rigging
- Key Features of Blender\"s Rigging Tools
- Step-by-Step Basic Rigging Process
- Advanced Rigging Techniques and Tips
- Working with Constraints and Modifiers
- Utilizing Drivers and Shape Keys for Animation
- Creating and Managing Armatures
- Weight Painting for Realistic Movement
- Animating Characters with Inverse Kinematics
- Free Resources: Models and Rigs for Practice
- Common Rigging Problems and Solutions
- Enhancing Your Rigging Workflow
- Conclusion and Further Learning Resources
Getting Started with Rigging
Blender offers a comprehensive set of rigging tools, including envelope, skeleton, automatic skinning, easy weight painting, mirror functionality, bone layers, and colored groups for organization. B-spline interpolated bones enhance the rigging process, allowing for smoother transitions and movements.
Understanding Constraints
Constraints in Blender are used to control an object\"s properties, such as location, rotation, and scale, by using static values or another object as a \"target.\" This indirect animation technique can animate constraint settings, influencing the object\"s animation through the targets used by its constraints.
Drivers and Shape Keys
Drivers offer a way to control property values with mathematical expressions or Python scripts, mapping the output to the driven property. Shape keys are utilized for object deformation into new shapes, ideal for facial animations and refining skeletal rigs.
Motion Paths
The Motion Paths tool visualizes the motion of points over a series of frames, useful for tracking the movement of object origins and bone joints in animations.
READ MORE:
Rigging Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting with basic rigging, adding bones for the chest, neck, and head is essential. For humanoid models, keeping these bones aligned in a straight line is recommended. Arm rigging introduces complexity, requiring precise placement of shoulder bones and careful adjustment for arm and hand bones. This tutorial details the process of adding and manipulating bones to create a basic humanoid rig, emphasizing the importance of naming conventions and duplication for symmetry.
- Chest, Neck, Head: Align bones in a straight line.
- Arms: Precisely place shoulder bones, adjust arm and hand bones.
- Scaling and Duplicating: Techniques for mirroring bones to the opposite side.
Advanced Rigging Techniques
Blender 2.8 introduces advanced rigging techniques, including parenting, armatures, and various constraints like copy limit, tracking, and transform constraints. Character rigging and inverse kinematics are covered, providing a solid foundation for creating complex rigs.

Free Models & Character Rigs
For practice, Blender offers free models and character rigs, such as detailed gladiators, futuristic assets with emissive textures, and stylized models like a great sword with magical properties. These assets are perfect for honing rigging and animation skills.
- Gladiator Model: Highly detailed, realistic model with proper muscle groups.
- Goblin Warrior: Features detailed textures and a menacing design.
- The Great Sword: A stylized model with glowing runes.
Learning to rig in Blender opens up a world of possibilities for animators and 3D artists. By mastering the tools and techniques provided in Blender, you can create intricate and lifelike animations that bring your characters to life.

Rigging Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting with basic rigging, adding bones for the chest, neck, and head is essential. For humanoid models, keeping these bones aligned in a straight line is recommended. Arm rigging introduces complexity, requiring precise placement of shoulder bones and careful adjustment for arm and hand bones. This tutorial details the process of adding and manipulating bones to create a basic humanoid rig, emphasizing the importance of naming conventions and duplication for symmetry.
- Chest, Neck, Head: Align bones in a straight line.
- Arms: Precisely place shoulder bones, adjust arm and hand bones.
- Scaling and Duplicating: Techniques for mirroring bones to the opposite side.
Advanced Rigging Techniques
Blender 2.8 introduces advanced rigging techniques, including parenting, armatures, and various constraints like copy limit, tracking, and transform constraints. Character rigging and inverse kinematics are covered, providing a solid foundation for creating complex rigs.
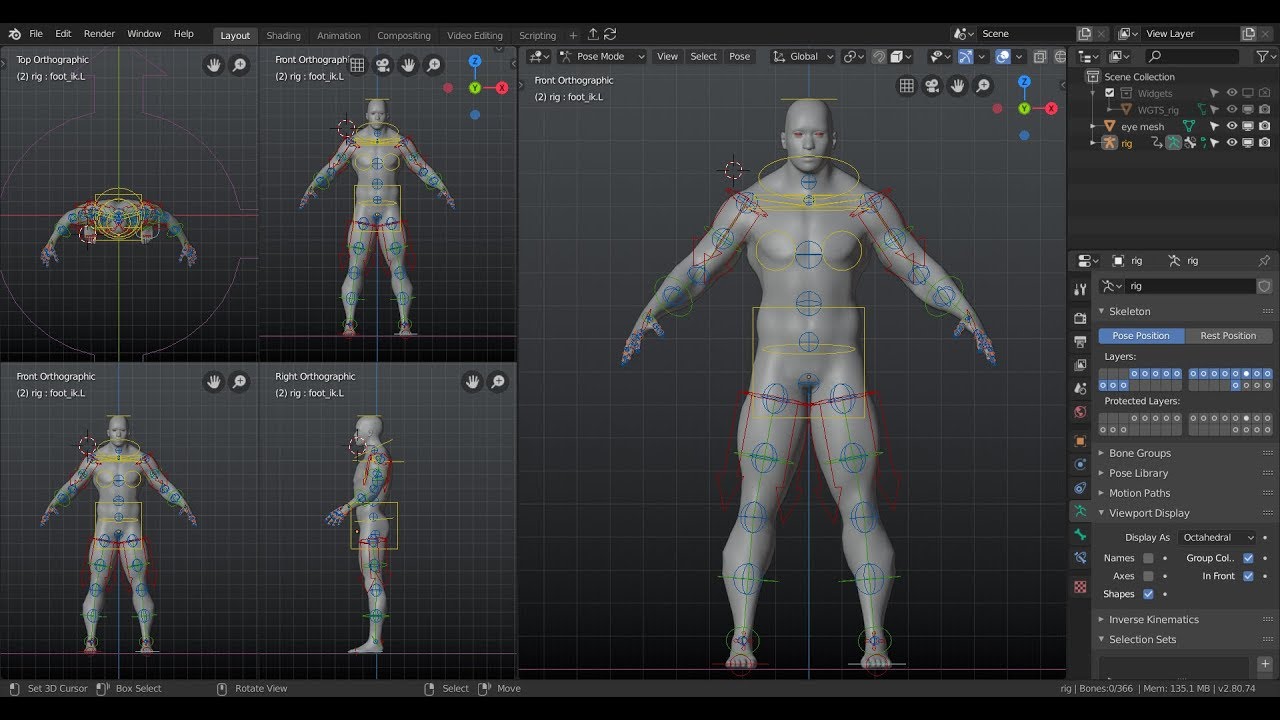
What is the process for rigging in Blender?
To rig a character in Blender, follow these steps:
- Open Blender and import your character model.
- Select the character model and switch to the Object Data Properties tab.
- Add an armature by pressing Shift + A and selecting Armature > Single Bone.
- Position the armature at the desired location and start creating bones that will define the rig.
- Parent the character model to the armature by selecting the character model first, then the armature, and pressing Ctrl + P and choosing With Automatic Weights.
- Enter Pose Mode by selecting the armature and pressing Ctrl + Tab.
- Adjust the bone positions to fit the character\'s limbs and create a functional rig.
- Test the rig by moving the bones in Pose Mode to ensure the character moves as expected.
- Refine the rig by adjusting weights and adding constraints if needed.
- Once satisfied, you can animate your rigged character in Blender!
_HOOK_
Blender - Completely Rigging A Character in 5 Minutes
Dive into the fascinating world of character rigging and bring your animated creations to life with fluid movements and realistic expressions. Learn the art of rigging and unlock endless possibilities in animation.
Easy and Quick Character Rigging in Blender - Blender Basics Tutorial
Discover the essential principles of Blender through this beginner-friendly tutorial on Blender basics. Master the fundamentals of 3D modeling, texturing, and rendering as you embark on your creative journey in the world of Blender.
Free Models & Character Rigs
For practice, Blender offers free models and character rigs, such as detailed gladiators, futuristic assets with emissive textures, and stylized models like a great sword with magical properties. These assets are perfect for honing rigging and animation skills.
- Gladiator Model: Highly detailed, realistic model with proper muscle groups.
- Goblin Warrior: Features detailed textures and a menacing design.
- The Great Sword: A stylized model with glowing runes.
Learning to rig in Blender opens up a world of possibilities for animators and 3D artists. By mastering the tools and techniques provided in Blender, you can create intricate and lifelike animations that bring your characters to life.

Free Models & Character Rigs
For practice, Blender offers free models and character rigs, such as detailed gladiators, futuristic assets with emissive textures, and stylized models like a great sword with magical properties. These assets are perfect for honing rigging and animation skills.
- Gladiator Model: Highly detailed, realistic model with proper muscle groups.
- Goblin Warrior: Features detailed textures and a menacing design.
- The Great Sword: A stylized model with glowing runes.
Learning to rig in Blender opens up a world of possibilities for animators and 3D artists. By mastering the tools and techniques provided in Blender, you can create intricate and lifelike animations that bring your characters to life.

Introduction to Blender Rigging
Rigging in Blender is a crucial step in the animation process, allowing animators to create a skeleton for a 3D model so it can move in realistic ways. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, understanding rigging in Blender opens up the possibility to bring characters and objects to life.
This section covers the basics of rigging in Blender, including essential tools, techniques, and step-by-step instructions to get started. Our aim is to demystify the rigging process, making it accessible for artists of all skill levels.
- Understanding Rigging: Rigging is the process of creating the bone structure of a 3D model to control its movements. It\"s like giving your model a skeleton.
- Why Rigging Matters: Without rigging, animating a character would be nearly impossible. Rigging allows for smooth and realistic movements.
- Tools and Features: Blender provides a comprehensive set of rigging tools, including automatic skinning, bone layers, and inverse kinematics for easier posing.
Before diving into the technical process, it\"s important to plan your rig according to the needs of your animation. A well-rigged character will save you time in the animation phase and bring more life to your creations.
- Start with a Plan: Consider the movements your character will need to make. This will determine the complexity of your rig.
- Creating Bones: Learn how to add bones to your model, which act as the framework for movement.
- Parenting and Skinning: Attach your model to the bones and ensure that the mesh deforms correctly when posed.
- Weight Painting: Refine the rig by painting weights, which control how different parts of the mesh move in relation to the bones.
- Testing Your Rig: Pose your character in various positions to test the rig\"s functionality and make necessary adjustments.
With patience and practice, rigging in Blender can become a seamless part of your 3D animation workflow. This introduction aims to get you started on the right foot, providing the foundation you need to explore more advanced rigging techniques.

Key Features of Blender\"s Rigging Tools
Blender\"s rigging tools are designed to be both powerful and user-friendly, enabling artists to bring their characters to life with realistic movements. These tools are integral to the animation process, providing the flexibility and control needed for detailed animation work. Here\"s an overview of the key features that make Blender a go-to choice for riggers and animators worldwide.
- Automatic Skinning: Blender simplifies the rigging process with automatic skinning options, making it easier to bind objects to bones.
- Bone Layers and Colored Groups: For complex rigs, Blender allows you to organize bones into layers and color-coded groups, improving workflow and readability.
- Forward and Inverse Kinematics: Blender supports both FK and IK, allowing for dynamic posing and animation. IK solvers can be added to any part of the armature, offering precise control over limb movements.
- Custom Shape Bones: Users can create custom shapes for bones, which is useful for creating user-friendly rigs that are easier to manipulate.
- Constraints and Drivers: With a wide range of constraints and drivers, Blender provides advanced control over bone properties and relationships, enabling more complex animations.
- Weight Painting: Blender\"s weight painting tools allow for fine-tuned control over how mesh deforms in relation to the bones, essential for achieving realistic movements.
- NLA Editor: The Nonlinear Animation (NLA) editor in Blender allows for mixing and blending of actions, giving animators powerful tools for creating complex sequences.
These features represent just a glimpse into Blender\"s rigging capabilities. Whether you\"re working on a simple character model or a complex creature, Blender\"s tools are designed to accommodate a wide range of rigging needs, making it a versatile choice for animators and 3D artists.

Step-by-Step Basic Rigging Process
Rigging is the process of creating a skeleton for a model so that it can move. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the basic rigging process in Blender, ensuring that you have a solid foundation for bringing your characters to life.
- Preparation: Before starting, ensure your model is complete and UV unwrapped if necessary. It\"s easier to rig a model that\"s correctly prepared.
- Add an Armature: Begin by adding an armature object to your scene. This will serve as the skeleton for your model. Go to Add > Armature.
- Place Bones: Enter Edit mode for the armature and start placing bones to match the major parts of your model (e.g., spine, limbs).
- Edit Bones: Adjust the bones to fit inside your model properly. Use extrude (E) to create new bones from selected joints for limbs and fingers.
- Name Your Bones: Properly naming bones is crucial for organization and later animation. Use a consistent naming scheme.
- Parent Mesh to Armature: With your model selected, shift-select the armature, then use Ctrl+P to parent the mesh to the armature. Choose \"With Automatic Weights\" for Blender to attempt automatic skinning.
- Weight Painting: Check the deformation by moving bones in Pose mode. Use Weight Paint mode to adjust how much influence each bone has on the mesh.
- Test the Rig: Pose your character in various ways to ensure the rig behaves as expected. Make adjustments as needed.
- Adjustments and Fine-tuning: Return to Weight Paint mode or Edit mode for the armature to refine your rig. This may include adding more bones for complex movements or adjusting weight paints for smoother deformations.
Following these steps will help you create a basic rig in Blender. Remember, rigging is an iterative process. Don\"t be afraid to go back and make adjustments as you test out how your model moves with the rig.

_HOOK_
Advanced Rigging Techniques and Tips
Mastering advanced rigging techniques in Blender enhances your ability to create more complex and nuanced animations. These methods leverage Blender\"s robust toolset to achieve precise control over your models, pushing your animations to the next level. Here are some advanced techniques and tips to help you refine your rigging skills.
- Re-targeting Body and Face: Advanced rigging often involves re-targeting, which allows you to transfer movements from one rig to another. This is particularly useful for facial rigging, where expressions need to be precise.
- Baking the Rig: Baking transforms complex rigs into simpler ones without losing the detailed animations, making it easier to manage and animate the rigs.
- Mesh Deform Cage: Utilizing a mesh deform cage can help in refining deformations around complicated areas, such as cloth or muscle movements, by providing an additional layer of control.
- Shape Keys for Cage Deformation: Incorporating shape keys into your rig can offer more flexibility in deformation, allowing for more expressive and varied animations.
- Weight Painting Hands and Face: Precise weight painting on hands and face is crucial for natural-looking movements and expressions. It ensures that the mesh deforms correctly in response to the underlying bone structure.
- Rigging Extra Objects: Sometimes, your character might interact with or carry objects. Learning how to rig these extra objects can add realism and depth to your animations.
- Understanding Facial Actions: A deep understanding of facial actions is key to creating believable facial expressions. This involves rigging the face to accommodate a wide range of emotions and speech.
These advanced techniques require patience and practice to master. However, they are essential for creating professional-quality animations that stand out. As you become more familiar with these methods, you\"ll find your workflow becoming more efficient and your animations more lifelike.
For detailed tutorials and more advanced techniques, Blender Studio offers comprehensive courses and resources that cover everything from basic to advanced rigging, including facial rigging and animation. Additionally, exploring free Blender models and character rigs can provide practical examples and practice opportunities.

Working with Constraints and Modifiers
Blender\"s rigging system includes an array of constraints and modifiers that can significantly enhance the functionality and flexibility of your rigs. Understanding how to effectively utilize these tools can elevate the quality of your animations, allowing for more complex and dynamic character movements.
- Constraints: Constraints allow for the control of an object’s properties, such as its location, rotation, and scale, by setting static values or linking these properties to other objects. This can facilitate sophisticated animation effects, like having a character look towards a moving target or objects following a predetermined path.
- Drivers: Drivers provide a method to automate the influence of properties based on the animation of other objects. They use a function or mathematical expression to control the properties, offering a layer of dynamic interaction within your rig. This can be particularly useful for facial animations or any scenario where the movement of one part should influence another.
- Shape Keys: Shape keys are pivotal for deformations and are often used in facial animations and muscle movement. They allow for the adjustment of mesh shape in a non-linear manner, giving animators the ability to fine-tune the mesh deformation at various points of an animation.
- Mesh Deform Cage: A technique used in advanced rigging involves the use of a mesh deform cage which encases the character. This cage then deforms the mesh inside it, allowing for complex movements and deformations that can be challenging to achieve with traditional bone systems alone.
These features represent just the beginning of what\"s possible with Blender\"s rigging tools. By mastering constraints and modifiers, you can unlock new levels of creativity and realism in your animations. For beginners and advanced users alike, Blender provides comprehensive resources and tutorials to get started and advance your skills.
Utilizing Drivers and Shape Keys for Animation
Blender\"s animation toolkit offers powerful features for creating detailed and nuanced animations. Two of these features, drivers and shape keys, are essential for adding complexity and realism to your animations. This section will guide you through the basics of using these tools to enhance your animation projects.
- Introduction to Drivers: Drivers are a feature in Blender that allow properties of one object to control the properties of another. This can be used to create complex relationships and automated movements within your scene. For example, you can use the rotation of a wheel to drive the movement of a car.
- Setting Up Drivers: To set up a driver, right-click on the property you want to control and choose \"Add Drivers\". You can then open the Graph Editor, switch to Drivers mode, and configure your driver by specifying the target object and the type of transformation that influences the driven property.
- Introduction to Shape Keys: Shape keys are used to deform objects in a smooth transition from one shape to another. They are particularly useful for facial animations and morphing objects in ways that are not easily achieved with armatures alone.
- Creating and Using Shape Keys: You can create shape keys in the Object Data tab of the Properties panel. After adding a Basis key, additional keys can be added to define different shapes. These keys can then be animated over time to transform the object smoothly from one shape to another.
- Combining Shape Keys with Drivers: For advanced control, shape keys can be driven by other properties, such as the rotation of a bone. This allows for automated transformations that react to the movements of your characters, adding a new level of dynamism to your animations.
By mastering drivers and shape keys, you unlock a world of possibilities for character animation and object transformation in Blender. These tools allow for a high degree of control and precision, making your animations more lifelike and engaging.
Creating and Managing Armatures
Creating and managing armatures in Blender is a foundational skill for any animator or 3D artist looking to bring their characters to life. Armatures act as the skeleton of your model, allowing for realistic and complex animations. This guide will walk you through the basics of creating and managing these crucial elements in Blender.
- Understanding Armatures: Armatures are the bones structure used to rig and animate 3D models. They are essential for defining how a character moves.
- Adding an Armature: To start, add an armature to your scene by selecting Add > Armature. This initial bone will serve as the basis for your entire skeleton.
- Editing Bones: In Edit Mode, you can extrude new bones from the existing ones to create the skeleton structure of your character. Remember, bones can be extruded to match the parts of the model like limbs, spine, and fingers.
- Naming Bones: Properly naming each bone is crucial for organization and later animation. Use a consistent naming convention that makes it easy to identify bones.
- Parenting Mesh to Armature: Parent your 3D model to the armature to link the two. This can be done by selecting your mesh, then the armature, and pressing Ctrl+P. Choose \"With Automatic Weights\" for Blender to attempt skinning automatically.
- Weight Painting: Weight painting allows you to fine-tune how the mesh deforms in relation to the bones. This step is vital for achieving realistic animations.
- Managing Armatures: Blender allows for advanced management of armatures through features like bone layers and colored groups. This helps in organizing complex rigs.
- Mirroring Bones: For symmetrical models, bones can be mirrored across the central axis to ensure uniformity in the rig. Use the mirror functionality to streamline the creation of limbs and other symmetrical parts of the skeleton.
- Testing and Tweaking: Always test your rig by posing it in various positions. Adjust weight paints and bone constraints as needed to ensure smooth and realistic movement.
Armatures are a powerful tool in Blender, enabling artists to animate characters with precision and flexibility. By following these steps, you\"ll be well on your way to mastering the art of rigging in Blender.
Weight Painting for Realistic Movement
Weight painting is a crucial step in the rigging process in Blender, enabling animators to define how mesh deforms in response to bone movements. Proper weight painting ensures that your character moves in a realistic and convincing manner. Here\"s a step-by-step guide to mastering weight painting for realistic movement.
- Understanding Weight Painting: Weight painting allows you to assign how much influence a bone has over different parts of the mesh. Areas painted in red have the most influence, while blue areas have the least.
- Entering Weight Paint Mode: Select your mesh, switch to Weight Paint mode. Here, you can visually adjust the influence bones have on the mesh by painting directly onto it.
- Selecting Bones for Painting: In Weight Paint mode, select the bone you wish to paint weights for. The mesh will display the current weight distribution for that bone.
- Adjusting Weights: Use the brush tools to paint weights. Add influence by painting with red, and reduce it by painting with blue. The goal is to create smooth transitions for natural movement.
- Testing and Adjusting: Regularly switch between Pose Mode and Weight Paint mode to test how the mesh deforms with the bone movements. Adjust the weights as necessary to correct any deformation issues.
- Mirroring Weights: For symmetrical models, you can mirror the weights from one side to the other, ensuring consistent deformation on both sides of the mesh.
- Utilizing Auto Normalize: Enable Auto Normalize in the tool settings to ensure that the total weights for each vertex sum up to 1. This prevents unexpected results during animation.
Weight painting is an iterative process. It might take several rounds of adjustments to get perfect results. Be patient and experiment with different brush strengths and weights to achieve the most realistic movement for your character.
_HOOK_
Animating Characters with Inverse Kinematics
Animating characters in Blender using Inverse Kinematics (IK) involves creating a more intuitive and efficient way to animate by manipulating the end effector of a chain of bones. This method allows for more natural movements and can significantly speed up the animation process. Here’s how to set up and utilize IK for character animation in Blender:
- Understanding Inverse Kinematics: IK simplifies the animation process by allowing you to move a chain of bones by manipulating just the final bone in the chain. This is particularly useful for limbs.
- Adding IK Constraints: Select the bone where you want the IK effect to end, and add an IK constraint. Specify the target bone and the chain length, which is the number of bones affected by the IK constraint.
- Adjusting IK Properties: Fine-tune the IK constraint properties to achieve the desired movement. Properties like Pole Target and IK stiffness can be adjusted for better control over the bone chain’s behavior.
- Creating Control Bones: For better manipulation, create separate control bones that do not deform the mesh but control the IK targets. This separates the animation controls from the deformation rig.
- Weight Painting for IK: Ensure that the bones influenced by IK are properly weight painted to the mesh for accurate deformation. This step is crucial for realistic movement.
- Testing and Tweaking: Animate your character using the IK controls and adjust the rig as necessary. IK setups often require tweaking to perfect the movement.
IK is a powerful tool for animating characters in Blender, making it easier to create realistic and complex movements. Remember, practice and experimentation are key to mastering IK animation.
Free Resources: Models and Rigs for Practice
Embarking on the rigging journey in Blender can be both exciting and overwhelming. Fortunately, the 3D community is generous, offering a plethora of free resources to help you refine your skills. Whether you\"re a beginner or an advanced user, these resources provide valuable practice opportunities.
- Concept Art Empire - Offers a variety of models, including an emissive texture model ideal for futuristic settings, a detailed Goblin Warrior, an Old Tower with hand-painted textures, and more. These models serve as excellent bases for modular assets or as standalone practice projects.
- The Rookies - Lists notable rigs like Robot RBT10, Sheik from Overwatch Universe re-imagined, Healthbot 1.0 for basic character personality practice, and several student-created rigs. It also highlights the Sony Pictures Animation\"s Hotel Transylvania Zombie Rig and Malcolm 2.0, known for its expressive facial rigging.
- Rigging Dojo - Features free Blender rigs in collaboration with Agora.Community and AnimChallenge, such as Annie & Tibbers and Braum from League of Legends, designed for study, practice, and community projects. These rigs require the RigOnTheFly addon for optimal use.
- Blender Studio - Provides access to fully rigged characters from Blender Studio\"s open movies. Characters include those from \"Sprite Fright,\" \"Sintel,\" \"Big Buck Bunny,\" and more, offering a wide range of rigs for practicing animation and rigging techniques.
These resources are designed to support your learning journey in Blender, offering a variety of challenges from basic rigging to advanced animation techniques. Remember, the key to mastery is practice, and with these free resources, you have plenty of opportunities to grow your skills.
Common Rigging Problems and Solutions
Rigging in Blender is a fundamental skill for animators and 3D modelers, but it comes with its set of challenges. Understanding common rigging problems and their solutions can significantly improve your workflow and the quality of your animations. Here are some typical issues and how to address them:
- Normals Facing the Wrong Direction: Incorrect normal direction can cause issues with lighting and textures. Use the \"Recalculate Outside\" function to correct normals pointing inward.
- Creating Effective Bone Weighting: Properly weight painting your mesh ensures that the rig deforms the model as intended. Utilize Blender\"s weight painting tools to assign the right amount of influence bones have over vertices.
- Choosing Between IK and FK: Decide whether Inverse Kinematics (IK) or Forward Kinematics (FK) best suits your animation needs. IK is useful for animating limbs, whereas FK provides better control for hierarchical chain movements like waving.
- Using Constraints for Better Control: Constraints like Parent, Point, Orient, and others are essential for attaching bones to controllers and defining their behavior. Correctly applying constraints will make your rig more intuitive to animate.
- Custom Controllers: Custom controllers can enhance the usability of your rig. Blender allows you to create and customize these controllers for more intuitive animation controls.
- Mesh and Armature Alignment: Ensuring your mesh and armature are correctly aligned is crucial for effective rigging. Use the \"Origin to 3D Cursor\" to set the base of your model, ensuring rotations and transformations behave as expected.
- Correcting Mesh Deformations: Mesh deformations can occur if the rig is not properly configured. Use Blender\"s mesh editing tools to adjust the mesh and correct any undesired deformations.
Each rigging challenge has a solution, and Blender provides the tools needed to address these issues effectively. With practice and patience, overcoming these common problems will become a natural part of your rigging process, leading to more realistic and dynamic animations.
Enhancing Your Rigging Workflow
Enhancing your rigging workflow in Blender involves understanding and implementing a series of steps and best practices to streamline the creation of rigs for animation. These strategies focus on efficiency and quality, enabling artists to produce sophisticated rigs with less effort. Following these guidelines will significantly improve your rigging process:
- Utilize Rigify for Fast Rig Creation: Rigify in Blender simplifies the rigging process by offering pre-built meta-rigs for various character types. Start by selecting a suitable meta-rig and customize it to fit your character, significantly speeding up the rigging process.
- Align Meta-Rig to Character: Carefully align the meta-rig with your character\"s geometry. This step ensures that the bones are correctly positioned relative to the character’s mesh, facilitating more natural movements.
- Customize Rigify Bone Groups and Layers: Organizing your rig with Rigify bone groups and layers can make it more user-friendly. This optional but recommended step allows for easier selection and manipulation of different parts of the rig during animation.
- Generate the Rig: With the meta-rig aligned and customized, use Rigify\"s \"Generate Rig\" button to automatically create the final rig. This process constructs a sophisticated rig ready for weight painting and animation.
- Test and Refine the Rig: After generating the rig, it\"s crucial to test it by parenting your character mesh to the rig using Blender’s automatic weights. This preliminary step allows you to evaluate the rig\"s functionality and make any necessary adjustments.
- Advanced Weight Painting: For characters requiring high-quality deformation, manual weight painting is essential. Utilize tools like the Easy Weights add-on to streamline this process, ensuring precise control over how the mesh deforms in response to bone movements.
- Create Corrective Shape Keys: To polish the rig, add corrective shape keys. This step allows you to fine-tune the mesh deformation for specific poses, enhancing the realism and quality of your animations.
By following these steps, you can create efficient and sophisticated rigs that respond well to animation, enhancing your overall workflow in Blender. Whether you\"re working on simple characters or complex scenes, these practices offer a structured approach to rigging that can adapt to your project\"s needs.
READ MORE:
Conclusion and Further Learning Resources
Embarking on your rigging journey in Blender is a continuous process of learning and improvement. With a plethora of resources available, from beginner tutorials to advanced rigging techniques, the possibilities are endless. Here\"s a roundup of further learning resources and some concluding thoughts to guide you on your journey:
- Explore Dedicated YouTube Channels: Channels like Luciano Muñoz and Index 3d offer in-depth tutorials on animation and rigging in Blender, catering to both beginners and seasoned professionals.
- Participate in Blender Community Projects: Engage with projects and discussions on the future of character animation and rigging, as shared in Blender\"s Developer Blog. This is a great way to stay updated on the latest developments and contribute to the conversation.
- Take Online Courses: Platforms like CG Cookie provide comprehensive courses on rigging in Blender, covering everything from the basics to more complex rigging challenges.
- Utilize Free Learning Materials: Blender Studio offers a range of animation fundamentals and resources to help you master character animation, from bouncing basics to character acting.
In conclusion, mastering rigging in Blender is a journey of exploration, practice, and community engagement. By leveraging the wealth of resources available, you can enhance your skills and bring your 3D creations to life. Remember, the Blender community is vibrant and supportive, offering endless opportunities for learning and growth. Continue to experiment, learn from others, and share your knowledge as you advance in your rigging endeavors.
Unlock the full potential of your 3D creations in Blender with our comprehensive guide to rigging. From basic bones to advanced animation techniques, we\"ll help you bring your characters to life in a vibrant, supportive community. Start your rigging journey today!
_HOOK_